1. Common abbreviations for Ethernet
1) 1TPCE = One (1) Twisted Pair 100 Megabit (C = century = 100) Ethernet
1 pair of twisted pair 100M Ethernet
2) RTPGE = Reduced Twisted Pair Gigabit Ethernet
simplified version of twisted pair Gigabit Ethernet
3) GEPOF = Gigabit Ethernet Over plastic optical fiber
based plastic fiber Gigabit Ethernet
. 4) 100BASE-Tl = 100 Megabit Baseband One Pair
100M Ethernet (1 twisted pair)
. 5). 1 Gigabit 1000BASE-Tl = Baseband One Pair
1000M Ethernet ( one pair of twisted pair)
. 6) RH = 1000BASE-Gigabit Ethernet Over plastic optical fiber
Gigabit Ethernet-based plastic optical fiber
7) OPEN / OPEN Alliance = One pair Ethernet network Alliance
single Ethernet network Alliance
8) OABR = (OPEN Alliance) BroadR-Reach
100BASE-T1 early name, was not involved in the IEEE, the league will open Broadcom's BroadR-Reach technology into the automotive sector;
9) TSN - network time sensitive
time sensitive network
10) AVB-Audio/Video bridging
technology
2. What is 100BASE-T1
100BASE-T1 is an integration based on the existing Ethernet technology.
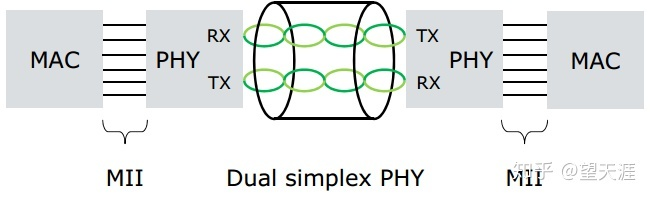
1) IEEE 100BASE-TX
- Dual simplex communication
- MLT-3 (multi-level transmission)-> 125Msps (million samples per second) 65~80MHz bandwidth)
- Two pairs of twisted pair
- No error correction coding
- No echo and crosstalk cancellation technology in DSP
- Decision Feedback Equalization Technology (DFE)
2)IEEE 1000BASE-T
- Full duplex communication
- 4D-PAM5->125Msps (million samples per second) 65~80MHz bandwidth)
- Four pairs of twisted pair
- Partial response transmission filter
- Additional level of error correction coding
- Echo and crosstalk cancellation technology in DSP
- Decision Feedback Equalization (DFE)
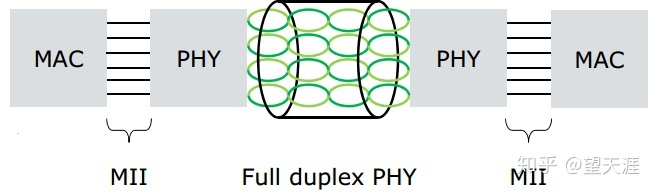
3)IEEE 100BASE-T1
- Full duplex communication
- PAM3-66.7Msps (million samples per second) 27MHz bandwidth
- Single pair twisted pair
- Echo cancellation technology
- Decision Feedback Equalization (DFE)


3. Ethernet VS traditional bus
3.1 Switch-type network communication

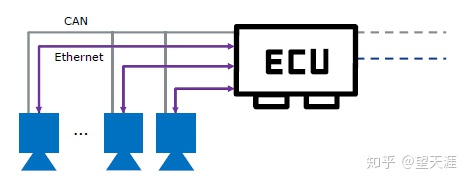
Figure: Comparison of CAN and Ethernet communication methods
1) All nodes on the traditional bus are connected to the same transmission medium; for example, multiple terminal nodes (ECUs) can be connected to a CAN bus, and the electrical signals on the CAN bus will also affect those connected to this bus. For all terminal nodes, we generally refer to CAN as CAN Bus or CAN Network.
2) Ethernet is a switched network (Switched Network) communication method. Switched communication means that all terminal nodes must be connected through a switch, and all transmitted information needs to be forwarded by the switch. In switch communication, a network cable can only be connected to two ports, and there is no fork. So we generally do not talk about the Ethernet bus, but the Ethernet network (Ethernet Network).
3.2 Connecting to the network-IP and MAC

3.3 Signal and PDU (Protocol Data Unit)

4. Application of automotive Ethernet
4.1 Bird's-eye image view-high-speed connection
1) Broadcom BroadR-Reach, 100 Mbit/s, full duplex, twisted pair
- Replace expensive shielded wiring harness
- Two-way communication
2) Utilize high bandwidth
3) MAC-based video stream with strict timing requirements
4) ADAS function enhancement (additional camera, millimeter wave radar, lidar, etc.)
- High resolution and frame rate, less compression
- Need a transmission rate of 1000Mbit/s and above
Ethernet video high-speed transmission
4.2 Ethernet as the backbone of the in-car network
In the future, the automobile bus will be the backbone network instead of the CAN bus by Ethernet, and the subnet will be composed of several domain controllers.
Set up a domain controller for each functional domain, the system interconnection within each domain can still use CAN and FlexRay communication bus. Different domain controllers are connected through higher-performance Ethernet as the backbone network, and data exchange is realized through Ethernet gateways, which together form an E/E architecture based on domain controllers.

4.3 In-vehicle Ethernet for power transmission
POE (Power Over Ethernet) is a technology that can supply power to connected terminal devices while transmitting data on a twisted pair cable, eliminating the need for external power cables for terminals and reducing the complexity of power supply.
The main power supply characteristic parameters of the POE standard power supply system are:
1) The voltage is between 44V and 57V, with a typical value of 48V.
2) The maximum allowable current is 550mA, and the maximum starting current is 500mA.
3) The typical working current is 10 ~ 350mA, and the overload detection current is 350 ~ 500mA.
4) Under no-load conditions, the maximum demand current is 5mA.
5) Provide PD (Power device) equipment with five levels of electrical power requests of 3.84~12.95W, with a maximum of 13W.
4.4 Car Ethernet wireless function
Wireless function is another advantage of car Ethernet. WiFi also has a variant for car use-WAVE (Car Environment Wireless Access Function); the introduction of car Ethernet will undoubtedly become the most important way to promote the introduction of WAVE into the car field. A good catalyst, which provides a physical basis for the realization of audio, video and high-definition maps in real-time communication, and also provides more imagination for the application of V2X technology.

Reference materials:
- Overview on Automotive Ethernet - Vector