DNS system forward resolution
1. DNS system
In daily life, people are accustomed to using domain names to access servers, but machines only recognize each other's IP addresses. There is a many-to-one relationship between domain names and IP addresses . An ip address does not necessarily correspond to one domain name, and one domain name can only correspond to one. IP address , the conversion between them is called domain name resolution , domain name resolution needs to be completed by a dedicated domain name resolution server , the whole process is automatic.
1.1 Definition of DNS
DNS is the abbreviation of "Domain Name System". As a distributed database that maps domain names and IP addresses to each other , it can make it easier for people to access the Internet.
DNS service uses TCP and UDP of port 53 , TCP port 53 for connection DNS server , UDP port 53 is used to resolve DNS .
The length of each first-level domain name is limited to 63 characters , and the total length of the domain name cannot exceed 253 characters .
1.2 Domain name structure
http://www.sina.com.cn./
http://主机名.二级域.顶级域根域/
Distributed data structure of DNS system

The top level of the tree structure is called the root domain , which is represented by ".". The corresponding server is called the root server . The resolution power of the entire domain name space belongs to the root server.
However, the root server cannot bear the huge load. The “delegation” mechanism is adopted to set up some top-level domains under the root domain , and then delegate the resolution power of different top-level domains to the corresponding top-level domain servers , such as delegating the resolution power of the com domain to com domain server, in the future, whenever the root server receives a domain name resolution request ending with com, it will forward it to the com domain server.
In the same way, in order to alleviate the pressure on the top-level domain, the Mangan second- level domain is set up , and the second-level domain is also set up a third-level domain or host
(1) The root domain
is at the top of the domain name space, and is generally represented by a "."
(2) The top-level domain
generally represents a type of organization or country.
如 .net (网络供应商)、.com(工商企业)、.org(团体组织)、.edu(教育机构)、.gov (政府部门)、.cn(中国国家域名)
(3) The second-level domain is
used to indicate a specific organization in the top-level domain. The second-level domain names below the national top-level domain are managed by the national network department.
如.cn顶级域名下面设置的二级域名: .com.cn、.net.cn、.edu.cn
(4) Subdomains The domains
at all levels created under the second-level domains are collectively referred to as subdomains. Each organization or user can freely apply for registration of their own domain names
(5) Host The
host is located at the lowest level of the domain name space and is a specific computer
如www.mail都是具体的计算机名字,可用www.sina.com.cn.、mail.sina.com.cn.来表示,这种表示方式称为FQDN(完全合格域名),也是这台主机在域名中的全名
1.3 DNS domain name resolution method
Forward resolution: Find the corresponding IP address according to the domain name
Reverse resolution: Find the corresponding domain name based on the IP address
1.4 DNS server type
(1) Primary domain name server: responsible for maintaining all domain name information of an area, it is the authoritative information source of all specific information, and the data can be modified. When constructing the main domain name server, you need to create the address data file for the area you are responsible for .
(2) Secondary domain name server: When the primary domain name server fails, shuts down or is overloaded, the secondary domain name server serves as a backup service to provide domain name resolution services. The resolution result provided from the domain name server is not determined by yourself, but comes from the main domain name server . When constructing the secondary domain name server , you need to specify the location of the master domain name server so that the server can automatically synchronize the address database of the area.
(3) Cache domain name server: It only provides the cache function of domain name resolution results to improve query speed and efficiency , but there is no domain name database .
It obtains the result of each domain name server query from a remote server, puts it in the cache, and uses it to respond to the same information later. The cache domain name server is not an authoritative server, because all the information provided is indirect . When constructing a cache domain name server, you must set the root domain or specify another DNS server as the source of resolution .
(4) Forwarding domain name server: responsible for local queries of all non-local domain names . After the forwarding domain name server receives the query request, it searches in its cache. If it cannot find it, it forwards the request to the specified domain name server in turn until the result is found, otherwise it returns the result that cannot be mapped.
1.5 Steps to construct DNS domain name resolution server
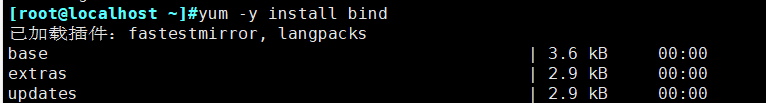
1. Install the bind package
yum -y install bind
2. Configure forward analysis
(1) First check the path of the configuration file to be modified
rpm -qc bind #查询bind软件配置文件所在路径
/etc/named.conf #主配置文件
/etc/named.rfc1912.zones #区域配置文件
/var/named/named. localhost #区域数据配置文件

