El DateFormat java, clase SimpleDateFormate fuente Detallado
Define una clase abstracta de formato
public abstract class Format implements Serializable, Cloneable {
private static final long serialVersionUID = -299282585814624189L;
protected Format() {
}
public final String format (Object obj) {
return format(obj, new StringBuffer(), new FieldPosition(0)).toString();
}
public abstract StringBuffer format(Object obj,
StringBuffer toAppendTo,
FieldPosition pos);
public AttributedCharacterIterator formatToCharacterIterator(Object obj) {
return createAttributedCharacterIterator(format(obj));
}
public abstract Object parseObject (String source, ParsePosition pos);
public Object parseObject(String source) throws ParseException {
ParsePosition pos = new ParsePosition(0);
Object result = parseObject(source, pos);
if (pos.index == 0) {
throw new ParseException("Format.parseObject(String) failed",
pos.errorIndex);
}
return result;
}
public Object clone() {
try {
return super.clone();
} catch (CloneNotSupportedException e) {
// will never happen
throw new InternalError(e);
}
}
//
// Convenience methods for creating AttributedCharacterIterators from
// different parameters.
//
AttributedCharacterIterator createAttributedCharacterIterator(String s) {
AttributedString as = new AttributedString(s);
return as.getIterator();
}
AttributedCharacterIterator createAttributedCharacterIterator(
AttributedCharacterIterator[] iterators) {
AttributedString as = new AttributedString(iterators);
return as.getIterator();
}
AttributedCharacterIterator createAttributedCharacterIterator(
String string, AttributedCharacterIterator.Attribute key,
Object value) {
AttributedString as = new AttributedString(string);
as.addAttribute(key, value);
return as.getIterator();
}
AttributedCharacterIterator createAttributedCharacterIterator(
AttributedCharacterIterator iterator,
AttributedCharacterIterator.Attribute key, Object value) {
AttributedString as = new AttributedString(iterator);
as.addAttribute(key, value);
return as.getIterator();
}
public static class Field extends AttributedCharacterIterator.Attribute {
// Proclaim serial compatibility with 1.4 FCS
private static final long serialVersionUID = 276966692217360283L;
/**
* Creates a Field with the specified name.
*
* @param name Name of the attribute
*/
protected Field(String name) {
super(name);
}
}
interface FieldDelegate {
public void formatted(Format.Field attr, Object value, int start,
int end, StringBuffer buffer);
public void formatted(int fieldID, Format.Field attr, Object value,
int start, int end, StringBuffer buffer);
}
}definición DateFormat
public abstract class DateFormat extends Format {
protected Calendar calendar;
protected NumberFormat numberFormat;
public final StringBuffer format(Object obj, StringBuffer toAppendTo,
FieldPosition fieldPosition)
{
if (obj instanceof Date)
return format( (Date)obj, toAppendTo, fieldPosition );
else if (obj instanceof Number)
return format( new Date(((Number)obj).longValue()),
toAppendTo, fieldPosition );
else
throw new IllegalArgumentException("Cannot format given Object as a Date");
}
public abstract StringBuffer format(Date date, StringBuffer toAppendTo,
FieldPosition fieldPosition);
public final String format(Date date)
{
return format(date, new StringBuffer(),
DontCareFieldPosition.INSTANCE).toString();
}
public Date parse(String source) throws ParseException
{
ParsePosition pos = new ParsePosition(0);
Date result = parse(source, pos);
if (pos.index == 0)
