Este artículo proviene de liuyubobobo de "Algoritmos y Estructuras de Datos - La construcción de los artículos" tutoriales de vídeo
El concepto básico mapa
En primer lugar comprender el mapa conceptual.
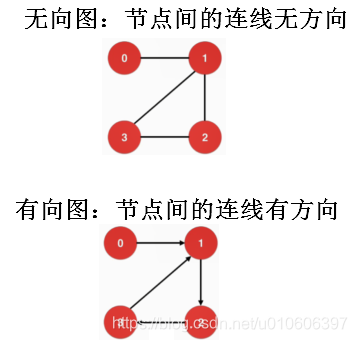

La figura aplicación matemática, código,
Generalmente se usa matriz de adyacencia representa un gráfico denso , utilizando la lista de adyacencia indica la figura escasa . se adyacencia matriz, se explicará La siguiente lista de adyacencia.

código de implementación:
// 稠密图 -- 邻接矩阵
public class DenseGraph {
private int nodeTotal; // 节点数
private int nodeEdgeNum; // 节点的边数
private boolean directed; // 是否为有向图
private boolean[][] data2Arr; // 图的具体数据
// 构造函数
public DenseGraph( int nodeTotal , boolean directed ){
assert nodeTotal >= 0;
this.nodeTotal = nodeTotal;
this.nodeEdgeNum = 0; // 初始化没有任何边
this.directed = directed;
// boolean型变量的默认值为false
// 图的数据data2Arr初始化为nodeTotal*nodeTotal的布尔矩阵, 每一个data2Arr[i][j]均为false, 表示没有任何边
data2Arr = new boolean[nodeTotal][nodeTotal];
}
public int getNodeTotal(){ return nodeTotal;} // 返回节点个数
public int getNodeEdgeNum(){ return nodeEdgeNum;} // 返回节点边的个数
// 向图中添加一个边
public void addEdge(int node1, int node2){
assert node1 >= 0 && node1 < nodeTotal;
assert node2 >= 0 && node2 < nodeTotal;
if( hasEdge(node1, node2) )
return;
data2Arr[node1][node2] = true;
if( !directed ){
//无向图,node2、node1也相连
data2Arr[node2][node1] = true;
}
nodeEdgeNum++;
}
// 验证图中是否有从node1到node2的边
public boolean hasEdge(int node1, int node2){
assert node1 >= 0 && node1 < nodeTotal;
assert node2 >= 0 && node2 < nodeTotal;
return data2Arr[node1][node2];
}
// 显示图的信息
public void show(){
for(int i = 0; i < nodeTotal; i ++ ){
for(int j = 0; j < nodeTotal; j ++ )
System.out.print(data2Arr[i][j]+"\t");
System.out.println();
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
DenseGraph dg = new DenseGraph(4, false);
dg.addEdge(1,2);
dg.show();
}
}
código de implementación
public class SparseGraph {
private int nodeTotal; // 节点数
private int nodeEdgeNum; // 节点的边数
private boolean directed; // 是否为有向图
private Vector<Integer>[] dataArrVector; // 图的具体数据
// 构造函数
public SparseGraph( int nodeTotal , boolean directed ){
assert nodeTotal >= 0;
this.nodeTotal = nodeTotal;
this.nodeEdgeNum = 0; // 初始化没有任何边
this.directed = directed;
// dataArrVector初始化为nodeTotal个空的vector, 表示每一个dataArrVector[i]都为空, 即没有任何边
dataArrVector = (Vector<Integer>[])new Vector[nodeTotal];
for(int i = 0 ; i < nodeTotal ; i ++)
dataArrVector[i] = new Vector<Integer>();
}
public int getNodeTotal(){ return nodeTotal;} // 返回节点个数
public int getNodeEdgeNum(){ return nodeEdgeNum;} // 返回节点边的个数
// 向图中添加一个边
public void addEdge(int node1, int node2){
assert node1 >= 0 && node1 < nodeTotal;
assert node2 >= 0 && node2 < nodeTotal;
dataArrVector[node1].add(node2);
if( node1 != node2 && !directed )
dataArrVector[node2].add(node1);
nodeEdgeNum++;
}
// 验证图中是否有从node1到node2的边
public boolean hasEdge(int node1, int node2){
assert node1 >= 0 && node1 < nodeTotal;
assert node2 >= 0 && node2 < nodeTotal;
for(int i = 0; i < dataArrVector[node1].size() ; i ++ )
if( dataArrVector[node1].elementAt(i) == node2)
return true;
return false;
}
// 显示图的信息
public void show(){
for(int i = 0; i < nodeTotal; i ++ ){
System.out.print("vertex " + i + ":\t");
for(int j = 0; j < dataArrVector[i].size() ; j ++ )
System.out.print(dataArrVector[i].elementAt(j) + "\t");
System.out.println();
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
SparseGraph dg = new SparseGraph(4, false);
dg.addEdge(1,2);
dg.show();
}
}La lectura de un archivo de datos de la figura.
