研究の序文
この論文では、YOLOv8-Pose アルゴリズムの TensorRT 高速推論を実装します。
TensorRT をインストールする
1. TensorRT の概要
公式ウェブサイトのリンク: https://developer.nvidia.com/tensorrt
NVIDIA ® TensorRT™ は、トレーニングされた深層学習モデルを最適化し、高性能の推論を可能にする SDK です。TensorRT には、トレーニングされた深層学習モデル用の深層学習推論オプティマイザーと、実行用のランタイムが含まれています。選択したフレームワークで深層学習モデルをトレーニングした後、TensorRT を使用すると、より高いスループットとより低いレイテンシでモデルを実行できるようになります。
公式のTensorRT紹介によると、これはトレーニング済みモデルTensorRT用の SDK であり、これを通じて NVIDIA デバイス上で高性能の推論を実行できます。トレーニング済みモデルにどのような最適化が行われるかについては、次の図に示すように、公式 Web サイトの図を参照してください。TensorRTTensorRT
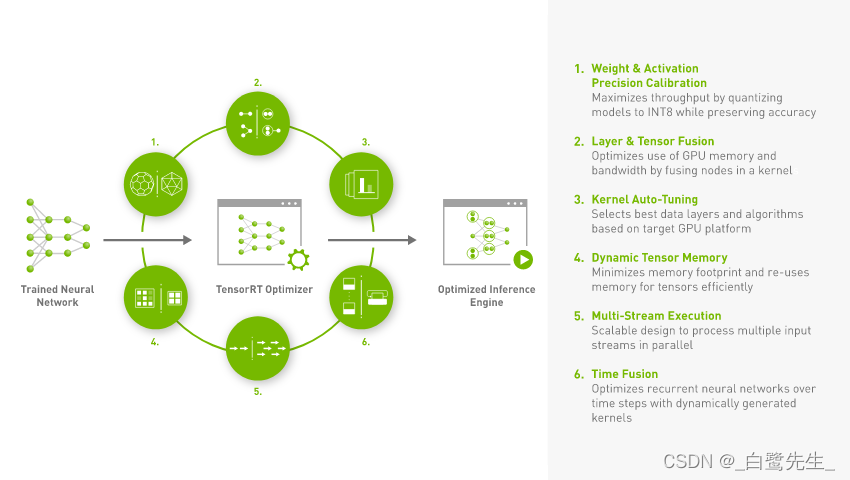
まとめると、主に以下の6点になります。
Reduced Precision: モデルの推論速度を向上させるために、モデルをINT8または のデータ型に量子化しますFP16(精度を維持するか、わずかに低下することを前提としています)。Layer and Tensor Fusion: 複数のレイヤー構造 (水平方向と垂直方向を含む) を融合することで、GPU メモリと帯域幅を最適化します。Kernel Auto-Tuning: 現在使用されている GPU プラットフォームに応じて、最適なデータ レイヤーとアルゴリズムを選択します。Dynamic Tensor Memory: メモリ フットプリントを最小限に抑え、テンソル用にメモリを効率的に再利用します。Multi-Stream Execution: スケーラブルな設計を使用して、複数の入力ストリームを並列処理します。Time Fusion: 動的に生成されたカーネルを使用して、時間ステップとともに変化する RNN ネットワークを最適化します。
2. TensorRT をダウンロードする
公式 Web サイトhttps://developer.nvidia.com/nvidia-tensorrt-8x-download
にアクセスして、対応するバージョンを見つけます。ここでは選択します。
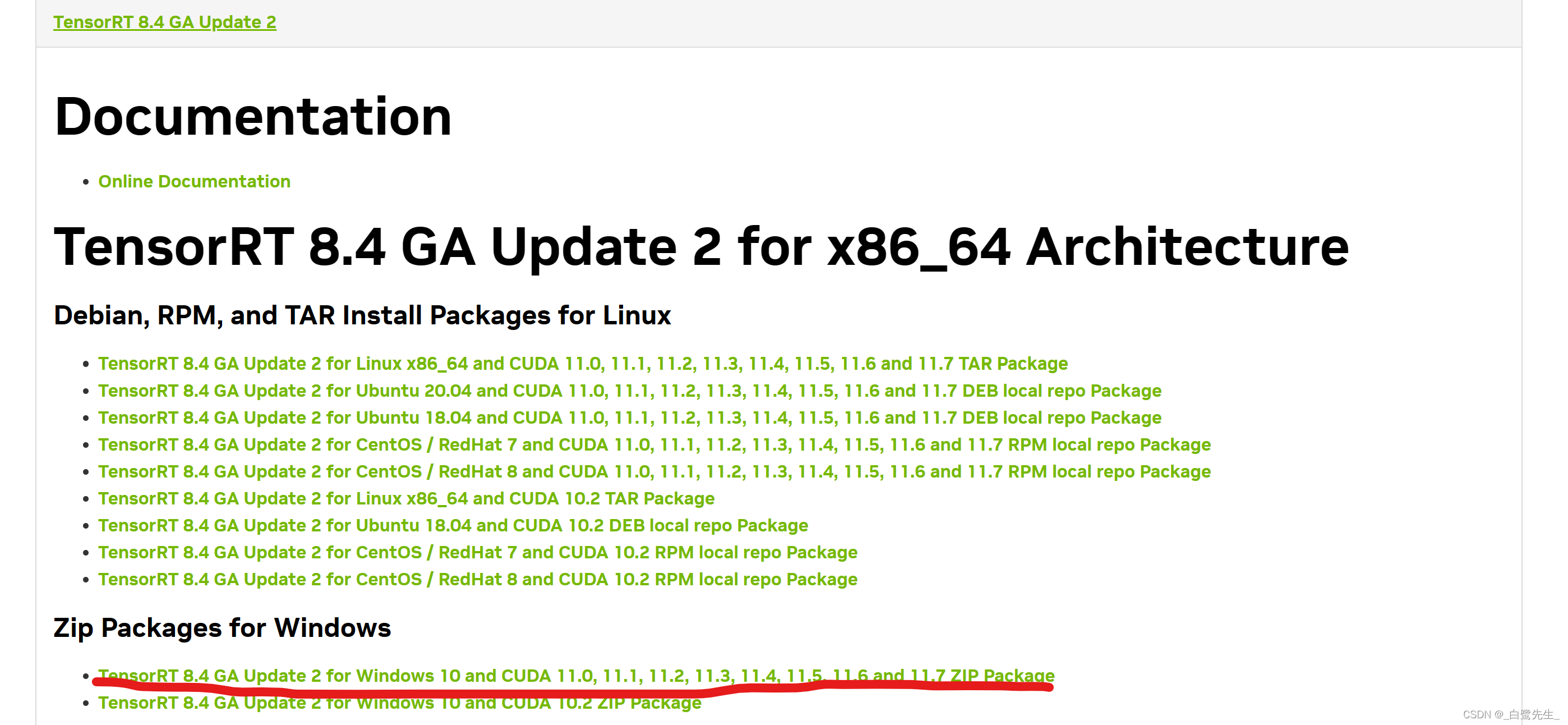
zip アーカイブをダウンロードして解凍します。
3. TensorRT のインストール
次の手順を任意の順序で実行します。
- TensorRT-8.4.3.1\bin の内容を C:\Program Files\NVIDIA GPU Computing Toolkit\CUDA\v11.3\bin にコピーします。
- TensorRTのインクルードフォルダをCUDAのインクルードフォルダにコピーする
- TensorRT-8.4.3.1\lib フォルダー内の lib ファイルを CUDA の lib フォルダーにコピーし、dll ファイルを CUDA の bin フォルダーにコピーします。

以下の図に示すように、pip install xxx.whl を使用して TensorRT-8.4.3.1 をフォルダーにインストールします。

Python を使用して、インストールが成功したかどうかを確認します。

TensorRTライブラリをインストールした後、モデル変換pycudaを開始できます。YOLO8-Pose
モデル変換
pthまずモデルをONNXモデルに変換し、次にONNXモデルをengineモデルに変換する必要があります。
ONNX モデルのエクスポート
まず、次のコマンドを使用して onnx モデルをエクスポートします。
yolo export model=yolov8s-pose.pt format=onnx opset=11 simplify=True
または、次のようなスクリプトを使用します。
from ultralytics import YOLO
# Load a model
model = YOLO("yolov8s-pose.pt") # load a pretrained model (recommended for training)
success = model.export(format="onnx", opset=11, simplify=True) # export the model to onnx format
assert success
エンジンモデルのエクスポート
次に、次のコマンドを使用してengineモデルを取得します。
yolo export model=yolov8s-pose.pt format=engine device=0
または、次のスクリプトを実行します。
from ultralytics import YOLO