throw new ParseException("Unparseable date: \"" + source + "\"" ,
pos.errorIndex);
return result;
}
public abstract Date parse(String source, ParsePosition pos);
public Object parseObject(String source, ParsePosition pos) {
return parse(source, pos);
}
public final static DateFormat getTimeInstance()
{
return get(DEFAULT, 0, 1, Locale.getDefault(Locale.Category.FORMAT));
}
public final static DateFormat getTimeInstance(int style)
{
return get(style, 0, 1, Locale.getDefault(Locale.Category.FORMAT));
}
public final static DateFormat getTimeInstance(int style,
Locale aLocale)
{
return get(style, 0, 1, aLocale);
}
public final static DateFormat getDateInstance()
{
return get(0, DEFAULT, 2, Locale.getDefault(Locale.Category.FORMAT));
}
public final static DateFormat getDateInstance(int style)
{
return get(0, style, 2, Locale.getDefault(Locale.Category.FORMAT));
}
public final static DateFormat getDateInstance(int style,
Locale aLocale)
{
return get(0, style, 2, aLocale);
}
public final static DateFormat getDateTimeInstance()
{
return get(DEFAULT, DEFAULT, 3, Locale.getDefault(Locale.Category.FORMAT));
}
public final static DateFormat getDateTimeInstance(int dateStyle,
int timeStyle)
{
return get(timeStyle, dateStyle, 3, Locale.getDefault(Locale.Category.FORMAT));
}
public final static DateFormat
getDateTimeInstance(int dateStyle, int timeStyle, Locale aLocale)
{
return get(timeStyle, dateStyle, 3, aLocale);
}
public final static DateFormat getInstance() {
return getDateTimeInstance(SHORT, SHORT);
}
public static Locale[] getAvailableLocales()
{
LocaleServiceProviderPool pool =
LocaleServiceProviderPool.getPool(DateFormatProvider.class);
return pool.getAvailableLocales();
}
public void setCalendar(Calendar newCalendar)
{
this.calendar = newCalendar;
}
public Calendar getCalendar()
{
return calendar;
}
public void setNumberFormat(NumberFormat newNumberFormat)
{
this.numberFormat = newNumberFormat;
}
public NumberFormat getNumberFormat()
{
return numberFormat;
}
}
DateFormat clase abstracta cumple la mayoría de los requisitos de presentación del tiempo, lo que proporciona tres métodos para obtener una instancia de un objeto:
DateFormat dateft= DateFormat.getDateInstance();
System.out.println(dateft.format(new Date()));
DateFormat dateft2=DateFormat.getTimeInstance();
System.out.println(dateft2.format(new Date()));
DateFormat dateft3=DateFormat.getDateTimeInstance();
System.out.println(dateft3.format(new Date()));El resultado:
08/20/2018
14:55:39
08/20/2018 14:55:39
DateFormat df1 = null ; // 声明一个DateFormat
DateFormat df2 = null ; // 声明一个DateFormat
df1 = DateFormat.getDateInstance(DateFormat.YEAR_FIELD,new Locale("zh","CN")) ; // 得到日期的DateFormat对象
df2 = DateFormat.getDateTimeInstance(DateFormat.YEAR_FIELD,DateFormat.ERA_FIELD,new Locale("zh","CN")) ; // 得到日期时间的DateFormat对象
System.out.println("DATE:" + df1.format(new Date())) ; // 按照日期格式化
System.out.println("DATETIME:" + df2.format(new Date())) ; // 按照日期时间格式化 FECHA: 2019 Nian 9 Yue 3 Ri
DATETIME: 2019 Nian 9 Yue 3 Ri Shi Xiawu 03 15 46 Miao Fen CST

El formato de estilo de juego principal por constantes DateFormat. Diferentes constantes pasan método, la longitud del resultado de control. DateFormat constantes de clase son las siguientes.
- CORTO: totalmente digital, como 12.5.10 o las 5:30 pm.
- MEDIO: más largo, como mayo 10,2016.
- LARGO: más tiempo, o como mayo 12,2016 11:15:32 am.
- COMPLETO: se especifica por completo, tales como el martes, mayo 10,2012 AD o 11: l5: 42am CST.
