table of Contents
B tree (B-tree, B-tree)
B-tree is a balanced multi-way search tree, Mostly used for the realization of file system and database;
If you look closely at the B-tree, what are the bright features?
1 个节点Can store more than 2 elements, can have more than 2 child nodes- Have some properties of binary search tree
- Balanced, all subtrees of each node have the same height
- Relatively short



Properties of m-order B-tree

How many levels of B-trees are generally used in database implementation?
- 200 ~ 300
B-tree vs. binary search tree
B-tree and binary search trees , are logically equivalent;
Combine multiple generations of nodes to get a super node
- 2 generations (current node and left and right child nodes) merged super node, with a maximum of 4 child nodes (at least 4-order B-tree)
- 3 generations (the current node and the grandchild nodes of the left and right child nodes) merged super node, with a maximum of 8 child nodes (at least 8-order B-tree)
- Super nodes merged in generation n, up to 2 n 2^n2n child nodes (at least2 n 2^n2n- order B tree)
m-order B-tree, at most log 2 m log_2mlog2M- generation merger;

search for
Similar to binary search tree search:
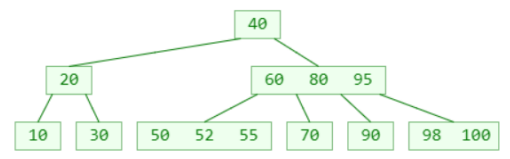
- First search for elements from small to large (from left to right) inside the node
- If it hits, the search ends
- If it is not hit, go to the corresponding child node to search for the element, and then repeat step 1
Add-Overflow
4th order B tree
The newly added element must be added to the leaf node :
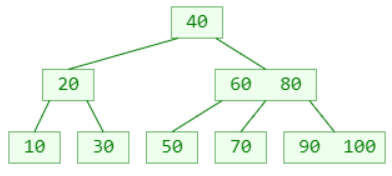
insert 55:
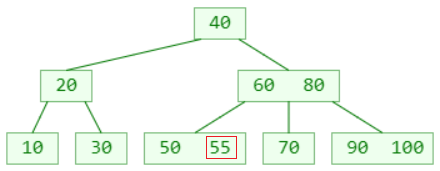
insert 95:
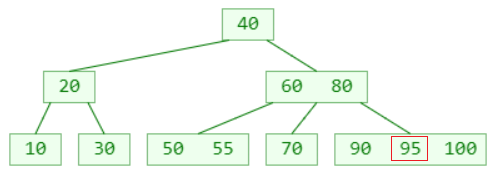
insert 98 again? (Assuming this is a 4th order B-tree)
- The number of elements of the leaf node in the bottom right corner will exceed the limit
- This phenomenon can be called:Overflow
Add-Overflow resolution (assuming 5th order)

The number of elements of the overflow node must be equal to m;
Suppose the position of the middle element of the overflow node is k
- Merge the element at position k upward with the parent node
- Put [0, k − 1] [0, k-1][0,k−1 ] and[k + 1, m − 1] [k + 1, m-1][k+1,m−1 ] The element at position is split into 2 child nodes
- The number of elements of these two child nodes must not be lower than the minimum limit ( ┌ m / 2 ┐ − 1 ┌ m/2 ┐ − 1┌ m / 2 ┐ − 1 ) [m divided by 2 and round up and minus 1]
After a split is completed, it may cause the parent node to overflow, still follow the above method to solve
- In the most extreme case, it may split all the way to the root node

Add demo [overflow]
Suppose this is a 4th-order B-tree , add 98, 52, 54 in sequence

delete
Delete-leaf node
If the element to be deleted is in the leaf node , just delete it directly;
Example: delete 30

Delete-non-leaf node
If you need to delete elements in non-leaf nodes in
- Find the predecessor or successor element first, and overwrite the value of the element to be deleted
- Then delete the predecessor or successor element
The predecessor or successor element of a non-leaf node must be in the leaf node;
- So the predecessor or successor element deleted here is the situation mentioned at the beginning: the deleted element is in the leaf node
- The actual deletion of elements occurs in the leaf nodes;
Example: delete 60

Delete-underflow
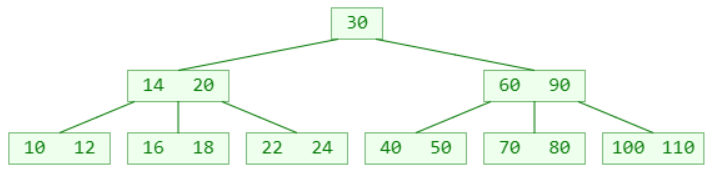
Delete 22? (Assuming this is a 5th-order B-tree)
- After one element is deleted from the leaf node, the number of elements may be lower than the minimum limit ( ≥ ┌ m / 2 ┐ − 1 ≥ ┌ m/2 ┐ − 1≥┌m/2┐−1 )
- This phenomenon is called:下溢(underflow)
Delete-Underflow resolution


The number of elements of the underflow node must be equal to ┌ m / 2 ┐ − 2 ┌ m/2 ┐ − 2┌m/2┐−2
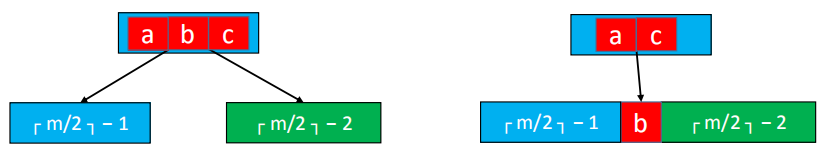
If the next sibling node of the underflow node is at least ┌ m / 2 ┐ ┌ m/2 ┐┌ m / 2 ┐ elements, one element can be borrowed from it
- Insert the element b of the parent node into position 0 (minimum position) of the underflow node
- Replace the element b of the parent node with the element a of the sibling node (the largest element)
- This kind of operation is actually: rotate

If the next sibling node of the underflow node, only ┌ m / 2 ┐ − 1 ┌ m/2 ┐ − 1┌ m / 2 ┐ − 1 element
- Move the element b of the parent node down to merge with the left and right child nodes
- The number of combined node elements is equal to ┌ m / 2 ┐ + ┌ m / 2 ┐ − 2 ┌ m/2 ┐ + ┌ m/2 ┐ − 2┌m/2┐+┌ m / 2 ┐ − 2 , not more than m − 1
- This operation may cause the parent node to underflow, still follow the above method to solve the problem, the underflow phenomenon may continue to propagate upward
Delete demo [underflow]
Assuming this is a 5th-order B-tree, deleting 22 will cause 20, 30 to underflow

4th order B tree

The properties of the 4-order B-tree:
- The number of elements x that all nodes can store :1 ≤ x ≤ 3
- The number of child nodes y of all non-leaf nodes :2 ≤ and ≤ 4