# Load a model
model = YOLO("yolov8s-pose.pt") # load a pretrained model (recommended for training)
success = model.export(format="engine", device=0) # export the model to engine format
assert success
エンジン モデルを取得したら、numpy前処理と後処理を使用して予測を実現する必要があります。
歪みのない画像のサイズ変更
まず、画像の歪みのなさを実現する必要がありますがresize、Bガイド版ではImageクラス描画画像とcv2読み取り画像を使用していますが、2種類の画像を変換することで前処理、後処理の時間が増加していましたが、これを大幅に削減しましたfps。したがって、この記事はすべて実装に基づいており、cv2歪みのない画像のresize修正は次のようになります。
#---------------------------------------------------#
# Image版本
#---------------------------------------------------#
def resize_image(image, size, letterbox_image):
iw, ih = image.size
w, h = size
if letterbox_image:
scale = min(w/iw, h/ih)
nw = int(iw*scale)
nh = int(ih*scale)
image = image.resize((nw,nh), Image.BICUBIC)
new_image = Image.new('RGB', size, (128,128,128))
new_image.paste(image, ((w-nw)//2, (h-nh)//2))
else:
new_image = image.resize((w, h), Image.BICUBIC)
return new_image
#---------------------------------------------------#
# cv2版本
#---------------------------------------------------#
def resize_image(image, size, letterbox_image):
ih, iw, _ = image.shape
h, w = size
if letterbox_image:
scale = min(w/iw, h/ih)
nw = int(iw * scale)
nh = int(ih * scale)
image = cv2.resize(image, (nw, nh), interpolation=cv2.INTER_CUBIC)
new_image = np.zeros((h, w, 3), dtype=np.uint8)
new_image[...] = 128
new_image[(h-nh)//2:(h-nh)//2+nh, (w-nw)//2:(w-nw)//2+nw, :] = image
else:
new_image = cv2.resize(image, (w, h), interpolation=cv2.INTER_CUBIC)
return new_image
resize_imageこの関数は、画像、希望のサイズ、および画像を操作するかどうかを示すブール値を受け取りますletterboxing。letterbox_imageの場合、True関数はアスペクト比を維持しながら画像のサイズを変更し、灰色の背景を持つ新しい画像の上に貼り付けて、空のスペースを埋めます。letterbox_image「はい」の場合False、関数は単に画像を希望のサイズに変更します。この関数はcv2、ライブラリを使用して画像をサイズ変更して貼り付けます。具体的には、 メソッドを使用してresize画像のサイズを変更し、ゼロと配列スライス メソッドを使用して灰色の背景を持つ新しい画像を作成し、サイズ変更した画像を新しい画像に貼り付けます。
デコード
デコード部分については、オリジナル版では torch を使用して実装していますが、この記事では numpy を使用して実装していますtorch.repeat()。np.title()
def non_max_suppression(
prediction,
conf_thres=0.25,
iou_thres=0.45,
classes=None,
agnostic=False,
multi_label=False,
labels=(),
max_det=300,
nc=0, # number of classes (optional)
max_time_img=0.05,
max_nms=30000,
max_wh=7680,
):
"""
Perform non-maximum suppression (NMS) on a set of boxes, with support for masks and multiple labels per box.
