1. 커링 검토
① Currying은 여러 매개변수가 있는 함수를 하나의 부분 매개변수 함수로 바꾸는 것을 의미합니다.
② 카레 기능(도구)의 구현 아이디어:
1) 원래 함수의 매개변수를 저장하기 위해 특별히 배열을 정의합니다.
2) 원래 함수의 매개변수(수량)가 부족할 때 함수를 반환(원래 함수의 매개변수를 모으기 위해)
3) 원래 함수의 매개변수(수량)가 충분하면 원래 함수를 호출합니다.
③코드:
// 1、原函数:
function sum(a, b, c, d) {
return a + b + c + d;
}
// 2、柯里化工具函数
function curry(cb) {
let arr = [];
function fn(...args) {
arr = [...arr, ...args];//收集参数
if (arr.length < cb.length) {// 函数.length 表示的是函数形参的个数
return fn;
} else {
return cb(...arr);
}
}
return fn;
}
// 3、(调用柯里化工具函数)把原函数柯里化
let cSum = curry(sum);
// 4、调用柯里化后的函数。
console.log(cSum(2, 3)(5)(6))
// console.log(cSum(2)(4)(5)(6))
// console.log(cSum(2, 4, 5)(6))
④커링의 역할: 함수의 매개변수 값을 재사용할 수 있습니다.
let f01 = cSum(2, 3)(5);// f01是持有 2,3,5的函数
f01(6);//求 2+3+5 + 6
f01(7);//求 2+3+5 +72. 보충: 클래스 정의
①ES5
// 1)、用构造函数:这种写法,会导致内存中定义了多个相同的函数。浪费了内存
function Doctor(name,dept){
this.name = name;
this.dept = dept;
// 这种写法,会导致内存中定义了多个相同的函数。浪费了内存。
this.seatZhen = function(){
console.log(this.name+"在坐诊………………");
}
}
let d1= new Doctor("宋和叶","神经科");
let d2 = new Doctor("纪朝锋","精神科");
// 2)、用构造函数结合原型(prototype)定义类
function Doctor(name,dept){
this.name = name;
this.dept = dept;
}
// 一个构造函数的原型属性上的属性和方法,可以被它的实例共享
Doctor.prototype.seatZhen = function(){
console.log(this.name+"在坐诊………………");
}
let d1= new Doctor("宋和叶","神经科");
let d2 = new Doctor("纪朝锋","精神科");
d1.seatZhen();
d2.seatZhen();② ES6에서
//ES6中用class:class定义类,是个语法糖。
class Doctor{
constructor(name,dept){
this.name = name;
this.dept = dept;
}
seatZhen(){
console.log(this.name+"在坐诊………………");
}
}