//获取不同格式化风格和中国环境的日期
DateFormat df1=DateFormat.getDateInstance(DateFormat.SHORT,Locale.CHINA);
DateFormat df2=DateFormat.getDateInstance(DateFormat.FULL,Locale.CHINA);
DateFormat df3=DateFormat.getDateInstance(DateFormat.MEDIUM,Locale.CHINA);
DateFormat df4=DateFormat.getDateInstance(DateFormat.LONG,Locale.CHINA);
//获取不同格式化风格和中国环境的时间
DateFormat df5=DateFormat.getTimeInstance(DateFormat.SHORT,Locale.CHINA);
DateFormat df6=DateFormat.getTimeInstance(DateFormat.FULL,Locale.CHINA);
DateFormat df7=DateFormat.getTimeInstance(DateFormat.MEDIUM,Locale.CHINA);
DateFormat df8=DateFormat.getTimeInstance(DateFormat.LONG,Locale.CHINA);
//将不同格式化风格的日期格式化为日期字符串
String date1=df1.format(new Date());
String date2=df2.format(new Date());
String date3=df3.format(new Date());
String date4=df4.format(new Date());
//将不同格式化风格的时间格式化为时间字符串
String time1=df5.format(new Date());
String time2=df6.format(new Date());
String time3=df7.format(new Date());
String time4=df8.format(new Date());
//输出日期
System.out.println("SHORT:"+date1+" "+time1);
System.out.println("FULL:"+date2+" "+time2);
System.out.println("MEDIUM:"+date3+" "+time3);
System.out.println("LONG:"+date4+" "+time4);SHORT:18-10-15 上午9:30
FULL:2018年10月15日 星期一 上午09时30分43秒 CST
MEDIUM:2018-10-15 9:30:43
LONG:2018年10月15日 上午09时30分43秒
练习一:把Date对象转换成String
Date date = new Date(1607616000000L);//Fri Dec 11 00:00:00 CST 2020
DateFormat df = new SimpleDateFormat(“yyyy年MM月dd日”);
String str = df.format(date);
//str中的内容为2020年12月11日
练习二:把String转换成Date对象
String str = ”2020年12月11日”;
DateFormat df = new SimpleDateFormat(“yyyy年MM月dd日”);
Date date = df.parse( str );
//Date对象中的内容为Fri Dec 11 00:00:00 CST 2020SimpleDateFormat
public class SimpleDateFormat extends DateFormat {
transient private NumberFormat originalNumberFormat;
transient private String originalNumberPattern;
transient private char minusSign = '-';
transient private boolean hasFollowingMinusSign = false;
transient private boolean forceStandaloneForm = false;
transient private char[] compiledPattern;
private Locale locale;
public SimpleDateFormat() {
this("", Locale.getDefault(Locale.Category.FORMAT));
applyPatternImpl(LocaleProviderAdapter.getResourceBundleBased().getLocaleResources(locale)
.getDateTimePattern(SHORT, SHORT, calendar));
}
public SimpleDateFormat(String pattern)
{
this(pattern, Locale.getDefault(Locale.Category.FORMAT));
}
public SimpleDateFormat(String pattern, Locale locale)
{
if (pattern == null || locale == null) {
throw new NullPointerException();
}
initializeCalendar(locale);
this.pattern = pattern;
this.formatData = DateFormatSymbols.getInstanceRef(locale);
this.locale = locale;
initialize(locale);
}
public SimpleDateFormat(String pattern, DateFormatSymbols formatSymbols)
{
if (pattern == null || formatSymbols == null) {
throw new NullPointerException();
}
this.pattern = pattern;
this.formatData = (DateFormatSymbols) formatSymbols.clone();
this.locale = Locale.getDefault(Locale.Category.FORMAT);
initializeCalendar(this.locale);
initialize(this.locale);
useDateFormatSymbols = true;
}
/* Initialize compiledPattern and numberFormat fields */
private void initialize(Locale loc) {
// Verify and compile the given pattern.
compiledPattern = compile(pattern);
/* try the cache first */
numberFormat = cachedNumberFormatData.get(loc);
if (numberFormat == null) { /* cache miss */
numberFormat = NumberFormat.getIntegerInstance(loc);
numberFormat.setGroupingUsed(false);
/* update cache */
cachedNumberFormatData.putIfAbsent(loc, numberFormat);
}
numberFormat = (NumberFormat) numberFormat.clone();
initializeDefaultCentury();
}
private void initializeCalendar(Locale loc) {
if (calendar == null) {
assert loc != null;
// The format object must be constructed using the symbols for this zone.
// However, the calendar should use the current default TimeZone.
// If this is not contained in the locale zone strings, then the zone
// will be formatted using generic GMT+/-H:MM nomenclature.
calendar = Calendar.getInstance(TimeZone.getDefault(), loc);
}
}
private char[] compile(String pattern) {
int length = pattern.length();
boolean inQuote = false;
StringBuilder compiledCode = new StringBuilder(length * 2);
StringBuilder tmpBuffer = null;
int count = 0, tagcount = 0;
int lastTag = -1, prevTag = -1;
for (int i = 0; i < length; i++) {
char c = pattern.charAt(i);
if (c == '\'') {
// '' is treated as a single quote regardless of being
// in a quoted section.