Arguments:
prediction (np.ndarray): An array of shape (batch_size, num_classes + 4 + num_masks, num_boxes)
containing the predicted boxes, classes, and masks. The array should be in the format
output by a model, such as YOLO.
conf_thres (float): The confidence threshold below which boxes will be filtered out.
Valid values are between 0.0 and 1.0.
iou_thres (float): The IoU threshold below which boxes will be filtered out during NMS.
Valid values are between 0.0 and 1.0.
classes (List[int]): A list of class indices to consider. If None, all classes will be considered.
agnostic (bool): If True, the model is agnostic to the number of classes, and all
classes will be considered as one.
multi_label (bool): If True, each box may have multiple labels.
labels (List[List[Union[int, float, np.ndarray]]]): A list of lists, where each inner
list contains the apriori labels for a given image. The list should be in the format
output by a dataloader, with each label being a tuple of (class_index, x1, y1, x2, y2).
max_det (int): The maximum number of boxes to keep after NMS.
nc (int, optional): The number of classes output by the model. Any indices after this will be considered masks.
max_time_img (float): The maximum time (seconds) for processing one image.
max_nms (int): The maximum number of boxes into torchvision.ops.nms().
max_wh (int): The maximum box width and height in pixels
Returns:
(List[np.ndarray]): A list of length batch_size, where each element is an array of
shape (num_boxes, 6 + num_masks) containing the kept boxes, with columns
(x1, y1, x2, y2, confidence, class, mask1, mask2, ...).
"""
# Checks
assert 0 <= conf_thres <= 1, f'Invalid Confidence threshold {
conf_thres}, valid values are between 0.0 and 1.0'
assert 0 <= iou_thres <= 1, f'Invalid IoU {
iou_thres}, valid values are between 0.0 and 1.0'
if isinstance(prediction, (list, tuple)): # YOLOv8 model in validation model, output = (inference_out, loss_out)
prediction = prediction[0] # select only inference output
bs = prediction.shape[0] # batch size
nc = nc or (prediction.shape[1] - 4) # number of classes
nm = prediction.shape[1] - nc - 4
mi = 4 + nc # mask start index
xc = prediction[:, 4:mi].max(axis=1) > conf_thres # candidates
# Settings
# min_wh = 2 # (pixels) minimum box width and height
time_limit = 0.5 + max_time_img * bs # seconds to quit after
redundant = True # require redundant detections
multi_label &= nc > 1 # multiple labels per box (adds 0.5ms/img)
merge = False # use merge-NMS
prediction = np.transpose(prediction, (0, 2, 1)) # shape(1,84,6300) to shape(1,6300,84)
prediction[..., :4] = xywh2xyxy(prediction[..., :4]) # xywh to xyxy
t = time.time()
output = [np.zeros((0, 6 + nm)) for _ in range(bs)]
for xi, x in enumerate(prediction): # image index, image inference
# Apply constraints
# x[((x[:, 2:4] < min_wh) | (x[:, 2:4] > max_wh)).any(1), 4] = 0 # width-height
x = x[xc[xi]] # confidence
# Cat apriori labels if autolabelling
if labels and len(labels[xi]):
lb = labels[xi]
v = np.zeros((len(lb), nc + nm + 5))
v[:, :4] = lb[:, 1:5] # box
v[np.arange(len(lb)), lb[:, 0].astype(int) + 4] = 1.0 # cls
x = np.concatenate((x, v), axis=0)
# If none remain process next image
if not x.shape[0]:
continue
# Detections matrix nx6 (xyxy, conf, cls)
box, cls, mask = np.split(x, (4, 4 + nc), axis=1)
if multi_label:
i, j = np.where(cls > conf_thres)
x = np.concatenate((box[i], x[i, 4 + j, None], j[:, None].astype(float), mask[i]), axis=1)
else: # best class only
conf = np.max(cls, axis=1, keepdims=True)
j = np.argmax(cls, axis=1)
j = np.expand_dims(j, axis=1)
x = np.concatenate((box, conf, j.astype(float), mask), axis=1)[conf.reshape(-1) > conf_thres]
