[Introduction to MySQL] (5) Flask uses MySQL to store data
This article is based on MySQL 8.0.29 and Python 3.8.
1. Introduction to flask_sqlalchemy
Flask-SQLAlchemy is an extension that adds SQLAlchemy support to Flask applications. It is also a database framework that supports multiple database backgrounds. It strives to simplify the use of SQLAlchemy in Flask, providing useful defaults and additional helpers to more easily accomplish common tasks. No need to care about the details of SQL processing, and operate the database by calling methods. This is the Chinese documentation of flask_sqlalchemy .
2. 安装pymysql,sqlalchemy,flask_sqlalchemy
pip install pymysql sqlalchemy flask_sqlalchemy
3. Configure a simple Flask application
from flask import Flask
from flask_sqlalchemy import SQLAlchemy
app = Flask(__name__)
app.config['SQLALCHEMY_DATABASE_URI'] = "mysql+pymysql://{}:{}@{}/{}?charset=utf8mb4" \
.format('root','密码','x.x.x.x:3306','数据库名')
app.config['SQLALCHEMY_COMMIT_ON_TEARDOWN'] = True # 每次请求结束后会自动提交数据库中的变动
app.config['SQLALCHEMY_TRACK_MODIFICATIONS'] = True # 事件系统跟踪修改
db = SQLAlchemy(app) # 实例化数据库对象,它提供访问Flask-SQLAlchemy的所有功能
4. Define a class (corresponding to a table in the database)
class Myuser(db.Model): # 所有模型的基类叫 db.Model,它存储在创建的SQLAlchemy实例上。
#定义表名
__tablename__ = 'myuser'
#定义字段
id = db.Column(db.Integer, primary_key=True)
name = db.Column(db.String(64), unique=False)
money = db.Column(db.Float, unique=False)
#__repr__()方法显示一个可读字符串,用于调试、测试
def __repr__(self):
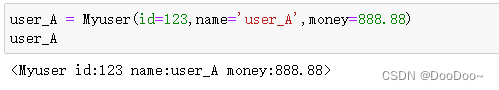
return '<Myuser id:{} name:{} money:{}>'.format(self.id,self.name,self.money)
Here's a simple example:
Common SQLalchemy column types
| type name | python type | describe |
|---|---|---|
| Integer | int | regular integer, usually 32 bits |
| SmallInteger | int | Short integer, usually 16 bits |
| BigInteger | int or long | Unlimited precision shaping |
| Float | float | floating point number |
| Numeric | decimal.Decimal | Fixed number |
| String | str | variable length string |
| Text | str | Variable-length strings, good for large amounts of text |
| Unicode | unicode | Variable-length Unicode strings |
| Boolean | bool | Boolean |
| Date | datetime.date | date type |
| Time | datetime.time | time type |
| Interval | datetime.timedelta | time interval |
| Enum | str | character list |
| PickleType | any Python object | Automatic Pickle Serialization |
| LargeBinary | str | binary |
Common SQLalchemy column options
| optional parameters | describe |
|---|---|
| primary_key | If set to True, the primary key for this list |
| unique | If set to True, the column does not allow identical values |
| index | If set to True, create an index for this column, and the query efficiency will be higher |
| nullable | If set to True, the column is allowed to be empty. If set to False, the column does not allow null values |
| default | Define the default value for the column |
5. Delete and create data tables
The following operations will affect all tables in the database:
# 删除旧表:
db.drop_all()
# 创建新表:
db.create_all()
6. Add, delete, modify and check the database
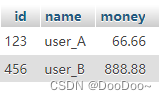
1. increase
user_A = Myuser(id=123, name='user_A', money=66.66)
user_B = Myuser(id=456, name='user_B', money=888.88)
#在将对象写入数据库之前,先将其添加到会话中(类似缓存)
# 插入单个对象
# db.session.add(user_A)
# 插入多个对象
db.session.add_all([user_A, user_B])
#会话提交到数据库后执行操作
db.session.commit()
result:
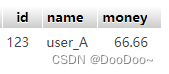
2. delete
db.session.delete(user_B)
db.session.commit()
result:
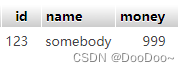
3. change
user_A.name = 'somebody'
user_A.money= 999
db.session.add(user_A)
db.session.commit()
result:
4. Check
Myuser.query.filter_by(id = 123).first()
Myuser.query.filter_by(name = 'somebody').all()

Commonly used SQLAlchemy query filters
| filter | illustrate |
|---|---|
| filter() | Appends the filter to the original query, returning a new query |
| filter_by() | Appends the equality filter to the original query, returning a new query |
| limit | Limit the results returned by the original query to the specified value |
| offset() | Offset the results returned by the original query and return a new query |
| order_by() | Sort the original query results according to the specified conditions and return a new query |
| group_by() | Group the original query results according to the specified conditions and return a new query |
Commonly used SQLAlchemy query executors
| method | illustrate |
|---|---|
| all() | Returns all results of a query as a list |
| first() | Returns the first result of the query, or None if not found |
| first_or_404() | Return the first result of the query, if not found, return 404 |
| get() | Returns the row corresponding to the specified primary key, or returns None if it does not exist |
| get_or_404() | Returns the row corresponding to the specified primary key, if it does not exist, returns 404 |
| count() | Returns the number of query results |
| paginated() | Returns a Paginate object that contains results within the specified range |