if ((i + 1) < length) {
c = pattern.charAt(i + 1);
if (c == '\'') {
i++;
if (count != 0) {
encode(lastTag, count, compiledCode);
tagcount++;
prevTag = lastTag;
lastTag = -1;
count = 0;
}
if (inQuote) {
tmpBuffer.append(c);
} else {
compiledCode.append((char)(TAG_QUOTE_ASCII_CHAR << 8 | c));
}
continue;
}
}
if (!inQuote) {
if (count != 0) {
encode(lastTag, count, compiledCode);
tagcount++;
prevTag = lastTag;
lastTag = -1;
count = 0;
}
if (tmpBuffer == null) {
tmpBuffer = new StringBuilder(length);
} else {
tmpBuffer.setLength(0);
}
inQuote = true;
} else {
int len = tmpBuffer.length();
if (len == 1) {
char ch = tmpBuffer.charAt(0);
if (ch < 128) {
compiledCode.append((char)(TAG_QUOTE_ASCII_CHAR << 8 | ch));
} else {
compiledCode.append((char)(TAG_QUOTE_CHARS << 8 | 1));
compiledCode.append(ch);
}
} else {
encode(TAG_QUOTE_CHARS, len, compiledCode);
compiledCode.append(tmpBuffer);
}
inQuote = false;
}
continue;
}
if (inQuote) {
tmpBuffer.append(c);
continue;
}
if (!(c >= 'a' && c <= 'z' || c >= 'A' && c <= 'Z')) {
if (count != 0) {
encode(lastTag, count, compiledCode);
tagcount++;
prevTag = lastTag;
lastTag = -1;
count = 0;
}
if (c < 128) {
// In most cases, c would be a delimiter, such as ':'.
compiledCode.append((char)(TAG_QUOTE_ASCII_CHAR << 8 | c));
} else {
// Take any contiguous non-ASCII alphabet characters and
// put them in a single TAG_QUOTE_CHARS.
int j;
for (j = i + 1; j < length; j++) {
char d = pattern.charAt(j);
if (d == '\'' || (d >= 'a' && d <= 'z' || d >= 'A' && d <= 'Z')) {
break;
}
}
compiledCode.append((char)(TAG_QUOTE_CHARS << 8 | (j - i)));
for (; i < j; i++) {
compiledCode.append(pattern.charAt(i));
}
i--;
}
continue;
}
int tag;
if ((tag = DateFormatSymbols.patternChars.indexOf(c)) == -1) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException("Illegal pattern character " +
"'" + c + "'");
}
if (lastTag == -1 || lastTag == tag) {
lastTag = tag;
count++;
continue;
}
encode(lastTag, count, compiledCode);
tagcount++;
prevTag = lastTag;
lastTag = tag;
count = 1;
}
if (inQuote) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException("Unterminated quote");
}
if (count != 0) {
encode(lastTag, count, compiledCode);
tagcount++;
prevTag = lastTag;
}
forceStandaloneForm = (tagcount == 1 && prevTag == PATTERN_MONTH);
// Copy the compiled pattern to a char array
int len = compiledCode.length();
char[] r = new char[len];
compiledCode.getChars(0, len, r, 0);
return r;
}
private static void encode(int tag, int length, StringBuilder buffer) {
if (tag == PATTERN_ISO_ZONE && length >= 4) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException("invalid ISO 8601 format: length=" + length);
}
if (length < 255) {
buffer.append((char)(tag << 8 | length));
} else {
buffer.append((char)((tag << 8) | 0xff));
buffer.append((char)(length >>> 16));
buffer.append((char)(length & 0xffff));
}
}
private void initializeDefaultCentury() {
calendar.setTimeInMillis(System.currentTimeMillis());
calendar.add( Calendar.YEAR, -80 );
parseAmbiguousDatesAsAfter(calendar.getTime());
}
@Override
public StringBuffer format(Date date, StringBuffer toAppendTo,
FieldPosition pos)
{
pos.beginIndex = pos.endIndex = 0;
return format(date, toAppendTo, pos.getFieldDelegate());
}
// Called from Format after creating a FieldDelegate
private StringBuffer format(Date date, StringBuffer toAppendTo,
FieldDelegate delegate) {
// Convert input date to time field list
calendar.setTime(date);
boolean useDateFormatSymbols = useDateFormatSymbols();
for (int i = 0; i < compiledPattern.length; ) {
int tag = compiledPattern[i] >>> 8;
int count = compiledPattern[i++] & 0xff;
if (count == 255) {
count = compiledPattern[i++] << 16;
count |= compiledPattern[i++];
}
switch (tag) {
case TAG_QUOTE_ASCII_CHAR:
toAppendTo.append((char)count);
break;
case TAG_QUOTE_CHARS:
toAppendTo.append(compiledPattern, i, count);
i += count;
break;
default:
subFormat(tag, count, delegate, toAppendTo, useDateFormatSymbols);