En general, la figura datos borde punto medio se registra en un archivo, crear tres siguiente archivo TXT, y la relación de la figura grabación lado del punto.
Aquí hay dos archivos de datos

testG1.txt
13 13
0 5
4 3
0 1
9 12
6 4
5 4
0 2
11 12
9 10
0 6
7 8
9 11
5 3
testG2.txt
6 8
0 1
0 2
0 5
1 2
1 3
1 4
3 4
3 5
testG.txt
7 8
0 1
0 2
0 5
0 6
3 4
3 5
4 5
4 6
La figura definición de interfaz de una
// 图的接口
public interface Graph {
public int getNodeTotal();
public int getNodeEdgeNum();
public void addEdge(int v, int w);
boolean hasEdge(int v, int w);
void show();
public Iterable<Integer> getNodeEdges(int v);
}Crear una clase para leer los gráficos
/**
* 从文件中读取一个图
*/
public class ReadGraph {
private Scanner scanner;
/**
* 读取文件,创建一个图
* @param graph
* @param filename
*/
public ReadGraph(Graph graph, String filename) {
// 读取文件
readFile(filename);
try {
// 文件第一行的两个数字是点数、边数
int V = scanner.nextInt();
if (V < 0)
throw new IllegalArgumentException("定点数非负");
assert V == graph.getNodeTotal();
int E = scanner.nextInt();
if (E < 0)
throw new IllegalArgumentException("边数非负");
// 从第二行开始,将数据添加到图对象中
for (int i = 0; i < E; i++) {
int v = scanner.nextInt();
int w = scanner.nextInt();
assert v >= 0 && v < V;
assert w >= 0 && w < V;
graph.addEdge(v, w);
}
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
private void readFile(String filename) {
assert filename != null;
try {
File file = new File(filename);
if (file.exists()) {
FileInputStream fis = new FileInputStream(file);
scanner = new Scanner(new BufferedInputStream(fis), "UTF-8");
scanner.useLocale(Locale.ENGLISH);
} else{
throw new IllegalArgumentException(filename + "doesn't exist.");
}
} catch (IOException ioe) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException("Could not open " + filename, ioe);
}
}
}Atravesando el mapa de profundidad, los componentes conectados

recorrido profundo, la comunicación código de componente, dirigiéndose a la profundidad de recorrido:
// 稠密图 -- 邻接矩阵
public class DenseGraph implements Graph{
private int nodeTotal; // 节点数
private int nodeEdgeNum; // 节点的边数
private boolean directed; // 是否为有向图
private boolean[][] data2Arr; // 图的具体数据
// 构造函数
public DenseGraph(int nodeTotal , boolean directed ){
assert nodeTotal >= 0;
this.nodeTotal = nodeTotal;
this.nodeEdgeNum = 0; // 初始化没有任何边
this.directed = directed;
// boolean型变量的默认值为false
// 图的数据data2Arr初始化为nodeTotal*nodeTotal的布尔矩阵, 每一个data2Arr[i][j]均为false, 表示没有任何边
data2Arr = new boolean[nodeTotal][nodeTotal];
}
public int getNodeTotal(){ return nodeTotal;} // 返回节点个数
public int getNodeEdgeNum(){ return nodeEdgeNum;} // 返回节点边的个数
// 向图中添加一个边
public void addEdge(int node1, int node2){
assert node1 >= 0 && node1 < nodeTotal;
assert node2 >= 0 && node2 < nodeTotal;
if( hasEdge(node1, node2) )
return;
data2Arr[node1][node2] = true;
if( !directed ){
//无向图,node2、node1也相连