let d1= new Doctor("宋和叶","神经科");
let d2 = new Doctor("纪朝锋","精神科");
d1.seatZhen();
d2.seatZhen();3. 프로토타입(체인) 상속
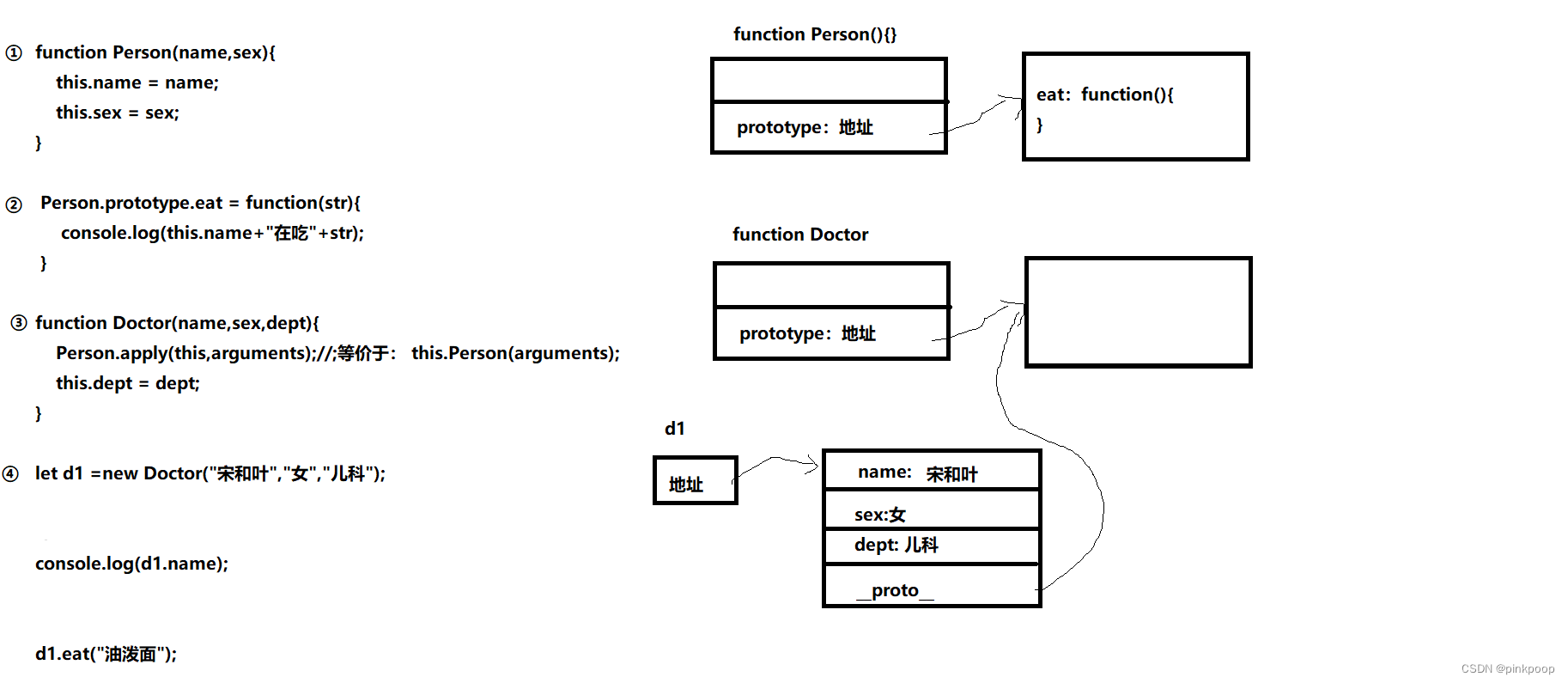
// 原型(链)继承,必须用ES5的写法。
// 1、父类
function Person(name, sex) {
this.name = name;
this.sex = sex;
}
Person.prototype.eat = function () {
}
// 2、子类1
function Doctor(dept) {
this.dept = dept;
}
// 建立继承关系(原型的方式):子类(构造函数)的原型属性 指向 父类的对象(实例)
Doctor.prototype = new Person("宋和叶", "女");
let d1 = new Doctor("神经科");
console.log(d1.name);
console.log(d1.eat);
let d1 = new Doctor("神经科");
// 3、子类2
function Programmer(lanuage){
this.lanuage = lanuage;
}
Programmer.prototype = new Person("纪朝锋","男");
let p1 = new Programmer("javascript");
p1.name;
p1.eat();4. 프로토타입(체인) 상속 시 유의사항
① 먼저 상속 관계를 완성한 후 서브 클래스 고유의 속성과 메서드를 추가합니다.
② 하위 클래스별 속성 및 메서드 작성 시 다시 프로토타입을 만들 수 없습니다(더 이상 프로토타입을 json 객체에 직접 할당할 수 없음).
// 1、父类
function Person(name,sex,books){
this.name = name;
this.sex = sex;
this.books = books;
}
Person.prototype.eat = function(str){
console.log(this.name+"在吃"+str+",天在看…………");
}
// 2、子类1
function Doctor(dept){
this.dept = dept;
}
// 建立继承关系(原型的方式):子类(构造函数)的原型属性 指向 父类的对象(实例)
Doctor.prototype = new Person("宋和叶","女",[]);
Doctor.prototype.seatZhen = function(){
console.log(this.name+"在坐诊……");
}
// 不能重新prototype属性
// Doctor.prototype = {
// seatZhen:function(){
// console.log(this.name+"在坐诊……");
// }
// }
let d1 = new Doctor("神经科");
d1.name = "纪朝锋";
let d2 = new Doctor("神经科");
d2.name="党艺华";
d1.eat("油条");
d1.seatZhen();
d2.eat("包子");5. 호출 및 적용 기능
① 전화 신청:
1. 호출과 적용 모두 함수(함수)의 메서드입니다.
