Mysql sub-database sub-table scheme
1. Why do you want to divide the table:
When the data in a table reaches tens of millions, the time it takes you to query once will increase. If there is a joint query, I think it may die there. The purpose of sub-tables is to reduce the burden on the database and shorten the query time.
One of the mechanisms in MySQL is table locking and row locking to ensure data integrity. Table locking means that none of you can operate on this table, and you must wait for me to finish operating the table. The same is true for row locking. Other SQL must wait for me to complete the operation of this data before operating on this data.
2. mysql proxy:amoeba
To do mysql cluster, use amoeba .
From the perspective of the upper-level java program, there is no need to know the source of the master server and the slave server, that is, the master-slave database server is transparent to the upper layer. It can be configured through amoeba .
3. Tables with large data volume and frequent access are divided into several tables
For example, for the database table of a certain website platform - the company table, the amount of data is very large. For this kind of large data scale that can be estimated, we will divide N tables in advance. The value of this N depends on the actual situation.
The current data volume of a website is at most 50 million pieces, and each table can be designed to hold 5 million pieces of data, that is, it is divided into 10 tables.
So how to judge whether the data capacity of a table is full? For the table to be added data in the program segment, do the operation of counting the number of records in the table before inserting it. When the data is less than 5 million, insert it directly. When the threshold value has been reached, you can create a new database table in the program segment ( or has been created in advance), and then perform the insert operation.
4. Use the merge storage engine to implement sub-tables
If it is more painful to separate the existing big data scales, the most painful thing is to change the code, because the sql statement in the program has already been written. The merge storage engine is used to implement table partitioning, which is more suitable.
