definition
B-tree can be seen as an extension of the search tree 2-3, i.e. it allows each node has child nodes M-1.
- There are at least two child nodes of the root node
- Each node has the M-1 key, and arranged in ascending order
- The value of the child node is located and the M key M-1 M-1 located at the corresponding Value, and between the M key
- Other nodes have at least M / 2 sub-node
FIG next order M = 4 is a B-tree:
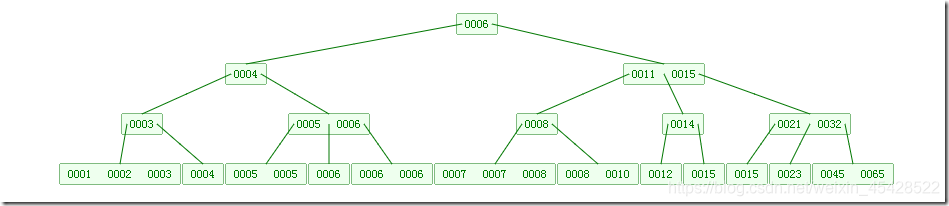
see 2-3 B-tree is a tree extension, it allows a node has more than two elements.
Insert and equilibration operation 2-3 B-tree, and the tree is very similar, not presented here. The following are sequentially inserted into the B-Tree
6 10 4 14 5 11 15 3 2 12 1 7 8 8 6 3 6 21 5 15 15 6 32 23 45 65 7 8 6 5 4
The animation:

B + Tree is a modification of the B-tree is a tree, with the difference that the B-tree comprising:
- There node k sub-node must have a key k;
- Non-leaf node has only the role of the index, with information about the records are stored in the leaf node in.
- All the leaf nodes of the tree constituting a sorted linked list can be traversed all the records in the order of sorted key.
Below, it is a B + tree:
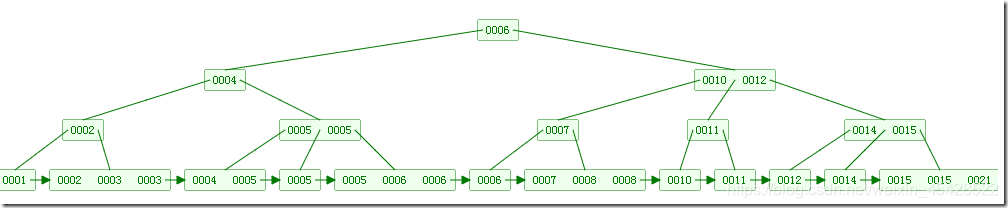
The figure is inserted animation B + tree:

the difference between B and B + tree is that, B + non-leaf node of the tree contains only navigation information does not contain the actual value of all of the leaf nodes and is connected linked list of nodes, easy to find and traverse section.
The advantage that the B + tree:
- Since B + tree does not contain data on the internal node, the page in memory that can store more key. Stored data more closely, with better spatial locality. Therefore, access data associated with the leaf node also has a better cache hit ratio.
- B + tree leaf node are relative to the chain, so the whole tree traversal linear convenience only once to a leaf node. And because the data is sequentially arranged and connected, it is easy to find and search range. While the B-tree is required for each layer recursive traversal. Adjacent elements may not be adjacent in memory, so there is no cache hit of good B + tree.