data2Arr[node2][node1] = true;
}
nodeEdgeNum++;
}
// 验证图中是否有从node1到node2的边
public boolean hasEdge(int node1, int node2){
assert node1 >= 0 && node1 < nodeTotal;
assert node2 >= 0 && node2 < nodeTotal;
return data2Arr[node1][node2];
}
// 显示图的信息
public void show(){
for(int i = 0; i < nodeTotal; i ++ ){
for(int j = 0; j < nodeTotal; j ++ )
System.out.print(data2Arr[i][j]+"\t");
System.out.println();
}
}
/**
* 获取相邻节点
* @param node
* @return
*/
public Iterable<Integer> adjacentNode(int node){
assert node >= 0 && node < nodeTotal;
Vector<Integer> nodeVector = new Vector<>();
// data2Arr[node]是一个数组,遍历此数组
for (int i=0; i<nodeTotal; i++){
// data2Arr[node][i]为true,则node和数值为i的节点相连
if (data2Arr[node][i]){
// 将节点i添加到数组中
nodeVector.add(i);
}
}
return nodeVector;
}
}
// 稀疏图 -- 邻接表
public class SparseGraph implements Graph{
private int nodeTotal; // 节点数
private int nodeEdgeNum; // 节点的边数
private boolean directed; // 是否为有向图
private Vector<Integer>[] dataArrVector; // 图的具体数据
// 构造函数
public SparseGraph(int nodeTotal , boolean directed ){
assert nodeTotal >= 0;
this.nodeTotal = nodeTotal;
this.nodeEdgeNum = 0; // 初始化没有任何边
this.directed = directed;
// dataArrVector初始化为nodeTotal个空的vector, 表示每一个dataArrVector[i]都为空, 即没有任何边
dataArrVector = (Vector<Integer>[])new Vector[nodeTotal];
for(int i = 0 ; i < nodeTotal ; i ++)
dataArrVector[i] = new Vector<Integer>();
}
public int getNodeTotal(){ return nodeTotal;} // 返回节点个数
public int getNodeEdgeNum(){ return nodeEdgeNum;} // 返回节点边的个数
// 向图中添加一个边
public void addEdge(int node1, int node2){
assert node1 >= 0 && node1 < nodeTotal;
assert node2 >= 0 && node2 < nodeTotal;
dataArrVector[node1].add(node2);
if( node1 != node2 && !directed )
dataArrVector[node2].add(node1);
nodeEdgeNum++;
}
// 验证图中是否有从node1到node2的边
public boolean hasEdge(int node1, int node2){
assert node1 >= 0 && node1 < nodeTotal;
assert node2 >= 0 && node2 < nodeTotal;
for(int i = 0; i < dataArrVector[node1].size() ; i ++ )
if( dataArrVector[node1].elementAt(i) == node2)
return true;
return false;
}
// 显示图的信息
public void show(){
for(int i = 0; i < nodeTotal; i ++ ){
System.out.print("vertex " + i + ":\t");
for(int j = 0; j < dataArrVector[i].size() ; j ++ )
System.out.print(dataArrVector[i].elementAt(j) + "\t");
System.out.println();
}
}
/**
* 获取相邻节点
* @param node
* @return
*/
public Iterable<Integer> adjacentNode(int node){
assert node >= 0 && node < nodeTotal;
// 邻接表,dataArrVector[node]中的节点都和node相连接
return dataArrVector[node];
}
}
// 连通分量
public class Components {
Graph G; // 图的引用
private boolean[] visited; // 记录深度遍历的过程中节点是否被访问
private int count; // 记录连通分量个数
private int[] id; // 每个节点所对应的连通分量标记
// 构造函数,求出无权图的连通分量
public Components(Graph graph){
// 算法初始化
G = graph;
// visited数组长度是图节点的个数
visited = new boolean[G.getNodeTotal()];
id = new int[G.getNodeTotal()];
count = 0;
