Concept of domain and active directory
Domain is a set of computers and users that is artificially defined by the enterprise network clock. The purpose is to conduct unified and centralized management of various resource objects of the collective clock.
Active Directory (Active Directory) is a small database that defines the attributes of various objects in the domain and logically forms a hierarchical structure for more effective display and management.
The domain controller (Domain Controller) stores the server of the Active Directory database and runs the ADDS (Active Directory Domain Service) service.
Overview: The
domain provides a collection environment. In the collection, various objects (computers, users) are included. The objects are stored in a database based on file collections. The name is called Active Directory. The Active Directory is stored in the domain control. On the server, an enterprise can have multiple domain controllers to achieve high availability and load balancing.
- Mandatory security policies and desktop/application environments for terminal computers and users, and can realize batch and automatic deployment, reducing the difficulty of daily management and work intensity of IT personnel.
- The access control of various services and resources (file and print sharing, etc.) in the domain can be flexibly combined with the hierarchical organizational structure of the enterprise to meet the management needs of complex authority allocation.
- The unified identity verification method can be integrated with a variety of windows application services (such as Exchange, Sharepoint, etc.) and third-party software to achieve single sign-on and improve user experience in switching between multiple services.
Summary: The
first aspect is to assist IT managers in the unified automatic deployment of some parameters of computers and users in the enterprise, and realize batch and automatic parameter deployment through management methods such as group policies in the domain, reducing IT managers’ Work difficulty and intensity.
Use the authority management mechanism to effectively control the access to resources in the enterprise (such as file sharing servers, printers) for different users in different departments to control the authority of the device.
Through domains and Active Directory, the unified identity verification of the enterprise is realized. Now more and more applications are deployed by enterprises. If each application has a set of login account system, the user experience is extremely poor. , Every business system requires a user name and password, and it must be logged in repeatedly for each use, but if you have a function of domain and active directory, you can make the application use Active Directory to achieve unified authentication and single sign-on , Not only supports windows, such as (Exchange, Sharepoint native products can achieve single sign-on), and other third-party products can also be re-developed, and can also support domains.
Role in the domain
- Domain Controller (DC), each enterprise can have multiple domain controllers
- The member server in the domain, the enterprise server operating system has joined the domain, if the domain controller is windows server 2012, the member server 3 can be win 2008, and there is no mandatory requirement that the version is the same. Both linux and mac can be added, but non-Microsoft computers can join The domain control may be subject to some limitations in terms of functions, and may require the application of third-party plug-ins to complete more complex management and monitoring tasks.
- The terminal computer in the domain. I mentioned the database of Microsoft AD Active Directory. It is essentially a file. The file is placed on the domain controller. By default, it is saved in the C/windows/ntds directory of the controller. The AD database file saves

