- There are 12 departments in a unit, and each department has a telephone, but the whole unit has only one outside line. When a call comes in, the switcher will transfer it to the internal line. It is known that the frequency of each department using the external line is (times/day): 5 20 10 12 8 43 5 6 9 15 19 32.
Use the idea of Huffman tree algorithm to design the internal telephone number, so that the operator dials as few times as possible. Requirements:
(1) Construct a binary tree according to the frequency of using outside calls;
(2) Output the designed internal phone numbers of each department.
#pragma warning(disable : 4996) //由于字符串拷贝函数strcpy已经被c++标准库弃用,所以必须在这里忽略警告,不然无法运行
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
typedef struct {
int weight;//节点的权值
int parent, lchild, rchild;//节点的双亲,左孩子,右孩子的下标
}HTNode, * HuffmanTree;//动态分配数组存储哈夫曼树
//选择函数
//选择出两个双亲节点为0,并且权值最小的节点
void Select(HuffmanTree HT, int end, int* s1, int* s2) {
int min1, min2;//min1存放较小的,min2存放第二小的
int i = 1;
while (HT[i].parent != 0 && i <= end) {
i++;
}
min1 = HT[i].weight;
*s1 = i;
i++;
while (HT[i].parent != 0 && i <= end) {
i++;
}
//对比找到的两个双亲节点为0的节点;
if (HT[i].weight < min1) {
min2 = min1;
*s2 = *s1;
min1 = HT[i].weight;
*s1 = i;
}
else {
min2 = HT[i].weight;
*s2 = i;
}
//对余下的节点遍历
for (int j = i + 1; j <= end; j++) {
if (HT[j].parent != 0)continue;
if (HT[j].weight < min1) {
min2 = min1;
min1 = HT[j].weight;
*s2 = *s1;
*s1 = j;
}
else if (HT[j].weight >= min1 && HT[j].weight < min2) {
min2 = HT[j].weight;
*s2 = j;
}
}
}
//生成哈夫曼树
void CreateHuffmanTree(HuffmanTree& HT, int n) {
if (n < 1)return;
const int m = 2 * n - 1;
HT = new HTNode[m + 1];//其实需要一个长度为2*n的顺序表,但是第0的位置不使用,[n,2*n-1]的位置是哈夫曼树
for (int i = 1; i <= m; i++) {
HT[i].parent = 0, HT[i].lchild = 0, HT[0].rchild = 0;
}
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++) {
cin >> HT[i].weight;
}
for (int i = n + 1; i <= m; i++) {
int s1 = 0, s2 = 0;
Select(HT, i - 1, &s1, &s2);
HT[s1].parent = HT[s2].parent = i;
HT[i].lchild = s1;
HT[i].rchild = s2;
HT[i].weight = HT[s1].weight + HT[s2].weight;
}
}
//这个编码之所以是字符数组的形式,主要是因为下面对编码的时候要求从后向前修改数组的值
typedef char** HuffmanCode;
//得到哈夫曼编码
void CreateHuffmanCode(HuffmanTree HT, HuffmanCode& HC, int n) {
int start, c, f;
HC = new char* [n + 1];
char* cd = new char[n];
cd[n - 1] = '\0';
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++) {
start = n - 1;
c = i;
f = HT[i].parent;
while (f != 0) {
start--;
if (HT[f].lchild == c)cd[start] = '0';
else cd[start] = '1';
c = f; f = HT[f].parent;
}
HC[i] = new char[n - start];
strcpy(HC[i], &cd[start]);
}
delete cd;
}
int main() {
HuffmanTree ht;
CreateHuffmanTree(ht, 12);
HuffmanCode HC;
CreateHuffmanCode(ht, HC, 12);
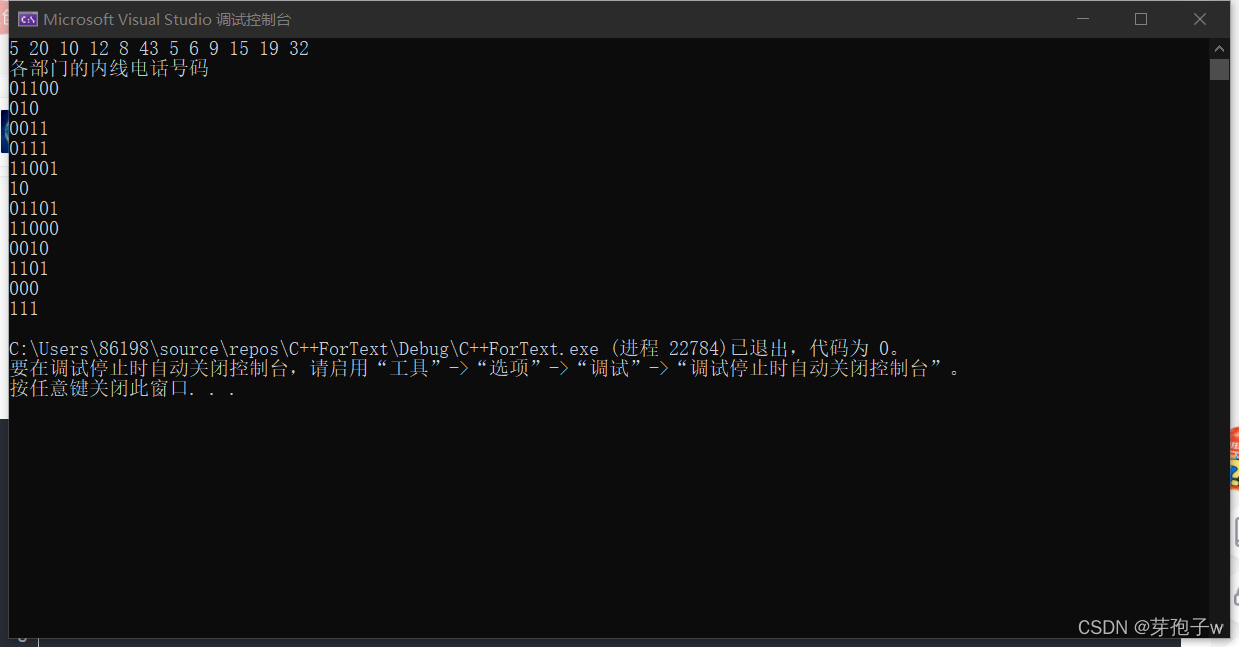
cout << "各部门的内线电话号码" << endl;
//这个位置如果不小心从0的位置开始会产生严重错误
for (int i = 1; i <= 12; i++) {
cout << HC[i] << endl;
}
return 0;
}
run screenshot