この問題を説明するには、例から始めます:PAT(A)1080大学院入学
方法1:
構造体配列を定義し、配列用の大きなストレージスペースを開いてから、値を初期化して割り当てます。
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
struct student {
int ge;
int gi;
int b[6] = {
0 };
};
int main()
{
struct student *stu;
int n, m, k;
// n申请人总数,m研究生院总数,k申请人可以选择的数量
cin >> n >> m >> k;
/*
int a[101] = { 0 }; // 每个研究生院的配额
for (int i = 0; i < m; i++)
{
int g;
cin >> g;
a[i] = g;
}
*/
//为结构体分配存储空间
stu = (struct student *)malloc(40000* sizeof(struct student));
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) // 为所有学生输入他的各项信息
{
int c, d, e;
cin >> c >> d;
stu[i].ge = c;
stu[i].gi = d;
for (int j = 0; j < k; j++)
{
cin >> e;
stu[i].b[j] = e;
}
}
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++)
for(int j=0; j<k; j++)
cout << stu[i].ge << " " << stu[i].gi << " " << stu[i].b[j] << endl;
system("pause");
return 0;
}
入力:
3 6 3
100100 0 1 2
60 60 2 3
5100 90 0 3 4
出力:出力
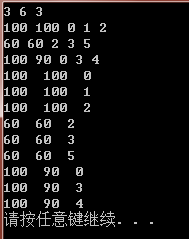
を通じて、入力データが各学生の構造に対応する情報に格納されていることがわかります。
方法2:
ベクトルを使用して動的配列割り当て操作を実行する
#include <iostream>
#include <vector>
#include <algorithm>
using namespace std;
struct stu {
int id;
double g1, g2;
int choice[6];
};
int main()
{
int n, m, k;
cin>>n>>m>>k;
vector<stu> students;
stu tmp;
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++)
{
tmp.id = i;
int a,b;
cin>>a>>b;
tmp.g1=a;
tmp.g2=b;
for (int j = 0; j < k; j++)
{
int c;
cin>>c;
tmp.choice[j]=c;
}
students.push_back(tmp);
}
for(int i=0; i<n; i++)
{
for(int j=0; j<k; j++)
cout<<students[i].g1<<" "<<students[i].g2<<" "<<students[i].choice[j]<<endl;
}
return 0;
}
入力:
5 6 3
100100 0 1 2
60 60 2 3
5100 90 0 3 4
90100 1 2 0
90 90 5 1 3
出力:出力
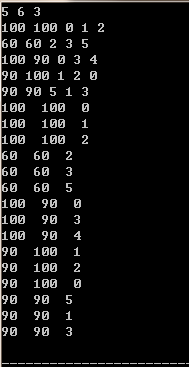
を通じて、入力データが各学生の構造に対応する情報に格納されていることがわかります。
したがって、動的配列構造の処理には、上記の2つの方法がありますが、PAT(A)1080の詳細な問題解決プロセスとコードについては、他のブログを参照してください。