Both services provided by the network layer 1
The network layer should provide the kind of service it to the transport layer? It is connection-oriented or connectionless it? This is actually responsible for reliable delivery issues by the network or end systems, the birth of two services on the basis of this problem, namely the virtual circuit services and packet data services.
1.2 VC service
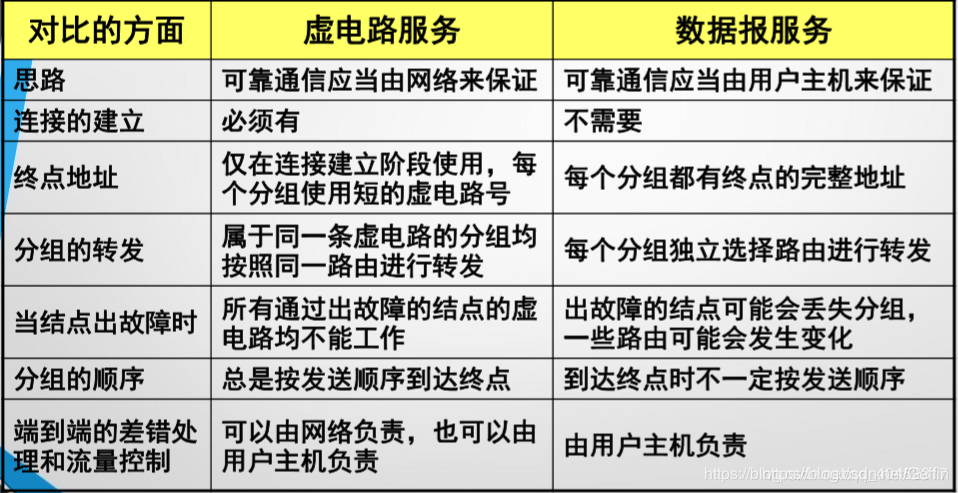
VC services and telecommunications networks similar to the use of connection-oriented communication, so that the network is responsible for reliable delivery.
The principle is to first establish communication before the virtual circuit to ensure that all network resources needed to communicate both sides. If we use a network protocol for reliable transmission, so that the packet can be transmitted sequentially to reach the terminal without errors, no loss, will not be repeated.
VC is a logical connection, this is only one virtual circuit represents a logical connection, the packet connection are transferred in the store and forward logic along this way, and not really a physical connection is established.
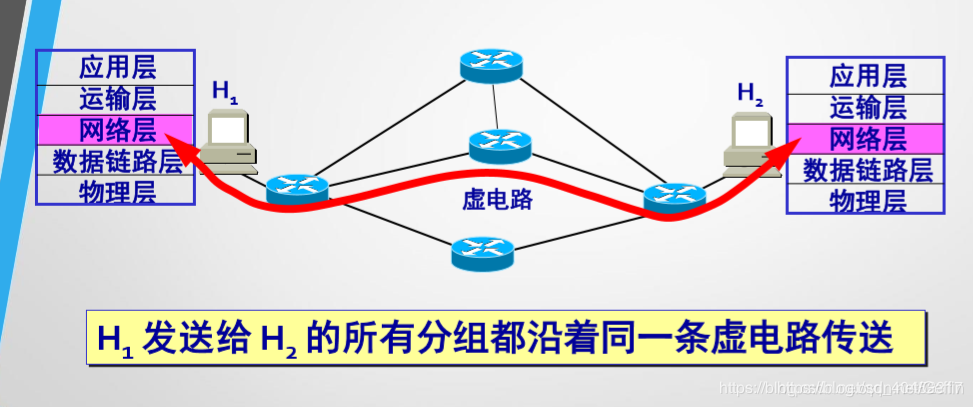
Virtual circuit working steps:
- Establish a connection, establishing a virtual circuit packet switching, network resources to ensure that the two communication parties.
- Both sides send packets along the virtual circuit has been established.
- The first part of the destination host does not need to fill in the complete address of the packet, simply fill out this number of virtual circuits, thus reducing the overhead of the packet. If this re-way communication using a network protocol for reliable transmission, so that the packet can be transmitted sequentially to reach the end without error, of course, not lost, will not be repeated.
- At the end of communication, releasing the established virtual circuit.
1.3 Datagram Service
On the Internet and the telecommunications network design uses a completely different idea, reliable communications to be guaranteed by the end system (host to host).
The idea is as follows:
- The network layer up only provide simple, flexible, connectionless datagram service to do its utmost to deliver. Network does not need to establish a connection when transmitting a packet. Each packet (i.e. IP data packets) transmitted independently, regardless of the packet (not numbered) in its front.