for example:
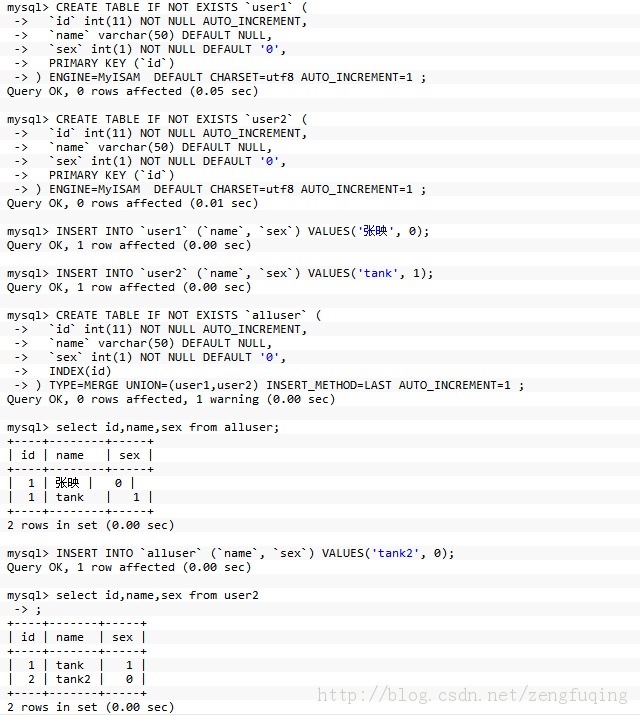
------------------- ---------- Gorgeous dividing line ----------------- ---------------------
database schema
1. Simple MySQL master-slave replication:
MySQL's master-slave replication solves the read-write separation of the database and greatly improves the read performance. The figure is as follows:
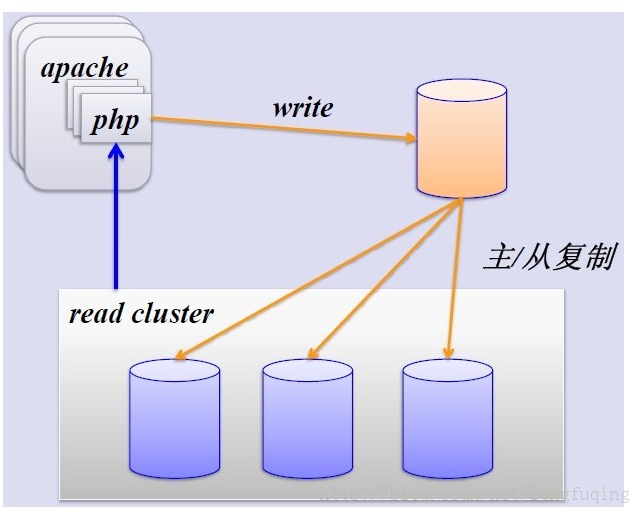
The master-slave replication process is shown in the following figure:
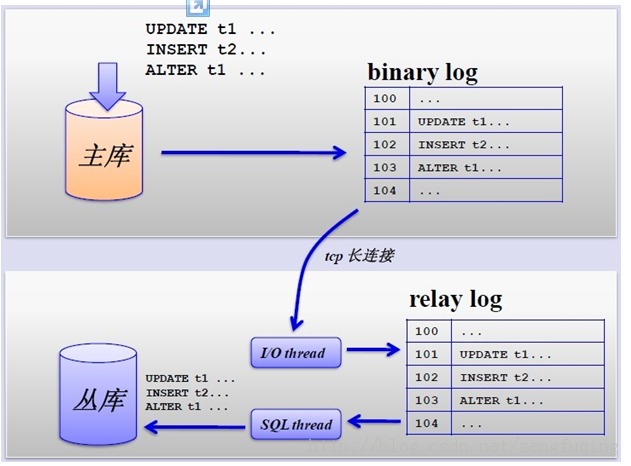
However, master-slave replication also brings a series of other performance bottlenecks:
1. Writes cannot be extended
2. Writes cannot be cached
3. Copy delay
4. The rate of lock table increases
5. The table becomes larger and the cache rate decreases
That problem must be solved, which leads to the following optimization scheme, let's take a look.
2. MySQL vertical partition
If the business is divided enough to be independent, it will be a good solution to put the data of different businesses on different database servers, and if one business crashes, it will not affect the normal operation of other businesses, and it will also play a load The role of offloading greatly improves the throughput of the database. The database architecture diagram after vertical partitioning is as follows:

However, although the businesses are sufficiently independent, some businesses are more or less connected, such as users, which are basically associated with each business. Moreover, this partitioning method cannot solve the problem of single table data. The problem of skyrocketing volume, so why not try split horizon?
3. MySQL horizontal sharding (Sharding)
This is a very good idea to group users according to certain rules (by id hash), and store the data of this group of users in a database shard, that is, a sharding, so that as the number of users increases, as long as the simple Just configure a server, the schematic diagram is as follows:
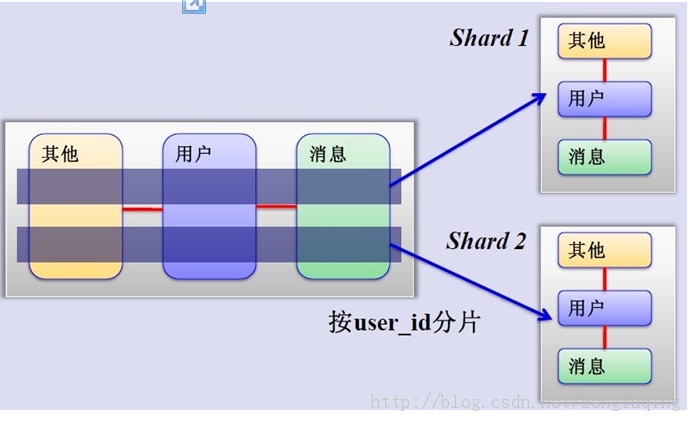
How to determine the shard where a user is located? You can create a data table corresponding to the user and the shard. For each request, first find the user's shard id from this table, and then query the relevant data from the corresponding shard, as shown in the following figure. :