但是B树也有优点,其优点在于,由于B树的每一个节点都包含key和value,因此经常访问的元素可能离根节点更近,因此访问也更迅速。下面是B 树和B+树的区别图:
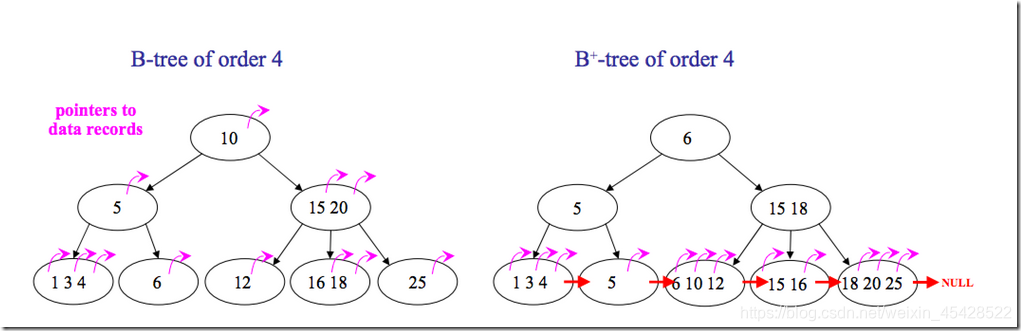
分析
对B树和B+树的分析和对前面讲解的2-3树的分析类似,
对于一颗节点为N度为M的子树,查找和插入需要logM-1N ~ logM/2N次比较。这个很好证明,对于度为M的B树,每一个节点的子节点个数为M/2 到 M-1之间,所以树的高度在logM-1N至logM/2N之间。
这种效率是很高的,对于N=62*1000000000个节点,如果度为1024,则logM/2N <=4,即在620亿个元素中,如果这棵树的度为1024,则只需要小于4次即可定位到该节点,然后再采用二分查找即可找到要找的值。
应用
B树和B+广泛应用于文件存储系统以及数据库系统中,在讲解应用之前,我们看一下常见的存储结构:
我们计算机的主存基本都是随机访问存储器(Random-Access Memory,RAM),他分为两类:静态随机访问存储器(SRAM)和动态随机访问存储器(DRAM)。SRAM比DRAM快,但是也贵的多,一般作为CPU的高速缓存,DRAM通常作为内存。这类存储器他们的结构和存储原理比较复杂,基本是使用电信号来保存信息的,不存在机器操作,所以访问速度非常快,具体的访问原理可以查看CSAPP,另外,他们是易失的,即如果断电,保存DRAM和SRAM保存的信息就会丢失。
我们使用的更多的是使用磁盘,磁盘能够保存大量的数据,从GB一直到TB级,但是 他的读取速度比较慢,因为涉及到机器操作,读取速度为毫秒级,从DRAM读速度比从磁盘度快10万倍,从SRAM读速度比从磁盘读快100万倍。下面来看下磁盘的结构:
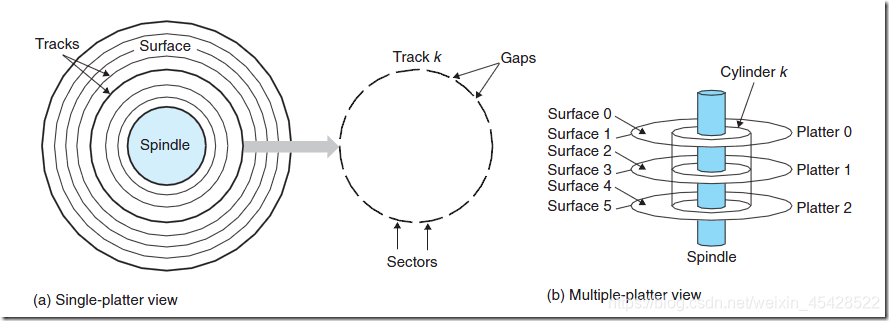
如上图,磁盘由盘片构成,每个盘片有两面,又称为盘面(Surface),这些盘面覆盖有磁性材料。盘片中央有一个可以旋转的主轴(spindle),他使得盘片以固定的旋转速率旋转,通常是5400转每分钟(Revolution Per Minute,RPM)或者是7200RPM。磁盘包含一个多多个这样的盘片并封装在一个密封的容器内。上图左,展示了一个典型的磁盘表面结构。每个表面是由一组成为磁道(track)的同心圆组成的,每个磁道被划分为了一组扇区(sector).每个扇区包含相等数量的数据位,通常是(512)子节。扇区之间由一些间隔(gap)隔开,不存储数据。
以上是磁盘的物理结构,现在来看下磁盘的读写操作:
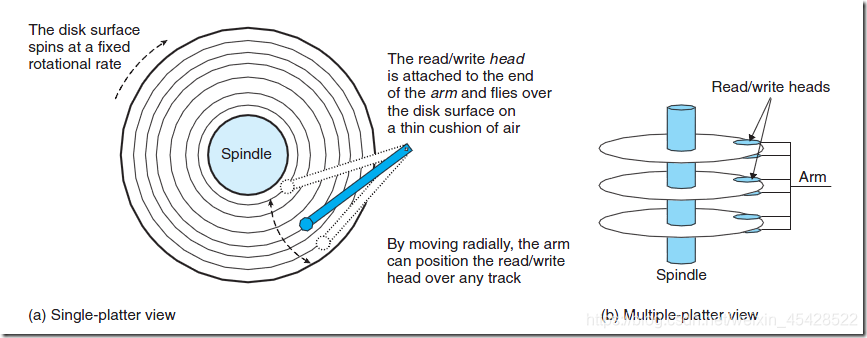
如上图,磁盘用读/写头来读写存储在磁性表面的位,而读写头连接到一个传动臂的一端。通过沿着半径轴前后移动传动臂,驱动器可以将读写头定位到任何磁道上,这称之为寻道操作。一旦定位到磁道后,盘片转动,磁道上的每个位经过磁头时,读写磁头就可以感知到位的值,也可以修改值。对磁盘的访问时间分为 寻道时间,旋转时间,以及传送时间。
由于存储介质的特性,磁盘本身存取就比主存慢很多,再加上机械运动耗费,因此为了提高效率,要尽量减少磁盘I/O,减少读写操作。为了达到这个目的,磁盘往往不是严格按需读取,而是每次都会预读,即使只需要一个字节,磁盘也会从这个位置开始,顺序向后读取一定长度的数据放入内存。这样做的理论依据是计算机科学中著名的局部性原理:
