1. Create a schema
These designs provide a way to hide the pattern created while creating a logical object, instead of using the new direct operator to instantiate an object. This makes the program more flexible when determining which objects need to be created for a given instance.
(// namely how to object)
- Factory pattern (Factory Pattern)
- Abstract Factory (Abstract Factory Pattern)
- Singleton (Singleton Pattern)
- Builders mode (Builder Pattern)
- Prototype model (Prototype Pattern)
2. Structural model
These design patterns focus on a combination of classes and objects. The concept of inheritance, and interfaces are used in combination define a new combined object function is obtained
(Ie // objects and who related)
- Adapter mode (Adapter Pattern)
- Bridge mode (Bridge Pattern)
- Filter mode (Filter, Criteria Pattern)
- Combined mode (Composite Pattern)
- Decorator (Decorator Pattern)
- Appearance Model (Facade Pattern)
- Flyweight (Flyweight Pattern)
- Agent mode (Proxy Pattern)
3. behavioral patterns
These design patterns attention to the interaction between objects
(// ie do between objects and object)
- Chain of Responsibility pattern (Chain of Responsibility Pattern)
- Command Mode (Command Pattern)
- Interpreter pattern (Interpreter Pattern)
- Iterator pattern (Iterator Pattern)
- Intermediary model (Mediator Pattern)
- Memo mode (Memento Pattern)
- The observer pattern (Observer Pattern)
- Mode state (State Pattern)
- Null Object mode (Null Object Pattern)
- Strategy Mode (Strategy Pattern)
- Template mode (Template Pattern)
- Visitor pattern (Visitor Pattern)
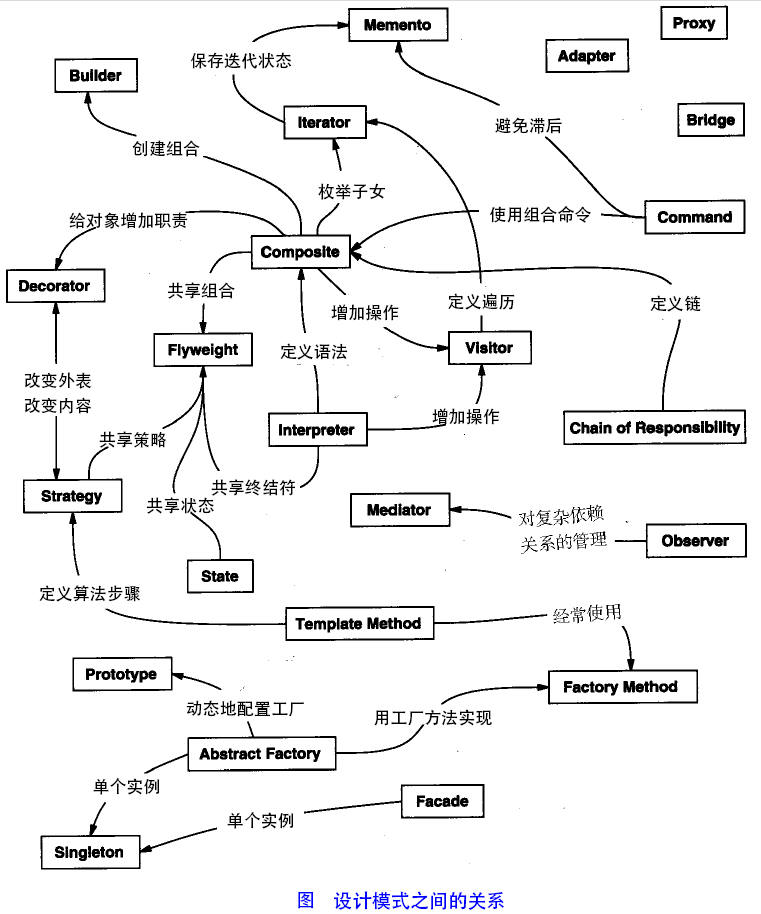
设计模式的六大原则
1、开闭原则(Open Close Principle)
开闭原则的意思是:对扩展开放,对修改关闭。在程序需要进行拓展的时候,不能去修改原有的代码,实现一个热插拔的效果。简言之,是为了使程序的扩展性好,易于维护和升级。想要达到这样的效果,我们需要使用接口和抽象类,后面的具体设计中我们会提到这点。
2、里氏代换原则(Liskov Substitution Principle)
里氏代换原则是面向对象设计的基本原则之一。 里氏代换原则中说,任何基类可以出现的地方,子类一定可以出现。LSP 是继承复用的基石,只有当派生类可以替换掉基类,且软件单位的功能不受到影响时,基类才能真正被复用,而派生类也能够在基类的基础上增加新的行为。里氏代换原则是对开闭原则的补充。实现开闭原则的关键步骤就是抽象化,而基类与子类的继承关系就是抽象化的具体实现,所以里氏代换原则是对实现抽象化的具体步骤的规范。
3、依赖倒转原则(Dependence Inversion Principle)
这个原则是开闭原则的基础,具体内容:针对接口编程,依赖于抽象而不依赖于具体。
4、接口隔离原则(Interface Segregation Principle)
这个原则的意思是:使用多个隔离的接口,比使用单个接口要好。它还有另外一个意思是:降低类之间的耦合度。由此可见,其实设计模式就是从大型软件架构出发、便于升级和维护的软件设计思想,它强调降低依赖,降低耦合。
5、迪米特法则,又称最少知道原则(Demeter Principle)
最少知道原则是指:一个实体应当尽量少地与其他实体之间发生相互作用,使得系统功能模块相对独立。
6、合成复用原则(Composite Reuse Principle)
合成复用原则是指:尽量使用合成/聚合的方式,而不是使用继承
PS:
开闭原则:实现热插拔,提高扩展性。
里氏代换原则:实现抽象的规范,实现子父类互相替换;
Rely on the reverse principle: an interface for programming, basic principles of opening and closing;
Interface segregation principle: reduce the coupling, the interface design alone, isolated from each other;
Demeter, also known as the principle of do not know: functional modules to be independent;
Synthesis multiplexing principle: try polymerization, in combination, instead of inheriting
The above concepts from major sites, copy summary of the book, invasion delete ~
2019-6-17