break;
}
}
return toAppendTo;
}
@Override
public AttributedCharacterIterator formatToCharacterIterator(Object obj) {
StringBuffer sb = new StringBuffer();
CharacterIteratorFieldDelegate delegate = new
CharacterIteratorFieldDelegate();
if (obj instanceof Date) {
format((Date)obj, sb, delegate);
}
else if (obj instanceof Number) {
format(new Date(((Number)obj).longValue()), sb, delegate);
}
else if (obj == null) {
throw new NullPointerException(
"formatToCharacterIterator must be passed non-null object");
}
else {
throw new IllegalArgumentException(
"Cannot format given Object as a Date");
}
return delegate.getIterator(sb.toString());
}
@Override
public Date parse(String text, ParsePosition pos)
{
checkNegativeNumberExpression();
int start = pos.index;
int oldStart = start;
int textLength = text.length();
boolean[] ambiguousYear = {false};
CalendarBuilder calb = new CalendarBuilder();
for (int i = 0; i < compiledPattern.length; ) {
int tag = compiledPattern[i] >>> 8;
int count = compiledPattern[i++] & 0xff;
if (count == 255) {
count = compiledPattern[i++] << 16;
count |= compiledPattern[i++];
}
switch (tag) {
case TAG_QUOTE_ASCII_CHAR:
if (start >= textLength || text.charAt(start) != (char)count) {
pos.index = oldStart;
pos.errorIndex = start;
return null;
}
start++;
break;
case TAG_QUOTE_CHARS:
while (count-- > 0) {
if (start >= textLength || text.charAt(start) != compiledPattern[i++]) {
pos.index = oldStart;
pos.errorIndex = start;
return null;
}
start++;
}
break;
default:
// Peek the next pattern to determine if we need to
// obey the number of pattern letters for
// parsing. It's required when parsing contiguous
// digit text (e.g., "20010704") with a pattern which
// has no delimiters between fields, like "yyyyMMdd".
boolean obeyCount = false;
// In Arabic, a minus sign for a negative number is put after
// the number. Even in another locale, a minus sign can be
// put after a number using DateFormat.setNumberFormat().
// If both the minus sign and the field-delimiter are '-',
// subParse() needs to determine whether a '-' after a number
// in the given text is a delimiter or is a minus sign for the
// preceding number. We give subParse() a clue based on the
// information in compiledPattern.
boolean useFollowingMinusSignAsDelimiter = false;
if (i < compiledPattern.length) {
int nextTag = compiledPattern[i] >>> 8;
if (!(nextTag == TAG_QUOTE_ASCII_CHAR ||
nextTag == TAG_QUOTE_CHARS)) {
obeyCount = true;
}
if (hasFollowingMinusSign &&
(nextTag == TAG_QUOTE_ASCII_CHAR ||
nextTag == TAG_QUOTE_CHARS)) {
int c;
if (nextTag == TAG_QUOTE_ASCII_CHAR) {
c = compiledPattern[i] & 0xff;
} else {
c = compiledPattern[i+1];
}
if (c == minusSign) {
useFollowingMinusSignAsDelimiter = true;
}
}
}
start = subParse(text, start, tag, count, obeyCount,
ambiguousYear, pos,
useFollowingMinusSignAsDelimiter, calb);
if (start < 0) {
pos.index = oldStart;
return null;
}
}
}
// At this point the fields of Calendar have been set. Calendar
// will fill in default values for missing fields when the time
// is computed.
pos.index = start;
Date parsedDate;
try {
parsedDate = calb.establish(calendar).getTime();
// If the year value is ambiguous,
// then the two-digit year == the default start year
if (ambiguousYear[0]) {
if (parsedDate.before(defaultCenturyStart)) {
parsedDate = calb.addYear(100).establish(calendar).getTime();
}
}
}
// An IllegalArgumentException will be thrown by Calendar.getTime()
// if any fields are out of range, e.g., MONTH == 17.
catch (IllegalArgumentException e) {
pos.errorIndex = start;
pos.index = oldStart;
return null;
}
return parsedDate;
}
private int matchString(String text, int start, int field, String[] data, CalendarBuilder calb)
{
int i = 0;
int count = data.length;
if (field == Calendar.DAY_OF_WEEK) {
i = 1;
}
// There may be multiple strings in the data[] array which begin with
// the same prefix (e.g., Cerven and Cervenec (June and July) in Czech).