# Filter by class
if classes is not None:
class_indices = np.array(classes)
mask = np.any(x[:, 5:6] == class_indices, axis=1)
x = x[mask]
# Apply finite constraint
# if not np.isfinite(x).all():
# x = x[np.isfinite(x).all(axis=1)]
# Check shape
n = x.shape[0] # number of boxes
if not n: # no boxes
continue
if n > max_nms: # excess boxes
sorted_indices = np.argsort(x[:, 4])[::-1]
x = x[sorted_indices[:max_nms]] # sort by confidence and remove excess boxes
# Batched NMS
c = x[:, 5:6] * (0 if agnostic else max_wh) # classes
boxes, scores = x[:, :4] + c, x[:, 4] # boxes (offset by class), scores
i = numpy_nms(boxes, scores, iou_thres) # NMS
i = i[:max_det] # limit detections
if merge and (1 < n < 3E3): # Merge NMS (boxes merged using weighted mean)
# Update boxes as boxes(i,4) = weights(i,n) * boxes(n,4)
iou = box_iou(boxes[i], boxes) > iou_thres # iou matrix
weights = iou * scores[None] # box weights
x[i, :4] = np.dot(weights, x[:, :4]).astype(float) / weights.sum(1, keepdims=True) # merged boxes
if redundant:
i = i[np.sum(iou, axis=1) > 1] # require redundancy
output[xi] = x[i]
if (time.time() - t) > time_limit:
break # time limit exceeded
return output
非最大抑制
元の非最大抑制は torch を使用して実装されていましたが、現在は numpy 実装に変更されており、pytorch への依存が軽減されています。
def box_area(boxes :array):
"""
:param boxes: [N, 4]
:return: [N]
"""
return (boxes[:, 2] - boxes[:, 0]) * (boxes[:, 3] - boxes[:, 1])
def box_iou(box1 :array, box2: array):
"""
:param box1: [N, 4]
:param box2: [M, 4]
:return: [N, M]
"""
area1 = box_area(box1) # N
area2 = box_area(box2) # M
# broadcasting, 两个数组各维度大小 从后往前对比一致, 或者 有一维度值为1;
lt = np.maximum(box1[:, np.newaxis, :2], box2[:, :2])
rb = np.minimum(box1[:, np.newaxis, 2:], box2[:, 2:])
wh = rb - lt # 右下角 - 左上角;
wh = np.maximum(0, wh) # [N, M, 2]
inter = wh[:, :, 0] * wh[:, :, 1]
iou = inter / (area1[:, np.newaxis] + area2 - inter)
return iou # NxM
def numpy_nms(boxes :array, scores :array, iou_threshold :float):
idxs = scores.argsort() # 按分数 降序排列的索引 [N]
keep = []
while idxs.size > 0: # 统计数组中元素的个数
max_score_index = idxs[-1]
max_score_box = boxes[max_score_index][None, :]
keep.append(max_score_index)
if idxs.size == 1:
break
idxs = idxs[:-1] # 将得分最大框 从索引中删除; 剩余索引对应的框 和 得分最大框 计算IoU;
other_boxes = boxes[idxs] # [?, 4]
ious = box_iou(max_score_box, other_boxes) # 一个框和其余框比较 1XM
idxs = idxs[ious[0] <= iou_threshold]
keep = np.array(keep) # Tensor
return keep
完全な tensorrt 推論コード:
'''
Author: [egrt]
Date: 2023-03-26 09:39:21
LastEditors: Egrt
LastEditTime: 2023-07-15 22:10:25
Description:
'''
import numpy as np
import time
import tensorrt as trt
import pycuda.driver as cuda
import pycuda.autoinit
import cv2
from numpy import array
def resize_image(image, size, letterbox_image):
ih, iw = image.shape[:2]
h, w = size
if letterbox_image:
scale = min(w/iw, h/ih)
nw = int(iw*scale)
nh = int(ih*scale)
image = cv2.resize(image, (nw,nh), interpolation=cv2.INTER_CUBIC)
new_image = 128 * np.ones((h, w, 3), dtype=np.uint8)
new_image[(h-nh)//2:(h-nh)//2+nh, (w-nw)//2:(w-nw)//2+nw, :] = image
else:
new_image = cv2.resize(image, (w, h), interpolation=cv2.INTER_CUBIC)
scale = [iw/w, ih/h]
return new_image, scale
def preprocess_input(image):
image /= 255.0
return image
def xywh2xyxy(x):
"""
Convert bounding box coordinates from (x, y, width, height) format to (x1, y1, x2, y2) format where (x1, y1) is the
top-left corner and (x2, y2) is the bottom-right corner.
Args:
x (np.ndarray | torch.Tensor): The input bounding box coordinates in (x, y, width, height) format.
Returns:
y (np.ndarray | torch.Tensor): The bounding box coordinates in (x1, y1, x2, y2) format.
