I. Overview
DockeripThe container will change every time the container is restarted .
This also means that if containers use ipaddresses to communicate, once a container is restarted, the restarted container will no longer be accessible.
The network Dockercan solve this problem.
DockerThe network has two main functions:
-
Interconnection and communication between containers and port mapping
-
When the container
IPchanges, it can directly communicate with the network through the service name without being affected
Therefore, as long as the container is under the same Dockernetwork, it can use the service name for direct access without worrying about restarting.
This is also Dockerthe most basic and common application scenario of the network.
Two, Docker's four network modes
| network mode | Command specification method | describe |
|---|---|---|
| bridge | –network bridge | ipAssign, set up , and connect the container to a docker0virtual network bridge for each container , which is also the default network mode |
| host | –network host | The container will not create its own network card, configuration ip, etc. , but use the host's ipand port |
| container | –network container name or id | The newly created container will not create its own network card and configure its own , but will share and port range ipwith a specified containerip |
| none | –network none | The container has its own Network namespace, but does not have any network settings for it |
If you think –network is too long, you can also use the abbreviation -net, the effect is the same
When Dockerthe installation is complete, generally three networks are created automatically:
NETWORK ID NAME DRIVER SCOPE
40547f9137a5 bridge bridge local
b40bdb8f0356 host host local
0c7f9938f868 none null local
You can use the following commands to view:
docker network ls
2.1 Bridge mode – bridge
DockerWhen the service starts, by default it creates a docker0 bridge the name docker0internal interface on it.
The name of the bridge network is that docker0it connects to other physical or virtual network cards at the kernel level, which puts all containers and local hosts on the same physical network.
DockerThe addressdocker0 and subnet mask of will be specified by default , so that the host and the container can communicate with each other through the bridge.ip
1) Schematic diagram of bridge mode
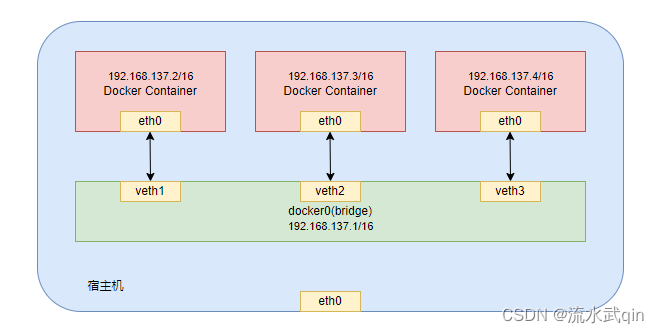
2) Bridge mode analysis
-
DockerUseLinuxthe bridging method to virtualize aDockercontainer network bridge (docker0) on the host machine.DockerEach time a container is started,Dockeran address is assigned to the container according to the network segment of the bridgeip.At the same time
Dockerthe bridge is the default gateway for each container.The containers in the same host are all connected to the same bridge, so that the containers can communicate directly through the Container-IP of the container.
-
docker runWhen creating a container,networkthe default network mode of the unspecified container is thebridgeone that is useddocker0.On the host machine
ifconfig, you can seedocker0and create it yourselfnetwork:eth0,eth1...represents NIC 1, NIC 2...loRepresents 127.0.0.1 (localhost)inet addrIndicatesipthe address of the network card
-
The bridge
docker0creates a pair of peer-to-peer virtual device interfaces: one callsveth, the other callseth0, matching pairs.-
The bridge mode of the entire host is
docker0similar to a switch with a bunch of interfaces, and each interface is calledveth,Create a virtual interface in the local host and the container respectively, and let them communicate with each other (such a pair of interfaces is called
veth pair); -
There is also a network card inside each container instance, and each interface is called
eth0; -
docker0Each of the abovevethmatches inside a container instanceeth0, paired in pairs.
-
2.2 Host mode –host
No network interface is created, and ipthe address to communicate with the outside world, no additional NATconversion is required.
Cannot publish port in host mode .
1) Schematic diagram of host mode
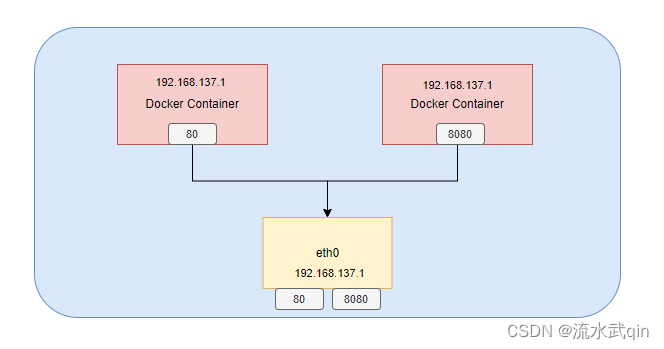
2) Host mode analysis
The container will not get a separate one Network Namespace, but will share one with the host Network Namespace.
The container will not virtualize its own network card but use the host's IP and port.
The container shares the host network ip, which has the advantage that the external host and the container can communicate directly.
Small expansion:
Docker--network=hostSpecify or at startup , if a mapped port -net=hostis also specified , the following warning will appear at this time:-p
NARNING: Published ports are discarded when using host network mode
And -pthe parameters set will not play any role, the port number will be based on the host port number, and will increase when repeated.