// We keep track of the longest match, and return that. Note that this
// unfortunately requires us to test all array elements.
int bestMatchLength = 0, bestMatch = -1;
for (; i<count; ++i)
{
int length = data[i].length();
// Always compare if we have no match yet; otherwise only compare
// against potentially better matches (longer strings).
if (length > bestMatchLength &&
text.regionMatches(true, start, data[i], 0, length))
{
bestMatch = i;
bestMatchLength = length;
}
}
if (bestMatch >= 0)
{
calb.set(field, bestMatch);
return start + bestMatchLength;
}
return -start;
}
private int matchString(String text, int start, int field,
Map<String,Integer> data, CalendarBuilder calb) {
if (data != null) {
// TODO: make this default when it's in the spec.
if (data instanceof SortedMap) {
for (String name : data.keySet()) {
if (text.regionMatches(true, start, name, 0, name.length())) {
calb.set(field, data.get(name));
return start + name.length();
}
}
return -start;
}
String bestMatch = null;
for (String name : data.keySet()) {
int length = name.length();
if (bestMatch == null || length > bestMatch.length()) {
if (text.regionMatches(true, start, name, 0, length)) {
bestMatch = name;
}
}
}
if (bestMatch != null) {
calb.set(field, data.get(bestMatch));
return start + bestMatch.length();
}
}
return -start;
}
Si la clase DateFormat el formato de fecha / hora, y no puede cumplir con los requisitos, es necesario utilizar una subclase --SimpleDateFormat clase DateFormat.
SimpleDateFormat es una manera local relacionada con la clase concreta de formatear y analizar las fechas, lo que permite el formateo (fecha → de texto), análisis (texto → fecha) y la normalización. SimpleDateFormat modo se puede seleccionar de manera que cualquier fecha / formato de tiempo definido por el usuario.
SimpleDateFormat clase tiene los siguientes 3 constructor principal.
- SimpleDateFormat (): utilizando el formato predeterminado por defecto y SimpleDateFormat estructura local.
- SimpleDateFormat (Patrón de encordado): con el formato especificado y la estructura regional predeterminada SimpleDateF ormato.
- SimpleDateFormat (Patrón de encordado, Locale locale): Ormat SimpleDateF con el formato de configuración especificado locale y especificar.

Escribir programas en Java, utilizando la clase SimpleDateFormat a formato e imprimir la fecha actual, el formato de fecha es "xxxx xx xx xxx días por semana minutos xx xx punto de segundos", códigos específicos son los siguientes:
import java.text.SimpleDateFormat;
import java.util.Date;
public class Test13
{
public static void main(String[] args)
{
Date now=new Date(); //创建一个Date对象,获取当前时间
//指定格式化格式
SimpleDateFormat f=new SimpleDateFormat("今天是 "+"yyyy 年 MM 月 dd 日 E HH 点 mm 分 ss 秒");
System.out.pnntln(f.format(now)); //将当前时间袼式化为指定的格式
}