单库单表
单库单表是最常见的数据库设计,例如,有一张用户(user)表放在数据库db中,所有的用户都可以在db库中的user表中查到。
单库多表
随着用户数量的增加,user表的数据量会越来越大,当数据量达到一定程度的时候对user表的查询会渐渐的变慢,从而影响整个DB的性能。如果使用mysql, 还有一个更严重的问题是,当需要添加一列的时候,mysql会锁表,期间所有的读写操作只能等待。
可以通过某种方式将user进行水平的切分,产生两个表结构完全一样的user_0000,user_0001等表,user_0000 + user_0001 + …的数据刚好是一份完整的数据。
多库多表
随着数据量增加也许单台DB的存储空间不够,随着查询量的增加单台数据库服务器已经没办法支撑。这个时候可以再对数据库进行水平区分。
分库分表规则
设计表的时候需要确定此表按照什么样的规则进行分库分表。例如,当有新用户时,程序得确定将此用户信息添加到哪个表中;同理,当登录的时候我们得通过用户的账号找到数据库中对应的记录,所有的这些都需要按照某一规则进行。
路由
通过分库分表规则查找到对应的表和库的过程。如分库分表的规则是user_id mod 4的方式,当用户新注册了一个账号,账号id的123,我们可以通过id mod 4的方式确定此账号应该保存到User_0003表中。当用户123登录的时候,我们通过123 mod 4后确定记录在User_0003中。
分库分表产生的问题,及注意事项
1. 分库分表维度的问题
假如用户购买了商品,需要将交易记录保存取来,如果按照用户的纬度分表,则每个用户的交易记录都保存在同一表中,所以很快很方便的查找到某用户的 购买情况,但是某商品被购买的情况则很有可能分布在多张表中,查找起来比较麻烦。反之,按照商品维度分表,可以很方便的查找到此商品的购买情况,但要查找 到买人的交易记录比较麻烦。
所以常见的解决方式有:
a.通过扫表的方式解决,此方法基本不可能,效率太低了。
b.记录两份数据,一份按照用户纬度分表,一份按照商品维度分表。
c.通过搜索引擎解决,但如果实时性要求很高,又得关系到实时搜索。
2. 联合查询的问题
联合查询基本不可能,因为关联的表有可能不在同一数据库中。
3. 避免跨库事务
避免在一个事务中修改db0中的表的时候同时修改db1中的表,一个是操作起来更复杂,效率也会有一定影响。
4. 尽量把同一组数据放到同一DB服务器上
例如将卖家a的商品和交易信息都放到db0中,当db1挂了的时候,卖家a相关的东西可以正常使用。也就是说避免数据库中的数据依赖另一数据库中的数据。
一主多备
在实际的应用中,绝大部分情况都是读远大于写。Mysql提供了读写分离的机制,所有的写操作都必须对应到Master,读操作可以在 Master和Slave机器上进行,Slave与Master的结构完全一样,一个Master可以有多个Slave,甚至Slave下还可以挂 Slave,通过此方式可以有效的提高DB集群的 QPS.
所有的写操作都是先在Master上操作,然后同步更新到Slave上,所以从Master同步到Slave机器有一定的延迟,当系统很繁忙的时候,延迟问题会更加严重,Slave机器数量的增加也会使这个问题更加严重。
此外,可以看出Master是集群的瓶颈,当写操作过多,会严重影响到Master的稳定性,如果Master挂掉,整个集群都将不能正常工作。
所以,1. 当读压力很大的时候,可以考虑添加Slave机器的分式解决,但是当Slave机器达到一定的数量就得考虑分库了。 2. 当写压力很大的时候,就必须得进行分库操作。
---------------------------------------------
MySQL使用为什么要分库分表
可以用说用到MySQL的地方,只要数据量一大, 马上就会遇到一个问题,要分库分表.
这里引用一个问题为什么要分库分表呢?MySQL处理不了大的表吗?
其实是可以处理的大表的.我所经历的项目中单表物理上文件大小在80G多,单表记录数在5亿以上,而且这个表
属于一个非常核用的表:朋友关系表.
但这种方式可以说不是一个最佳方式. 因为面临文件系统如Ext3文件系统对大于大文件处理上也有许多问题.
这个层面可以用xfs文件系统进行替换.但MySQL单表太大后有一个问题是不好解决: 表结构调整相关的操作基
本不在可能.所以大项在使用中都会面监着分库分表的应用.
从Innodb本身来讲数据文件的Btree上只有两个锁, 叶子节点锁和子节点锁,可以想而知道,当发生页拆分或是添加
新叶时都会造成表里不能写入数据.
所以分库分表还就是一个比较好的选择了.
那么分库分表多少合适呢?
经测试在单表1000万条记录一下,写入读取性能是比较好的. 这样在留点buffer,那么单表全是数据字型的保持在
800万条记录以下, 有字符型的单表保持在500万以下.
如果按 100库100表来规划,如用户业务:
500万*100*100 = 50000000万 = 5000亿记录.