the main database file of the .dit Active Directory in the directory by default . The file capacity will not be very large. The Active Directory file will not contain massive amounts of data. Even if there are tens of thousands of PCs, the data stored in each object is relatively small. Several hundred M.
Auxiliary files (transaction log, checkpoint file)
cooperate with the processing of domain control. When the user wants to write data to the Active Directory due to special reasons (power failure, system failure), the user has not had time to write data in the future, which caused a failure. After restarting, the last write Is the imported data lost?
How to deal with it? With the help of the transaction log file, the transaction log file will not be very large. Each transaction log file is numbered in sequence. When there is a write request, the write request will be written to the main data in the memory in the future. Write to the transaction log. The transaction log is small and will be very fast. In the transaction log, even if the computer is powered off and restarted, the checkpoint file is used to record the last log and which data was not written to the main data file. You can use the check Point file data write recovery can ensure that the working environment of the domain controller causes data loss due to the special reasons of the domain controller.
The reserved file is mainly used to prevent the hard disk of the domain controller from being full for some reason. Once the domain controller is full, it cannot work normally. Therefore, before the hard disk is full, write some data to In the reserved file.
During the maintenance of the AD database, operations such as service start and stop, file set redirection, offline management, backup and recovery can be performed when necessary.
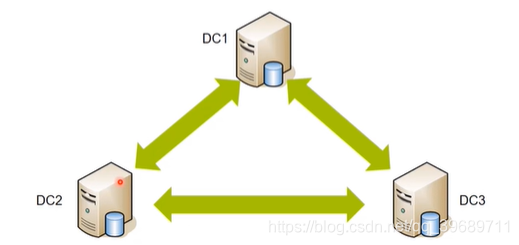
AD database synchronization between domain controllers
The AD database will be synchronized and replicated between DCs regularly or automatically when changes occur. The frequency and time window of the synchronization replication can be configured and defined.
In an enterprise, if there are three domain controllers, there are also three copies of Active Directory. The three copies should be exactly the same. If the administrator logs in to one domain controller and modifies the parameters, the other two will also be synchronized.
The synchronization between domain controllers can achieve high availability. The realization is to directly synchronize the changes of parameter increments.
Special domain controller
Read Only Domain Controller
- Rodc saves a read-only copy of the AD database in the domain controller
- It is not allowed to make changes to the database locally on the RODC
- RODC is suitable for deployment in remote branches without local management requirements
Application scenarios (very common use) The
enterprise has planned a domain. In a remote branch, there are not many local users and no IT administrators, but a domain controller is still needed to improve the user’s local login experience. When using other city’s domain controller Active Directory to synchronize to this branch’s domain controller, and make it an RODC, the advantage: if the domain controller is illegally logged in, it has no way to change the relevant data to ensure safety. It is not an RODC, if the authority of the domain controller is modified, it will be reversely synchronized to other active directories, which is very dangerous.
In
many sqa enterprises, especially some companies with factories in various places, some of the domain controllers deployed in the branches are RODCs, and only one-way data synchronization can be performed, and modification operations can only be performed by logging in to the headquarters domain controller.
Global Category Server
- GC is a special domain controller. At least one is deployed in a domain
- GC is used to synchronize data with other domains in a multi-domain environment (but not all data is synchronized, usually only 5% to 10% of the total AD database), in order to optimize the global or cross-border application of Exchange server The efficiency of domain search.
Application scenario
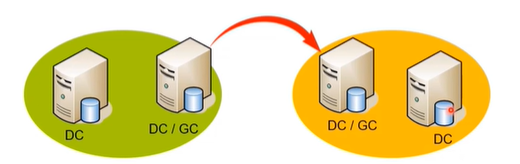
Two domains are deployed in the enterprise. There is a problem: because the domain is the boundary of management, the computer information in one domain does not need to be transmitted to other domains by default, and all data synchronization is only in the same domain.
The role of GC: When synchronizing data in other domains, you can filter one of the object attributes for selection, and you do not need to synchronize all data.
Domain and Active Directory planning
Need to combine the business environment and business needs of the enterprise
What is suitable for multi-domain
A domain can contain 1 million objects, and most enterprises only need to have one domain technically.
Multi-domain deployment may need to be considered when the following demand situations occur
- IT management policies need to have separate or independent IT control boundaries
- Changes in the domain of influence due to company reorganization or merger
- The transformation and migration of domains require the coexistence of new and old domains
Multi-domain term

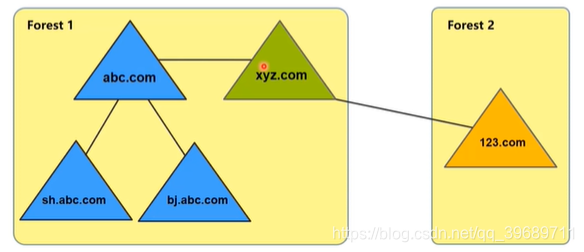
Trust relationship between domains
The trust relationship can realize cross-domain authentication and resource access. If there is no trust relationship between the domains, users in each domain can only access the resources in the domain. Depending on the scenario, some trust relationships exist by default, and some Need to be configured manually.
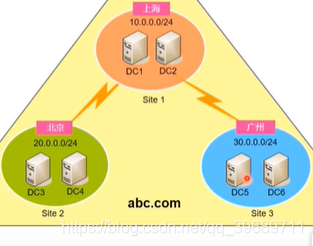
What is a site?
Site refers to a network that contains a specific IP subnet and is associated with a specific domain controller in the same domain. The purpose of deploying multiple sites is to optimize the replication and synchronization of the DCs between the sites, and at the same time enable the overcome end to communicate with the nearest DC first , Optimize the operation of login verification.
Planning recommendations
There is no unified standard for domain planning, but it is recommended to simplify it as much as possible and use single domain as much as possible. If there is no special requirement, use single domain as much as possible, and the workload is small.
Enterprise size, network bandwidth, IT control interface, legal and political requirements, and company merger plans are common considerations.
General recommendations for enterprise domain planning:
SMEs use a single domain, branch offices under the headquarters can use parent-child domains or single domain multi-sites, and multiple independent business subsidiaries under the group use single forest and multiple domains.
Maintain domain control,
1. Manually stop the domain control service

2.