"""
y = np.copy(x)
y[..., 0] = x[..., 0] - x[..., 2] / 2 # top left x
y[..., 1] = x[..., 1] - x[..., 3] / 2 # top left y
y[..., 2] = x[..., 0] + x[..., 2] / 2 # bottom right x
y[..., 3] = x[..., 1] + x[..., 3] / 2 # bottom right y
return y
def box_area(boxes :array):
"""
:param boxes: [N, 4]
:return: [N]
"""
return (boxes[:, 2] - boxes[:, 0]) * (boxes[:, 3] - boxes[:, 1])
def box_iou(box1 :array, box2: array):
"""
:param box1: [N, 4]
:param box2: [M, 4]
:return: [N, M]
"""
area1 = box_area(box1) # N
area2 = box_area(box2) # M
# broadcasting, 两个数组各维度大小 从后往前对比一致, 或者 有一维度值为1;
lt = np.maximum(box1[:, np.newaxis, :2], box2[:, :2])
rb = np.minimum(box1[:, np.newaxis, 2:], box2[:, 2:])
wh = rb - lt # 右下角 - 左上角;
wh = np.maximum(0, wh) # [N, M, 2]
inter = wh[:, :, 0] * wh[:, :, 1]
iou = inter / (area1[:, np.newaxis] + area2 - inter)
return iou # NxM
def numpy_nms(boxes :array, scores :array, iou_threshold :float):
idxs = scores.argsort() # 按分数 降序排列的索引 [N]
keep = []
while idxs.size > 0: # 统计数组中元素的个数
max_score_index = idxs[-1]
max_score_box = boxes[max_score_index][None, :]
keep.append(max_score_index)
if idxs.size == 1:
break
idxs = idxs[:-1] # 将得分最大框 从索引中删除; 剩余索引对应的框 和 得分最大框 计算IoU;
other_boxes = boxes[idxs] # [?, 4]
ious = box_iou(max_score_box, other_boxes) # 一个框和其余框比较 1XM
idxs = idxs[ious[0] <= iou_threshold]
keep = np.array(keep) # Tensor
return keep
def non_max_suppression(
prediction,
conf_thres=0.25,
iou_thres=0.45,
classes=None,
agnostic=False,
multi_label=False,
labels=(),
max_det=300,
nc=0, # number of classes (optional)
max_time_img=0.05,
max_nms=30000,
max_wh=7680,
):
"""
Perform non-maximum suppression (NMS) on a set of boxes, with support for masks and multiple labels per box.
Arguments:
prediction (np.ndarray): An array of shape (batch_size, num_classes + 4 + num_masks, num_boxes)
containing the predicted boxes, classes, and masks. The array should be in the format
output by a model, such as YOLO.
conf_thres (float): The confidence threshold below which boxes will be filtered out.
Valid values are between 0.0 and 1.0.
iou_thres (float): The IoU threshold below which boxes will be filtered out during NMS.
Valid values are between 0.0 and 1.0.
classes (List[int]): A list of class indices to consider. If None, all classes will be considered.
agnostic (bool): If True, the model is agnostic to the number of classes, and all
classes will be considered as one.
multi_label (bool): If True, each box may have multiple labels.
labels (List[List[Union[int, float, np.ndarray]]]): A list of lists, where each inner
list contains the apriori labels for a given image. The list should be in the format
output by a dataloader, with each label being a tuple of (class_index, x1, y1, x2, y2).
max_det (int): The maximum number of boxes to keep after NMS.
nc (int, optional): The number of classes output by the model. Any indices after this will be considered masks.
max_time_img (float): The maximum time (seconds) for processing one image.
max_nms (int): The maximum number of boxes into torchvision.ops.nms().
max_wh (int): The maximum box width and height in pixels
Returns:
(List[np.ndarray]): A list of length batch_size, where each element is an array of
shape (num_boxes, 6 + num_masks) containing the kept boxes, with columns
(x1, y1, x2, y2, confidence, class, mask1, mask2, ...).
"""
# Checks
assert 0 <= conf_thres <= 1, f'Invalid Confidence threshold {
conf_thres}, valid values are between 0.0 and 1.0'
assert 0 <= iou_thres <= 1, f'Invalid IoU {
iou_thres}, valid values are between 0.0 and 1.0'
if isinstance(prediction, (list, tuple)): # YOLOv8 model in validation model, output = (inference_out, loss_out)
prediction = prediction[0] # select only inference output
bs = prediction.shape[0] # batch size
nc = nc or (prediction.shape[1] - 4) # number of classes
nm = prediction.shape[1] - nc - 4
mi = 4 + nc # mask start index
xc = prediction[:, 4:mi].max(axis=1) > conf_thres # candidates
# Settings
# min_wh = 2 # (pixels) minimum box width and height
time_limit = 0.5 + max_time_img * bs # seconds to quit after
redundant = True # require redundant detections
multi_label &= nc > 1 # multiple labels per box (adds 0.5ms/img)
merge = False # use merge-NMS
prediction = np.transpose(prediction, (0, 2, 1)) # shape(1,84,6300) to shape(1,6300,84)
prediction[..., :4] = xywh2xyxy(prediction[..., :4]) # xywh to xyxy
t = time.time()
output = [np.zeros((0, 6 + nm)) for _ in range(bs)]
for xi, x in enumerate(prediction): # image index, image inference
# Apply constraints
# x[((x[:, 2:4] < min_wh) | (x[:, 2:4] > max_wh)).any(1), 4] = 0 # width-height
x = x[xc[xi]] # confidence
# Cat apriori labels if autolabelling
if labels and len(labels[xi]):
lb = labels[xi]
v = np.zeros((len(lb), nc + nm + 5))
v[:, :4] = lb[:, 1:5] # box
v[np.arange(len(lb)), lb[:, 0].astype(int) + 4] = 1.0 # cls
x = np.concatenate((x, v), axis=0)
# If none remain process next image
if not x.shape[0]:
continue
# Detections matrix nx6 (xyxy, conf, cls)
box, cls, mask = np.split(x, (4, 4 + nc), axis=1)
if multi_label:
i, j = np.where(cls > conf_thres)
x = np.concatenate((box[i], x[i, 4 + j, None], j[:, None].astype(float), mask[i]), axis=1)
else: # best class only
conf = np.max(cls, axis=1, keepdims=True)
j = np.argmax(cls, axis=1)
j = np.expand_dims(j, axis=1)
x = np.concatenate((box, conf, j.astype(float), mask), axis=1)[conf.reshape(-1) > conf_thres]
# Filter by class
if classes is not None:
class_indices = np.array(classes)
mask = np.any(x[:, 5:6] == class_indices, axis=1)
x = x[mask]
# Apply finite constraint
# if not np.isfinite(x).all():
# x = x[np.isfinite(x).all(axis=1)]
# Check shape
n = x.shape[0] # number of boxes