2. 호출과 적용 모두 원래 함수를 호출하고 있습니다.
3. 호출 및 적용은 원래 기능에서 이것의 포인트를 변경할 수 있습니다.
4. 호출 및 적용의 첫 번째 매개변수는 원래 함수의 이 지점입니다.
5. 호출은 함수와 객체를 분리할 수 있습니다(결합도: 종속도/연관도. 높은 응집도, 낮은 결합도).
6. 호출과 적용의 차이점(단지 형식의 차이):
1) 두 번째 매개변수부터 뒤에 오는 호출 함수의 매개변수는 원래 함수의 매개변수입니다.
2) 적용 함수에는 두 개의 매개변수만 있고 두 번째 매개변수는 배열이며 배열에는 원래 함수의 매개변수가 포함됩니다. 이런 식으로 apply의 두 번째 매개 변수는 인수를 사용할 수 있습니다.
②예제 코드
let person = {
name: "张三疯",
eat: function () {
console.log(this.name + "在吃");
}
}
person.eat();
let dog = {
name: "小黑"
}
person.eat.call(dog);
function eat(str) {
console.log(this.name + "在吃" + str);
}
eat("食物");
let dog = {
name: "小黑"
}
eat.call(dog, "油泼面");//等价于:dog.eat("油泼面");
let doctor = {
name: "张三疯"
}
eat.call(doctor, "方便面");//等价于:doctor.eat("方便面");
eat.apply(doctor, ["油条"])
3、call和apply的区别
eat.call(doctor, "方便面");//等价于:doctor.eat("方便面");
eat.apply(doctor, ["油条"])//等价于:doctor.eat("油条");
function eat(str, song) {
console.log(this.name + "吃着" + str + ",唱着" + song);
}
let dog = {
name: "小黑"
}
function fn01() {
console.log("arguments", arguments);
eat.apply(dog, arguments);
// arguments也是函数的内置对象,该对象是个伪数组(不是数组,
// 但是可以使用数组的length,下标),里面存储着函数的实参
}
fn01("火锅", "最炫民族风");6. 함수 호출, 적용, 바인딩
① 바인드와 콜 및 적용의 차이점:
동일한 지점: 바인드, 호출, 적용은 이것의 방향을 바꿀 수 있습니다.
차이점: 1. bind는 원래 함수를 호출하지 않고 새 함수를 생성하며(bind의 반환 값은 새 함수임) 새 함수에서 this가 bind의 개체입니다. bind는 강한 결속이라는 의미를 가지고 있습니다. bind가 호출되는 한 개체와 함수는 영원히 바인딩됩니다. 2. 호출 및 적용은 원래 함수를 호출합니다.
② 예시:
function eat(str){
console.log(this.name+"在吃"+str);
}
let dog = {
name:"小黑"
}
let pig = {
name:"小白"
}
// 1)、bind
let fn01 = eat.bind(dog);//fn01 这个函数,就是dog和eat绑定在一起的函数。只要调用fn01,this必
然是dog
fn01("油泼面");
fn01("狗粮");
let fn02 = eat.bind(pig);//fn02 这个函数,就是pig和eat绑定在一起的函数。只要调用fn02,this必
然是pig
fn02("玉米");
fn02("米饭");
// 2)、call
eat.call(dog,"油泼面");// 如果希望this是dog,那就call dog
eat.call(dog,"狗粮");
eat.call(pig,"玉米");// 如果希望this是pig,那就call pig
eat.call(pig,"米饭");7. 호출 및 적용 상속
①하위 클래스 생성자에서 호출과 적용을 사용하여 부모 클래스 생성자에서 이(하위 클래스 객체)를 변경합니다.