}Hoy en día el 15 de octubre, 2018 9:00 Lunes 26 minutos y 23 segundos
Obtener la hora actual
import hunter.text.SimpleDateFormat;
import java.util.Date;
public class Main{
public static void main(String[] args){
SimpleDateFormat sdf = new SimpleDateFormat();// 格式化时间
sdf.applyPattern("yyyy-MM-dd HH:mm:ss a");// a为am/pm的标记
Date date = new Date();// 获取当前时间
System.out.println("现在时间:" + sdf.format(date)); // 输出已经格式化的现在时间(24小时制)
}
}Las marcas de tiempo convertida en tiempo
import hunter.text.SimpleDateFormat;
import java.util.Date;
public class Main{
public static void main(String[] args){
Long timeStamp = System.currentTimeMillis(); //获取当前时间戳
SimpleDateFormat sdf=new SimpleDateFormat("yyyy-MM-dd");
String sd = sdf.format(new Date(Long.parseLong(String.valueOf(timeStamp)))); // 时间戳转换成时间
System.out.println(sd);
}
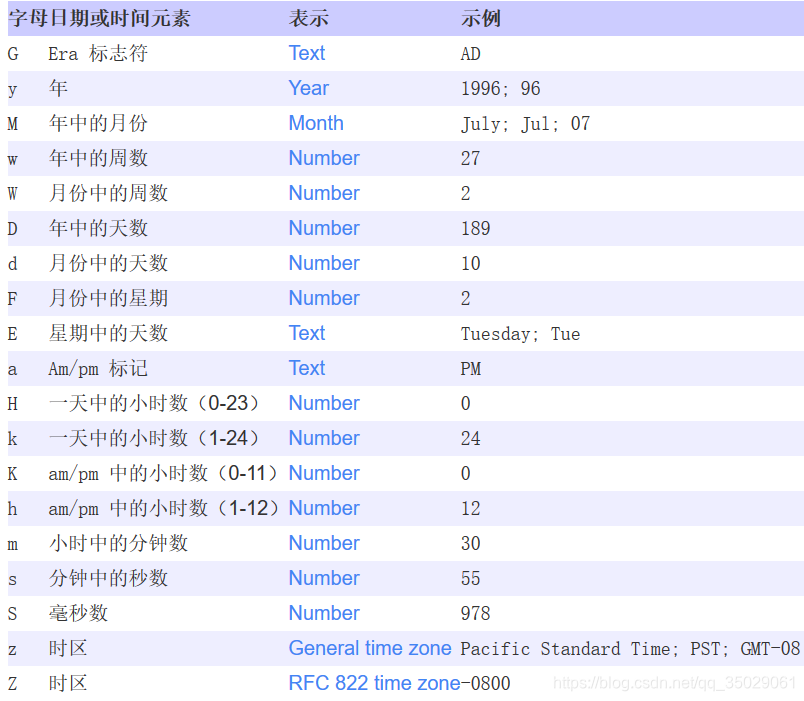
}
package dates;
import java.text.DateFormat;
import java.text.ParseException;
import java.text.SimpleDateFormat;
import java.util.Date;
import java.util.Locale;
public class TestSimpleDateFormat {
public static void main(String args[]) throws ParseException {
TestSimpleDateFormat test = new TestSimpleDateFormat();
test.testDateFormat();
}
public void testDateFormat() throws ParseException {
//创建日期
Date date = new Date();
//创建不同的日期格式
DateFormat df1 = DateFormat.getInstance();
DateFormat df2 = new SimpleDateFormat("yyyy-MM-dd hh:mm:ss EE");
DateFormat df3 = DateFormat.getDateInstance(DateFormat.FULL, Locale.CHINA); //产生一个指定国家指定长度的日期格式,长度不同,显示的日期完整性也不同
DateFormat df4 = new SimpleDateFormat("yyyy年MM月dd日 hh时mm分ss秒 EE", Locale.CHINA);
DateFormat df5 = new SimpleDateFormat("yyyy-MM-dd hh:mm:ss EEEEEE", Locale.US);
DateFormat df6 = new SimpleDateFormat("yyyy-MM-dd");
DateFormat df7 = new SimpleDateFormat("yyyy年MM月dd日");
//将日期按照不同格式进行输出
System.out.println("-------将日期按照不同格式进行输出------");
System.out.println("按照Java默认的日期格式,默认的区域 : " + df1.format(date));
System.out.println("按照指定格式 yyyy-MM-dd hh:mm:ss EE ,系统默认区域 :" + df2.format(date));
System.out.println("按照日期的FULL模式,区域设置为中文 : " + df3.format(date));
System.out.println("按照指定格式 yyyy年MM月dd日 hh时mm分ss秒 EE ,区域为中文 : " + df4.format(date));
System.out.println("按照指定格式 yyyy-MM-dd hh:mm:ss EE ,区域为美国 : " + df5.format(date));
System.out.println("按照指定格式 yyyy-MM-dd ,系统默认区域 : " + df6.format(date));
//将符合该格式的字符串转换为日期,若格式不相配,则会出错
Date date1 = df1.parse("07-11-30 下午2:32");
Date date2 = df2.parse("2007-11-30 02:51:07 星期五");
Date date3 = df3.parse("2007年11月30日 星期五");
Date date4 = df4.parse("2007年11月30日 02时51分18秒 星期五");
Date date5 = df5.parse("2007-11-30 02:51:18 Friday");
Date date6 = df6.parse("2007-11-30");
System.out.println("-------输出将字符串转换为日期的结果------");
System.out.println(date1);
System.out.println(date2);
System.out.println(date3);
System.out.println(date4);
System.out.println(date5);
System.out.println(date6);
}
}