if not n: # no boxes
continue
if n > max_nms: # excess boxes
sorted_indices = np.argsort(x[:, 4])[::-1]
x = x[sorted_indices[:max_nms]] # sort by confidence and remove excess boxes
# Batched NMS
c = x[:, 5:6] * (0 if agnostic else max_wh) # classes
boxes, scores = x[:, :4] + c, x[:, 4] # boxes (offset by class), scores
i = numpy_nms(boxes, scores, iou_thres) # NMS
i = i[:max_det] # limit detections
if merge and (1 < n < 3E3): # Merge NMS (boxes merged using weighted mean)
# Update boxes as boxes(i,4) = weights(i,n) * boxes(n,4)
iou = box_iou(boxes[i], boxes) > iou_thres # iou matrix
weights = iou * scores[None] # box weights
x[i, :4] = np.dot(weights, x[:, :4]).astype(float) / weights.sum(1, keepdims=True) # merged boxes
if redundant:
i = i[np.sum(iou, axis=1) > 1] # require redundancy
output[xi] = x[i]
if (time.time() - t) > time_limit:
break # time limit exceeded
return output
class YOLO(object):
_defaults = {
#---------------------------------------------------------------------#
# 模型文件存放的路径
#---------------------------------------------------------------------#
"model_path" : 'Triangle_215_yolov8s_pretrain.engine',
#---------------------------------------------------------------------#
# 输入图像的分辨率大小
#---------------------------------------------------------------------#
"input_shape" : [640, 640],
#---------------------------------------------------------------------#
# 只有得分大于置信度的预测框会被保留下来
#---------------------------------------------------------------------#
"confidence" : 0.5,
#---------------------------------------------------------------------#
# 非极大抑制所用到的nms_iou大小
#---------------------------------------------------------------------#
"nms_iou" : 0.3,
}
@classmethod
def get_defaults(cls, n):
if n in cls._defaults:
return cls._defaults[n]
else:
return "Unrecognized attribute name '" + n + "'"
#---------------------------------------------------#
# 初始化YOLO
#---------------------------------------------------#
def __init__(self, **kwargs):
self.__dict__.update(self._defaults)
for name, value in kwargs.items():
setattr(self, name, value)
self._defaults[name] = value
#---------------------------------------------------#
# 获得种类和先验框的数量
#---------------------------------------------------#
self.class_names = ['sjb_rect']
self.num_classes = len(self.class_names)
self.kpts_shape = [3, 3]
self.bbox_color = (150, 0, 0)
self.bbox_thickness = 6
# 框类别文字
self.bbox_labelstr= {
'font_size':1, # 字体大小
'font_thickness':2, # 字体粗细
'offset_x':0, # X 方向,文字偏移距离,向右为正
'offset_y':-10, # Y 方向,文字偏移距离,向下为正
}
# 关键点 BGR 配色
self.kpt_color_map = {
0:{
'name':'angle_30', 'color':[255, 0, 0], 'radius':6}, # 30度角点
1:{
'name':'angle_60', 'color':[0, 255, 0], 'radius':6}, # 60度角点
2:{
'name':'angle_90', 'color':[0, 0, 255], 'radius':6}, # 90度角点
}
# 点类别文字
self.kpt_labelstr = {
'font_size':1.5, # 字体大小
'font_thickness':3, # 字体粗细
'offset_x':10, # X 方向,文字偏移距离,向右为正
'offset_y':0, # Y 方向,文字偏移距离,向下为正
}
# 骨架连接 BGR 配色
self.skeleton_map = [
{
'srt_kpt_id':0, 'dst_kpt_id':1, 'color':[196, 75, 255], 'thickness':2}, # 30度角点-60度角点
{
'srt_kpt_id':0, 'dst_kpt_id':2, 'color':[180, 187, 28], 'thickness':2}, # 30度角点-90度角点
{
'srt_kpt_id':1, 'dst_kpt_id':2, 'color':[47,255, 173], 'thickness':2}, # 60度角点-90度角点
]
self.generate()
#---------------------------------------------------#
# 生成模型
#---------------------------------------------------#
def generate(self):
#---------------------------------------------------#
# 建立yolo模型,载入yolo模型的权重
#---------------------------------------------------#
engine = self.load_engine(self.model_path)
self.context = engine.create_execution_context()
self.inputs, self.outputs, self.bindings = [], [], []
self.stream = cuda.Stream()
for binding in engine:
size = engine.get_binding_shape(binding)
dtype = trt.nptype(engine.get_binding_dtype(binding))
host_mem = np.empty(size, dtype=dtype)
host_mem = np.ascontiguousarray(host_mem)
device_mem = cuda.mem_alloc(host_mem.nbytes)
self.bindings.append(int(device_mem))
if engine.binding_is_input(binding):
self.inputs.append({
'host': host_mem, 'device': device_mem})
else:
self.outputs.append({
'host': host_mem, 'device': device_mem})
def load_engine(self, engine_path):
TRT_LOGGER = trt.Logger(trt.Logger.ERROR)
with open(engine_path, 'rb') as f, trt.Runtime(TRT_LOGGER) as runtime:
return runtime.deserialize_cuda_engine(f.read())
def forward(self, img):
self.inputs[0]['host'] = np.ravel(img)
# transfer data to the gpu
for inp in self.inputs:
cuda.memcpy_htod_async(inp['device'], inp['host'], self.stream)
# run inference
self.context.execute_async_v2(
bindings=self.bindings,
stream_handle=self.stream.handle)
# fetch outputs from gpu
for out in self.outputs:
cuda.memcpy_dtoh_async(out['host'], out['device'], self.stream)
# synchronize stream
self.stream.synchronize()
return [out['host'] for out in self.outputs]
#---------------------------------------------------#
# 检测图片
#---------------------------------------------------#
def detect_image(self, image):
#---------------------------------------------------------#
# 在这里将图像转换成RGB图像,防止灰度图在预测时报错。
# 代码仅仅支持RGB图像的预测,所有其它类型的图像都会转化成RGB
#---------------------------------------------------------#
image = cv2.cvtColor(image, cv2.COLOR_BGR2RGB)
image_data, scale = resize_image(image, (self.input_shape[1], self.input_shape[0]), False)
#---------------------------------------------------------#
# 添加上batch_size维度
# h, w, 3 => 3, h, w => 1, 3, h, w
#---------------------------------------------------------#
image_data = np.expand_dims(np.transpose(preprocess_input(np.array(image_data, dtype='float32')), (2, 0, 1)), 0)