for( int i = 0 ; i < G.getNodeTotal() ; i ++ ){
// 刚才开始,所有节点都没遍历
visited[i] = false;
// 刚才开始,每个节点不属于任何连通分量
id[i] = -1;
}
// 求图的连通分量
for( int i = 0 ; i < G.getNodeTotal() ; i ++ )
if( !visited[i] ){
// i未遍历,深度遍历i
deepFirstSearch(i);
// i深度遍历完了,连通分量++
count++;
}
}
// 图的深度优先遍历
void deepFirstSearch(int node){
// 当前节点设置为已经遍历
visited[node] = true;
// 当前节点属于连通分量count
id[node] = count;
// 深度遍历当前节点的相邻节点
for( int i: G.adjacentNode(node) ){
if( !visited[i] )
deepFirstSearch(i);
}
}
// 返回图的连通分量个数
int count(){
return count;
}
// 查询点node1和点node2是否连通
boolean isConnected(int node1, int node2){
assert node1 >= 0 && node1 < G.getNodeTotal();
assert node2 >= 0 && node2 < G.getNodeTotal();
return id[node1] == id[node2];
}
}// 深度遍历寻址
public class Path {
private Graph G; // 图的引用
private int startNode; // 起始点
private boolean[] visited; // 记录深度遍历的过程中节点是否被访问
private int[] from; // 记录路径, from[i]表示查找的路径上i的上一个节点
// 构造函数, 寻路算法, 寻找图graph从startNode点到其他点的路径
public Path(Graph graph, int startNode){
// 算法初始化
G = graph;
assert startNode >= 0 && startNode < G.getNodeTotal();
visited = new boolean[G.getNodeTotal()];
from = new int[G.getNodeTotal()];
for( int i = 0 ; i < G.getNodeTotal() ; i ++ ){
visited[i] = false;
from[i] = -1;
}
this.startNode = startNode;
// 寻路算法
deepFirstSearch(startNode);
}
// 图的深度优先遍历
private void deepFirstSearch(int node ){
visited[node] = true;
// node的相邻节点
for( int i : G.adjacentNode(node) )
// 相邻节点未被遍历过
if( !visited[i] ){
// from[i]位置存储上一个节点node
from[i] = node;
deepFirstSearch(i);
}
}
// 查询从startNode点到targetNode点是否有路径
boolean hasPath(int targetNode){
assert targetNode >= 0 && targetNode < G.getNodeTotal();
return visited[targetNode];
}
// 查询从s点到w点的路径, 存放在vec中
Vector<Integer> path(int targetNode){
assert hasPath(targetNode) ;
// 栈,先进后出
Stack<Integer> s = new Stack<Integer>();
// 通过from数组逆向查找到从startNode到targetNode的路径, 存放到栈中
int p = targetNode;
// p不为-1,即节点p有上一个节点,上一个节点存放在from[p]中
while( p != -1 ){
s.push(p);
p = from[p];
}
// 从栈中依次取出元素,获得顺序的从startNode到targetNode的路径
Vector<Integer> res = new Vector<Integer>();
while( !s.empty() )
res.add( s.pop() );
return res;
}
// 打印出从startNode到targetNode的路径
void showPath(int targetNode){
assert hasPath(targetNode) ;
Vector<Integer> vec = path(targetNode);
for( int i = 0 ; i < vec.size() ; i ++ ){
System.out.print(vec.elementAt(i));
if( i == vec.size() - 1 )
System.out.println();
else
System.out.print(" -> ");
}
}
}
// 测试图的联通分量、深度遍历寻址
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//// TestG1.txt
//String filename1 = "note\\src\\main\\java\\com\\datastructure_arithmetic\\testG1.txt";
//SparseGraph g1 = new SparseGraph(13, false);
//ReadGraph readGraph1 = new ReadGraph(g1, filename1);
//Components component1 = new Components(g1);
//System.out.println("TestG1.txt, 连通分量: " + component1.count());
//System.out.println();
//
//// TestG2.txt