当一个数据被用到时,其附近的数据也通常会马上被使用。
程序运行期间所需要的数据通常比较集中。
由于磁盘顺序读取的效率很高(不需要寻道时间,只需很少的旋转时间),因此对于具有局部性的程序来说,预读可以提高I/O效率。
预读的长度一般为页(page)的整倍数。页是计算机管理存储器的逻辑块,硬件及操作系统往往将主存和磁盘存储区分割为连续的大小相等的块,每个存储块称为一页(在许多操作系统中,页得大小通常为4k),主存和磁盘以页为单位交换数据。当程序要读取的数据不在主存中时,会触发一个缺页异常,此时系统会向磁盘发出读盘信号,磁盘会找到数据的起始位置并向后连续读取一页或几页载入内存中,然后异常返回,程序继续运行。
文件系统及数据库系统的设计者利用了磁盘预读原理,将一个节点的大小设为等于一个页,这样每个节点只需要一次I/O就可以完全载入。为了达到这个目的,在实际实现B-Tree还需要使用如下技巧:
每次新建一个节点的同时,直接申请一个页的空间( 512或者1024),这样就保证一个节点物理上也存储在一个页里,加之计算机存储分配都是按页对齐的,就实现了一个node只需一次I/O。如,将B树的度M设置为1024,这样在前面的例子中,600亿个元素中只需要小于4次查找即可定位到某一存储位置。
同时在B+树中,内节点只存储导航用到的key,并不存储具体值,这样内节点个数较少,能够全部读取到主存中,外接点存储key及值,并且顺序排列,具有良好的空间局部性。所以B及B+树比较适合与文件系统的数据结构。下面是一颗B树,用来进行内容存储。
另外B/B+树也经常用做数据库的索引,这方面推荐您直接看张洋的MySQL索引背后的数据结构及算法原理 这篇文章,这篇文章对MySQL中的如何使用B+树进行索引有比较详细的介绍,推荐阅读。
总结
In front of the two articles introduced the balanced search tree, the tree of 2-3, after the red-black tree, this article describes the file systems and database systems commonly used in B / B + tree, he passed the extension of the number of storage for each node, such that continuous data can be accessed faster positioning and can effectively reduce the search time, improve spatial locality so as to reduce IO memory operation. He is widely used for file systems and databases, such as:
- Windows: HPFS file system
- Mac: HFS, HFS + file system
- Linux: ResiserFS, XFS, Ext3FS, JFS file system
- Database: ORACLE, MYSQL, SQLSERVER, etc.
This article reprinted from: http://www.cnblogs.com/yangecnu/p/Introduce-B-Tree-and-B-Plus-Tree.html