#---------------------------------------------------------#
# 将图像输入网络当中进行预测!
#---------------------------------------------------------#
outputs = self.forward(image_data)[::-1]
#---------------------------------------------------------#
# 将预测框进行堆叠,然后进行非极大抑制
#---------------------------------------------------------#
results = non_max_suppression(outputs, conf_thres=self.confidence, iou_thres=self.nms_iou, nc=1)[0]
if results is None:
return image
top_label = np.array(results[:, 5], dtype = 'int32')
top_conf = results[:, 4]
top_boxes = results[:, :4]
top_kpts = results[:, 6:].reshape(len(results), self.kpts_shape[0], self.kpts_shape[1])
#---------------------------------------------------------#
# 图像绘制
#---------------------------------------------------------#
for i, c in list(enumerate(top_label)):
predicted_class = self.class_names[int(c)]
box = top_boxes[i]
score = top_conf[i]
left, top, right, bottom = box.astype('int32')
left = int(left * scale[0])
top = int(top * scale[1])
right = int(right * scale[0])
bottom = int(bottom * scale[1])
image = cv2.rectangle(image, (left, top), (right, bottom), self.bbox_color, self.bbox_thickness)
label = '{} {:.2f}'.format(predicted_class, score)
# 写框类别文字:图片,文字字符串,文字左上角坐标,字体,字体大小,颜色,字体粗细
image = cv2.putText(image, label, (left+self.bbox_labelstr['offset_x'], top+self.bbox_labelstr['offset_y']),
cv2.FONT_HERSHEY_SIMPLEX, self.bbox_labelstr['font_size'], self.bbox_color, self.bbox_labelstr['font_thickness'])
bbox_keypoints = top_kpts[i] # 该框所有关键点坐标和置信度
# 画该框的骨架连接
for skeleton in self.skeleton_map:
# 获取起始点坐标
srt_kpt_id = skeleton['srt_kpt_id']
srt_kpt_x = int(bbox_keypoints[srt_kpt_id][0]*scale[0])
srt_kpt_y = int(bbox_keypoints[srt_kpt_id][1]*scale[1])
# 获取终止点坐标
dst_kpt_id = skeleton['dst_kpt_id']
dst_kpt_x = int(bbox_keypoints[dst_kpt_id][0]*scale[0])
dst_kpt_y = int(bbox_keypoints[dst_kpt_id][1]*scale[1])
# 获取骨架连接颜色
skeleton_color = skeleton['color']
# 获取骨架连接线宽
skeleton_thickness = skeleton['thickness']
# 画骨架连接
image = cv2.line(image, (srt_kpt_x, srt_kpt_y),(dst_kpt_x, dst_kpt_y),color=skeleton_color,thickness=skeleton_thickness)
# 画该框的关键点
for kpt_id in self.kpt_color_map:
# 获取该关键点的颜色、半径、XY坐标
kpt_color = self.kpt_color_map[kpt_id]['color']
kpt_radius = self.kpt_color_map[kpt_id]['radius']
kpt_x = int(bbox_keypoints[kpt_id][0]*scale[0])
kpt_y = int(bbox_keypoints[kpt_id][1]*scale[1])
# 画圆:图片、XY坐标、半径、颜色、线宽(-1为填充)
image = cv2.circle(image, (kpt_x, kpt_y), kpt_radius, kpt_color, -1)
# 写关键点类别文字:图片,文字字符串,文字左上角坐标,字体,字体大小,颜色,字体粗细
kpt_label = str(self.kpt_color_map[kpt_id]['name'])
image = cv2.putText(image, kpt_label, (kpt_x+self.kpt_labelstr['offset_x'], kpt_y+self.kpt_labelstr['offset_y']),
cv2.FONT_HERSHEY_SIMPLEX, self.kpt_labelstr['font_size'], kpt_color, self.kpt_labelstr['font_thickness'])
image = cv2.cvtColor(image, cv2.COLOR_RGB2BGR)
return image
if __name__=='__main__':
yolo = YOLO()
#----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------#
# mode用于指定测试的模式:
# 'predict' 表示单张图片预测,如果想对预测过程进行修改,如保存图片,截取对象等,可以先看下方详细的注释
# 'video' 表示视频检测,可调用摄像头或者视频进行检测,详情查看下方注释。
# 'fps' 表示测试fps,使用的图片是img里面的street.jpg,详情查看下方注释。
# 'dir_predict' 表示遍历文件夹进行检测并保存。默认遍历img文件夹,保存img_out文件夹,详情查看下方注释。
#----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------#
mode = "video"
#----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------#
