1. Serialization of binary tree
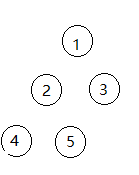
Serialization: As shown in the figure, serialize in the preceding order to get the string 1!2!3!4!-1!-1!5!-1!-1!3!-1!-1!, where ! means The end of a value, -1 means the node is empty.
Deserialization: The inverse operation of serialization.
attached code
TreeNode* PreMakeTree(TreeNode* root,int value[]) { // ifsizeof(data)/sizeof(int) int e=value[k++]; if(e==-1) root=NULL; else{ root=(TreeNode*)malloc(sizeof(struct TreeNode)); root->val=e;; root->left=PreMakeTree(root->left,value); root->right=PreMakeTree(root->right,value); } return root; } void PreOrder(TreeNode* root) { if(root!=NULL) { printf("%d!",root->val); PreOrder(root->left); PreOrder(root->right); }else printf("-1!"); }
2. Hierarchical traversal of binary tree
1. Maintain last and nlast pointers.
2. At the beginning last=root
3. Each time the queue is enqueued, nlast is updated to the current enqueue node
4. When current=last, perform a newline operation and update to nlast at the same time
attached code
void LevelOrder1(TreeNode* root) { TreeNode* last; TreeNode* nlast; queue<TreeNode*> q; q.push(root); last=root; while(!q.empty()){ TreeNode* current=q.front(); q.pop(); printf("%d ",current->val); if(current->left!=NULL) { q.push(current->left); nlast=current->left; } if(current->right!=NULL) { q.push(current->right); nlast=current->right; } if(current==last) { printf("\n"); last=nlast; } } }