//String filename2 = "note\\src\\main\\java\\com\\datastructure_arithmetic\\testG2.txt";
//SparseGraph g2 = new SparseGraph(6, false);
//ReadGraph readGraph2 = new ReadGraph(g2, filename2);
//Components component2 = new Components(g2);
//System.out.println("TestG2.txt, 连通分量: " + component2.count());
String filename1 = "note\\src\\main\\java\\com\\datastructure_arithmetic\\testG1.txt";
SparseGraph g = new SparseGraph(13, false);
ReadGraph readGraph = new ReadGraph(g, filename1);
g.show();
System.out.println();
Path path = new Path(g,0);
System.out.println("Path from 0 to 6 : ");
path.showPath(6);
}
}La figura no autorizado: no hay conexión entre la longitud dos nodos de los puntos, en comparación con una conexión entre dos puntos, y 0 no está conectado.

Las colas pueden ser implementados utilizando la figura amplitud de recorrido, la amplitud de la ruta más corta se puede determinar no traversal derecha de la figura
// 广度优先遍历
public class ShortestPath {
private Graph G; // 图的引用
private int startNode; // 起始点
private boolean[] visited; // 记录dfs的过程中节点是否被访问
private int[] from; // 记录路径, from[i]表示查找的路径上i的上一个节点
private int[] ord; // 记录路径中节点的次序。ord[i]表示i节点在路径中的次序。
// 构造函数, 寻路算法, 寻找图graph从startNode点到其他点的路径
public ShortestPath(Graph graph, int startNode){
// 算法初始化
G = graph;
assert startNode >= 0 && startNode < G.getNodeTotal();
visited = new boolean[G.getNodeTotal()];
from = new int[G.getNodeTotal()];
ord = new int[G.getNodeTotal()];
for( int i = 0 ; i < G.getNodeTotal() ; i ++ ){
visited[i] = false;
from[i] = -1;
ord[i] = -1;
}
this.startNode = startNode;
// 无向图最短路径算法, 从startNode开始广度优先遍历整张图
Queue<Integer> q = new LinkedList<Integer>();
q.add(startNode);
visited[startNode] = true;
ord[startNode] = 0;
while( !q.isEmpty() ){
int v = q.remove();
for( int i : G.adjacentNode(v) )
if( !visited[i] ){
q.add(i);
visited[i] = true;
from[i] = v;
ord[i] = ord[v] + 1;
}
}
}
// 查询从startNode点到target点是否有路径
public boolean hasPath(int target){
assert target >= 0 && target < G.getNodeTotal();
return visited[target];
}
// 查询从startNode点到target点的路径, 存放在vec中
public Vector<Integer> path(int target){
assert hasPath(target) ;
Stack<Integer> s = new Stack<Integer>();
// 通过from数组逆向查找到从startNode到target的路径, 存放到栈中
int p = target;
while( p != -1 ){
s.push(p);
p = from[p];
}
// 从栈中依次取出元素, 获得顺序的从startNode到target的路径
Vector<Integer> res = new Vector<Integer>();
while( !s.empty() )
res.add( s.pop() );
return res;
}
// 打印出从startNode点到target点的路径
public void showPath(int target){
assert hasPath(target) ;
Vector<Integer> vec = path(target);
for( int i = 0 ; i < vec.size() ; i ++ ){
System.out.print(vec.elementAt(i));
if( i == vec.size() - 1 )
System.out.println();
else
System.out.print(" -> ");
}
}
// 查看从startNode点到target点的最短路径长度
// 若从startNode到target不可达,返回-1
public int length(int w){
assert w >= 0 && w < G.getNodeTotal();
return ord[w];
}
}