# video_path 用于指定视频的路径,当video_path=0时表示检测摄像头
# 想要检测视频,则设置如video_path = "xxx.mp4"即可,代表读取出根目录下的xxx.mp4文件。
# video_save_path 表示视频保存的路径,当video_save_path=""时表示不保存
# 想要保存视频,则设置如video_save_path = "yyy.mp4"即可,代表保存为根目录下的yyy.mp4文件。
# video_fps 用于保存的视频的fps
#
# video_path、video_save_path和video_fps仅在mode='video'时有效
# 保存视频时需要ctrl+c退出或者运行到最后一帧才会完成完整的保存步骤。
#----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------#
video_path = "triangle_9.mp4"
video_save_path = "output.mp4"
video_fps = 25.0
#----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------#
# test_interval 用于指定测量fps的时候,图片检测的次数。理论上test_interval越大,fps越准确。
# fps_image_path 用于指定测试的fps图片
#
# test_interval和fps_image_path仅在mode='fps'有效
#----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------#
test_interval = 100
fps_image_path = "img/test.jpg"
#-------------------------------------------------------------------------#
# dir_origin_path 指定了用于检测的图片的文件夹路径
# dir_save_path 指定了检测完图片的保存路径
#
# dir_origin_path和dir_save_path仅在mode='dir_predict'时有效
#-------------------------------------------------------------------------#
dir_origin_path = "img/"
dir_save_path = "img_out/"
if mode == "predict":
'''
1、如果想要进行检测完的图片的保存,利用r_image.save("img.jpg")即可保存,直接在predict.py里进行修改即可。
2、如果想要获得预测框的坐标,可以进入yolo.detect_image函数,在绘图部分读取top,left,bottom,right这四个值。
3、如果想要利用预测框截取下目标,可以进入yolo.detect_image函数,在绘图部分利用获取到的top,left,bottom,right这四个值
在原图上利用矩阵的方式进行截取。
4、如果想要在预测图上写额外的字,比如检测到的特定目标的数量,可以进入yolo.detect_image函数,在绘图部分对predicted_class进行判断,
比如判断if predicted_class == 'car': 即可判断当前目标是否为车,然后记录数量即可。利用draw.text即可写字。
'''
while True:
img = input('Input image filename:')
try:
image = cv2.imread(img)
except:
print('Open Error! Try again!')
continue
else:
r_image = yolo.detect_image(image)
cv2.imshow('result', r_image)
c = cv2.waitKey(0)
elif mode == "video":
capture = cv2.VideoCapture(video_path)
if video_save_path!="":
fourcc = cv2.VideoWriter_fourcc(*'XVID')
size = (int(capture.get(cv2.CAP_PROP_FRAME_WIDTH)), int(capture.get(cv2.CAP_PROP_FRAME_HEIGHT)))
out = cv2.VideoWriter(video_save_path, fourcc, video_fps, size)
ref, frame = capture.read()
if not ref:
raise ValueError("未能正确读取摄像头(视频),请注意是否正确安装摄像头(是否正确填写视频路径)。")
fps = 0.0
while(True):
t1 = time.time()
# 读取某一帧
ref, frame = capture.read()
if not ref:
break
# 进行检测
frame = yolo.detect_image(frame)
fps = ( fps + (1./(time.time()-t1)) ) / 2
print("fps= %.2f"%(fps))
frame = cv2.putText(frame, "fps= %.2f"%(fps), (0, 40), cv2.FONT_HERSHEY_SIMPLEX, 1, (0, 255, 0), 2)
cv2.imshow("video",frame)
c= cv2.waitKey(1) & 0xff
if video_save_path!="":
out.write(frame)
if c==27:
capture.release()
break
print("Video Detection Done!")
capture.release()
if video_save_path!="":
print("Save processed video to the path :" + video_save_path)
out.release()
cv2.destroyAllWindows()
elif mode == "fps":
img = cv2.imread(fps_image_path)
tact_time = yolo.get_FPS(img, test_interval)
print(str(tact_time) + ' seconds, ' + str(1/tact_time) + 'FPS, @batch_size 1')
elif mode == "dir_predict":
import os
from tqdm import tqdm
img_names = os.listdir(dir_origin_path)
for img_name in tqdm(img_names):
if img_name.lower().endswith(('.bmp', '.dib', '.png', '.jpg', '.jpeg', '.pbm', '.pgm', '.ppm', '.tif', '.tiff')):
image_path = os.path.join(dir_origin_path, img_name)
image = cv2.imread(image_path)
r_image = yolo.detect_image(image)
if not os.path.exists(dir_save_path):
os.makedirs(dir_save_path)
r_image.save(os.path.join(dir_save_path, img_name.replace(".jpg", ".png")), quality=95, subsampling=0)
else:
raise AssertionError("Please specify the correct mode: 'predict', 'video', 'fps', 'dir_predict'.")