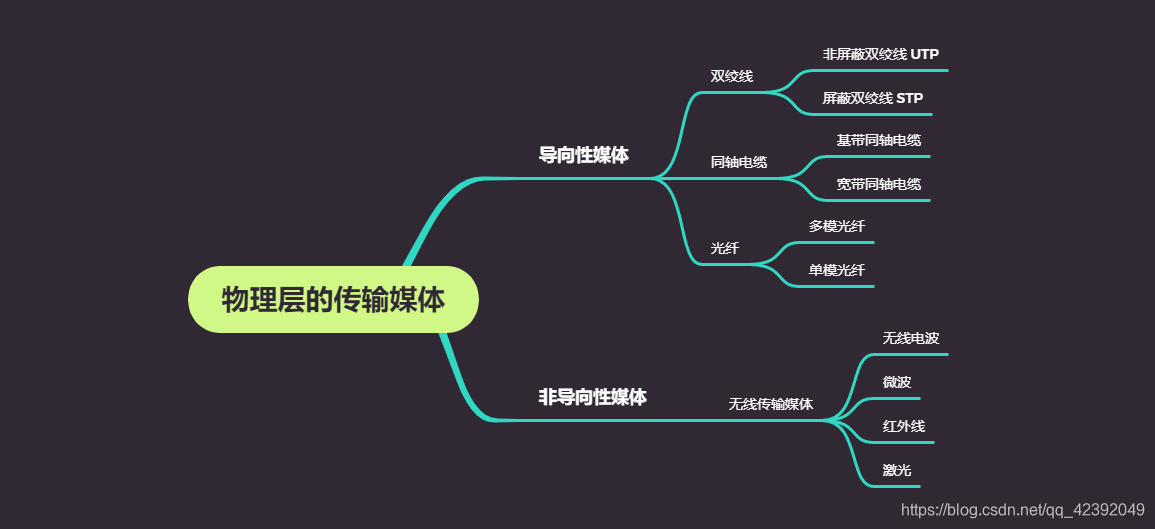
Transmission media: the physical carrier that actually transmits information between adjacent nodes
Oriented media: actual physical cables-twisted pair, coaxial cable, optical fiber
Non-oriented media: free space (water, air)-no actual physical cables
(1) Twisted-pair wire
Two copper wires covered with insulating material (such as plastic) are twisted together.

Why are twisted-pairs used to reduce electrical signal interference. The higher the twist, the higher the bandwidth. The higher the price, the higher the price of the
twisted pair cable. Twisted pair cable: multiple pairs of twisted pairs are placed in a protective layer.
Unshielded twisted pair UTP: used for LAN, divided into several types of
shielded twisted pair STP: anti-electromagnetic interference Strong ability, high price, complicated installation
(2) Coaxial cable
A pair of conductors are constructed in the form of "coaxial"
Features: strong anti-interference ability, high data rate
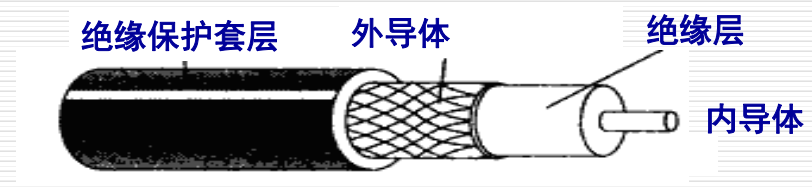
Inner conductor: transfer data
Outer conductor: shield interference
Commonly used two types of coaxial cables
① Baseband coaxial cables ( coaxial cables with an impedance of 50 Ω)
Features: thin, light, direct transmission of discrete digital signals, used for LAN
② Broadband coaxial cables (with an impedance of 75 Ω) Shaft cable)
features: thick, heavy, analog signal transmission, used in cable television systems
(3) Optical fiber
A thin and soft medium that transmits optical pulses.
Features:
①The transmission rate is up to ten or even hundreds of Gbps, free of electromagnetic interference, and the signal attenuation of the optical cable up to 100km is extremely low, making it difficult to eavesdrop.
②Remote-oriented type Media, especially cross-sea link
③High-cost optical equipment, optical fiber is used in long-distance telephone network, Internet backbone network Fiber
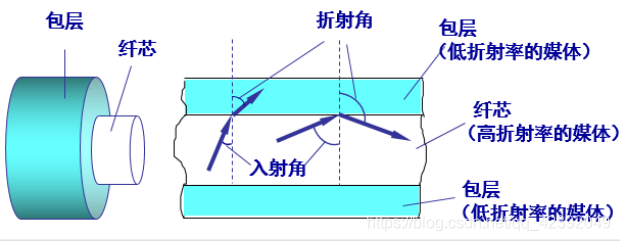
core: ultra-pure silicon, synthetic glass, plastic
Cladding: plastic sheath
Type
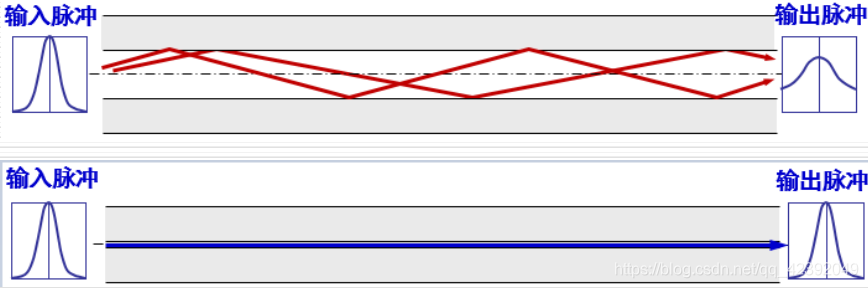
①Multimode fiber: one fiber can transmit light from different angles, the light source adopts light-emitting diode
②Single-mode fiber: the diameter is small, so that the light propagates forward without refraction, the light source is a semiconductor laser
(4) wireless transmission media
utilization Electromagnetic waves propagate in free space to achieve communication
Reference book:
[1] "Computer Network Tutorial" (2nd Edition), Gao
Chuanshan, etc., Higher Education Press [2] "Computer Network-Top-Down Method", Kurose & Ross, translated by Chen Ming, (Original book 6th edition), Machinery Industry Press
[3] "Guide to Review of Computer Network Postgraduate Examination in 2021", edited by Wangdao Forum, Electronic Industry Press