② 단점 : 부모 클래스의 프로토타입 속성에 대한 내용(속성 및 메소드) 상속 불가
function Person(name,sex){
this.name = name;
this.sex = sex;
}
// Person.prototype.eat = function(str){
// console.log(this.name+"在吃"+str);
// }
function Doctor(name,sex,dept){
// apply的继承。
let obj = this;
Person.apply(obj,arguments);//没有把所谓的构造函数(Person)当构造函数使用(就当一个普通函数);等价于: this.Person(arguments);
this.dept = dept;
}
let d1 =new Doctor("宋和叶","女","儿科");
let d2 = new Doctor("纪朝锋","男","骨科");
console.log(d1.name);
console.log(d2.name);
d1.eat("油泼面");8. 조합 상속
프로토타입(체인) 상속을 호출과 결합하고 상속을 적용합니다. 각자의 강점을 발휘합니다.
① 프로토타입 상속: 부모 클래스의 프로토타입 속성에 대한 내용(속성 및 메서드)을 상속받는다.
②상속 호출 및 적용 : 부모 클래스 생성자의 속성과 메소드를 상속 받습니다.
function Person(name,sex){
if(arguments.length>0){
this.name = name;
this.sex = sex;
}
}
Person.prototype.eat = function(str){
console.log(this.name+"在吃"+str);
}
function Doctor(name,sex,dept){
// call和apply继承:把父类构造函数里的属性和方法继承下来。
Person.apply(this,arguments);
this.dept = dept;
}
// 原型继承:把父类原型属性上内容(属性和方法)继承下来。
Doctor.prototype = new Person();
let d1 =new Doctor("宋和叶","女","儿科");
let d2 = new Doctor("纪朝锋","男","骨科");
console.log(d1.name);
console.log(d2.name);
d1.eat("油泼面");
9. ES6의 상속
①상속 관계의 키워드: 확장하다;
② super()는 서브클래스 생성자에서 호출되어야 하며, 서브클래스 생성자의 첫 번째 문장에 작성되어야 한다.
③ ES6의 이런 표기법은 문법적 설탕(필기법을 바꿈, 본질은 같다)
class Person{
constructor(name,sex){
this.name = name;
this.sex = sex;
}
eat(str){
console.log(this.name+"在吃"+str);
}
}
// extends关键字完成继承关系
class Doctor extends Person{
constructor(name,sex,dept){
// super就是父类
super(name,sex);//这就相当于调用了父类的构造函数。这句话必须放在子类构造函数里的第一句话
this.dept = dept;
}
}
let d1 =new Doctor("宋和叶","女","儿科");
let d2 = new Doctor("纪朝锋","男","骨科");
console.log(d1.name);
console.log(d2.name);
d1.eat("油泼面");10. (확장) ES6 구문 슈가 검증
function Person(name, sex) {
if (arguments.length > 0) {
this.name = name;
this.sex = sex;
// this.eat = function(str){
// console.log(this.name+"在吃"+str);
// }
}
}
Person.prototype.eat = function (str) {
console.log(this.name + "在吃" + str);
}
function Doctor(name, sex, dept) {
Person.apply(this, arguments);
this.dept = dept;
}
// Doctor.prototype = new Person();
let d1 = new Doctor("宋和叶", "女", "儿科");
let d2 = new Doctor("纪朝锋", "男", "骨科");
console.log(d1.eat === d2.eat);//如果把eat方法写在构造函数里,那么是false(因为,每次调用构造函数,都会重新定义函数) )
console.log(d1.eat === d2.eat);//如果把eat方法写在原型属性上,那么是true11. (확장) 정식 클래스의 상속관계를 보라.
①js 언어 자체의 클래스 상속 관계
console.dir(Array);
//继承关系: Array ---> Function --> Object
let arr = new Array(10);
console.dir(arr);
console.log(arr.__proto__ == Array.prototype);②dom 객체가 속한 클래스와 그 상속 관계
let box = document.getElementById("box"); //box对象是 类 HTMLDivElement 的实例
console.dir(box);
div是 HTMLDivElement的对象,即就是: div属于 HTMLDivElement 类型。
继承关系: HTMLDivElement--> HTMLElement-->Element-->Node-->EventTarget-->Object
console.log(box.constructor===HTMLDivElement);
let t = document.createElement("div");
let t2 = new HTMLDivElement();//不行, 因为 HTMLDivElement,不是真正的构造函数,实际是个接口01. 프로토타입 상속의 개략도

02. 호출 및 적용 상속의 개략도