(2) Modify the main configuration file
vim /etc/named.conf
options {
listen-on port 53 { 192.168.80.10; }; #监听53端口, ip地址使用提供服务的本地IP,也可用any表示所有
# listen-on-v6 port 53 { ::1; } #ipv6行如不使用可以注释掉或者删除
directory "/var/named"; #区域数据文件的默认存放位置
dump-file "/var/named/data/cache_dump.db"; #域名缓存数据库文件的位置
statistics-file "/var/named/data/named_stats.txt"; #状态统计文件的位置
memstatistics-file "/var/named/data/named_mem_stats.txt"; #内存统计文件的位置
allow-query { 192.168.80.0/24; 172.16.100.0/24; }; 允许使用本DNS解析服务的网段,也可用any代表所有
.......
};
zone "." IN { #正向解析"."根区域
type hint; #类型为根区域
file "named.ca"; #区域数据文件为named.ca,记录了13台根域服务器的域名和IP地址等信息
};
include "/etc/named.rfc1912.zones"; #包含区域配置文件里的所有配置
include "/etc/named.root.key";

(3) Modify the zone configuration file and add the forward zone configuration
vim /etc/named.rfc1912.zones #可在文件里有模版,可复制粘贴后修改
zone "benet.com" IN { 正向解析"benet.com"区域
type master; #类型为主区域
file "benet.com.zone"; 指定区域数据文件为benet.com.zone
allow-update { none; };
};

(4) Configure the forward zone data file
cd /var/named/
cp -p named. localhost benet.com.zone #保留源文件的权限和属主的属性复制
vim /var/named/benet.com.zone
$TTL 1D #设置缓存解析结果的有效时间
@ IN SOA benet.com. admin.benet.com. (
0 ; serial
1D ; refresh
1H ; retry
1W ;expire
3H ) ;minimun
NS benet. com. #记录当前区域的DNS服务器的名称
A 192.168.80.10 #记录主机IP地址
IN MX 10 mail.benet. com #MX为邮件交换记录,数字越大优先级越低
www IN A 192.168.80.10 (要顶格写) #记录正向解析www.benet.com对应的IP
mail IN A 192.168.80.11
ftp IN CNAME www #CNAME使用别名, ftp是www的别名
* IN A 192.168.80.100 #泛域名解析, "*"代表任意主机名
#"@"这里是一个变量,当前DNS区域
#SOA标记用于同步主从服务器的区域数据,如更新序列号相同则不会更新
#"benet.com."此为完全合格域名(FQDN) ,后面有个"."不能漏掉
#"admin. benet.com."表示管理员邮箱,这里的"@"是变量,所以用“."代替

(5) Start the service and close the firewall
systemctl start named
systemctl stop firewalld
setenforce 0
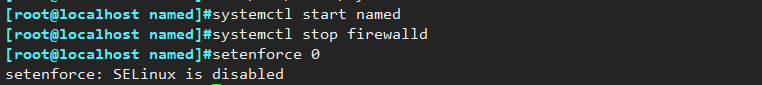
#If the service fails to start, you can check the log file to troubleshoot the error
tail -f /var/log/messages #如果服务启动卡住,可以执行下面命令解决
rndc-confgen -r /dev/urandom -a
(6) Add the DNS server address in the client's domain name resolution configuration file
vi /etc/resolv.conf #修改完后立即生效
nameserver 192.168.80.10
或
vi /etc/sysconfig/network-scripts/ifcfg-ens33 #修改完后需要重启网卡
DNS1=192.168.80.10
systemctl restart network
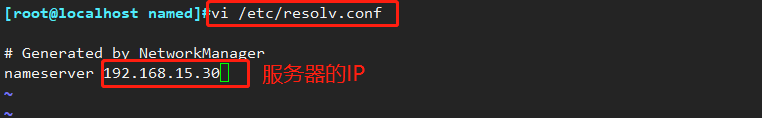
Or

vi /etc/sysconfig/network-scripts/ifcfg-ens33 Don’t forget to restart after the change
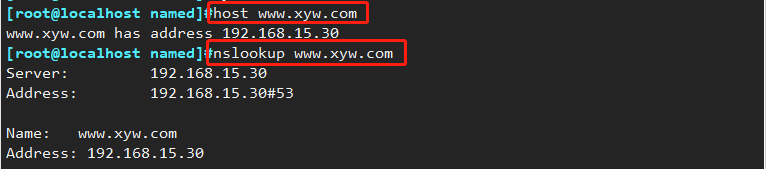
(7) Test DNS resolution
host www.benet.com
nslookup www.benet.com