You can choose to ignore this warning or use Dockerother network modes, such as--network=bridge
2.3 Container mode – container
1) Schematic diagram of the container mode
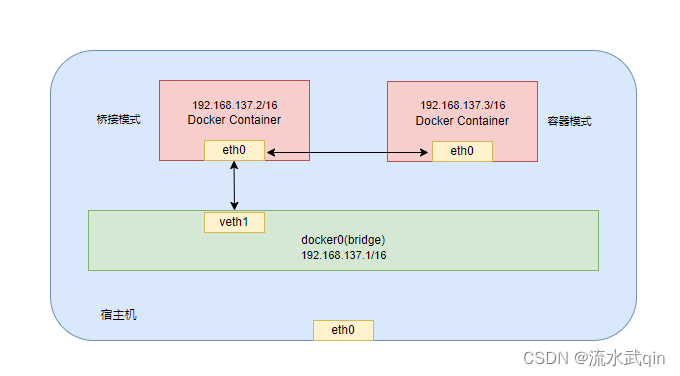
2) Container mode analysis
The newly created container shares a network configuration with an existing container ipinstead of sharing it with the host.
The newly created container will not create its own network card, configure its own ip, but share it with a specified container ip, port range, etc.
In addition to the network aspects of the two containers, other things such as file systems and process lists are still isolated.
2.4 none mode
In nonemode, no Dockernetwork configuration is done for the container.
That is to say, this Dockercontainer has no ipinformation such as network card, router, and routing, but only one lointerface.
The lo flag means that the network function is disabled, that is: 127.0.0.1, which means local loopback
We need to add a network card, configure IP, etc. for the Docker container by ourselves.
3. Commonly used commands
Before learning Dockervarious network modes, you must first understand Dockerthe common commands of the network.
2.1 View network
docker network ls
2.2 Create a network
# 基础用法
docker network create 网络名称
# 创建网络时是可以添加一系列参数的:
# --driver:驱动程序类型
# --gateway:主子网的IPV4和IPV6的网关
# --subnet:代表网段的CIDR格式的子网
# mynet:自定义网络名称
docker network create --driver=bridge --gateway=192.168.137.1 --subnet=192.168.137.0/16 mynet
When no option is specified, the default –driver (network mode) is also bridge (bridge)
But gateway and subnet will be automatically generated
2.3 View network data sources
docker network inspect 网络名称
2.4 Connect the container to the specified network
docker network connect 网络名称 容器名称
2.5 Disconnect the container from the network
docker network disconnect 网络名称 容器名称
2.6 Delete all unused networks
docker network prune
2.7 Delete one or more networks
docker network rm 网络名称
4. Example of use
4.1 Mount the network when creating the container
1) Create a bridge type network
docker network create --driver=bridge --gateway=192.168.137.1 --subnet=192.168.137.0/16 myNet1
2) Specify the network when creating and running the container
docker run --name containerName -p 80:80 -d --network myNet1 myNginx
3) You can disconnect the network when you don't want to use it
docker network disconnect myNet1 myNginx
4.2 Connecting to a new network when the container already exists
1) Create a bridge type network
docker network create --driver=bridge --gateway=192.168.137.1 --subnet=192.168.137.0/16 myNet2
2) Connect a new network for the container
# 执行后myNginx容器的网络就变成了myNet2
docker network connect myNet2 myNginx
3) You can disconnect the network when you don't want to use it
docker network disconnect myNet2 myNginx
4.3 Use docker-compose to mount the network to a group of containers
There are the following docker-compose.ymlfiles.
Generally speaking, when using a group of containers arranged by the following command, a network will be created by default, and all the containers will be added to the network.
docker-compose up -d
This is why this group of containers can directly use the service name to communicate directly.
version: '3'
services:
nginx:
image: nginx:alpine
container_name: nginx-dev
environment:
- TZ=Asia/Shanghai
ports:
- "80:80"
volumes:
- /usr/local/docker/workspace/nginx/html:/usr/share/nginx/html
- /usr/local/docker/workspace/nginx/conf/nginx.conf:/etc/nginx/conf.d/default.conf
mysql:
image: mysql:8
container_name: mysql-dev
environment:
- TZ=Asia/Shanghai
- MYSQL_ROOT_PASSWORD=89225300
- MYSQL_DATABASE=nacos_config
- MYSQL_USER=gddst
- MYSQL_PASSWORD=123456
ports:
- "3306:3306"
volumes:
- /usr/docker/docker/workspace/mysql/data:/var/lib/mysql
- /usr/docker/docker/workspace/mysql/mysql.cnf:/etc/mysql/conf.d/mysql.cnf
- /usr/docker/docker/workspace/mysql/initdb:/docker-entrypoint-initdb.d
But if you want to display the specified network, you can refer to the following configuration:
networks:
mynet:
driver: bridge
ipam:
config:
- subnet: "192.168.0.101/16"
gateway: 192.168.0.100
After configuring the network, you can specify the network to use under each service, here is nginxan example:
version: '3'
services:
nginx:
image: nginx:alpine
container_name: nginx-dev
environment:
- TZ=Asia/Shanghai
ports:
- "80:80"
volumes:
- /usr/local/docker/workspace/nginx/html:/usr/share/nginx/html
- /usr/local/docker/workspace/nginx/conf/nginx.conf:/etc/nginx/conf.d/default.conf
networks:
- mynet
networks:
mynet:
driver: bridge
ipam:
config:
- subnet: "192.168.0.101/16"
gateway: 192.168.0.100
In this way, when the container is orchestrated, all containers will be added to mynetthis custom network.