- The network layer does not provide a commitment to service quality. That packet is transmitted, it may be wrong, lost, duplicated or out of order, of course, does not guarantee packet delivery time.
If desired reliable communication network should be responsible for reliable delivery transport layer, e.g. error handling, flow control and the like.
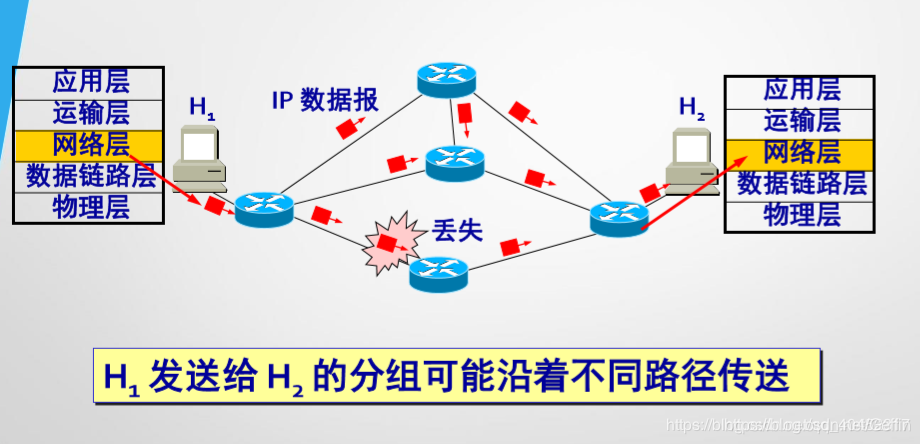
The difference between the two is 1.4
2 ARP protocol
2.1 What is the ARP protocol?
ARP, that is Address Resolution Protocol, for the ARP. Which is a function of the target host IP address, searches the MAC address of the target host, in order to ensure smooth communication. Each equipped with TCP / IP protocol computer has a ARP cache table, the table of IP address and MAC address is one to one.
2.2 Why do we need ARP protocol?
We are concerned at the network layer is an IP address, MAC address was our concern at the data link layer. In a network, the communication packet based on the OSI model data package from the top down, when the network layer regardless of which protocol to use, the actual data frame is transmitted in the network link we must use the MAC address, so we need to obtain the object of the ARP protocol MAC address of the host to complete the package and forwarding data.
2.3 ARP Address Resolution
Each host has an ARP cache, IP address, each of the hosts and routers on the LAN which has the MAC address mapping table. When the host A transmits an IP datagram to be to present a host B on the LAN, the IP address can view the presence or absence of the first host B in its ARP cache. If, you can find the corresponding MAC address, and then writes the MAC address of the MAC frame, then the frame is sent to the hardware MAC address through the LAN.
In fact, popular to say, the ARP protocol logic address (IP address) to a physical address (MAC address) mapping.
2.4 ARP works
We make the following assumptions, at the same LAN, we know the IP address and MAC address of host A, host B knows the IP address of Host A needs to communicate with Host B, we now need to know the MAC address of host B. It comprises the following steps:
- When sending data, the host A to find its own ARP cache table for the destination IP address directly if the MAC address of host B, which was written in the frame can be transmitted. Otherwise, the host A will send a broadcast on the network, ask the host B MAC address to all hosts on the same subnet.
- After the host receives the other broadcast request, it compares its own IP address and the IP address of Host A requests are the same, different, directly discarding the request, it will send the same response to an ARP message, the IP address and MAC address of host B It tells the host in the form of unicast A.
2.5 Note
ARP is to solve the problem of mapping IP address of the host or router on the same LAN and MAC address. If you are looking for host and source host not on the same local area network, then they would find one in the ARP MAC address of a router on the local LAN, and sends the packet to the router, so the router forwards the packet to the next network, the rest of the work is done by the next network.
3 ICMP protocol
3.1 What is the ICMP protocol?
ICMP, namely Internet Control Message Protocol, Internet Control Message Protocol. Because of its work based on the IP protocol, it is a network layer protocol. ICMP protocol functional reasons, to confirm the IP packet destination address and the notification successfully reached during transmission of the IP packet is discarded.
3.2 ICMP messages
ICMP messages can be divided into two categories:
- Error message: Error message notification causes of errors (traceroute)
- Query message: for the diagnosis query message (ping)
3.3 ICMP packet format
ICMP following positions:

ICMP is transmitted within IP datagrams, the IP header followed by packet. IP header is 20 bytes in the case of FIG IP packet header without optional part, if the IP header contains optional part is greater than 20 bytes.
ICMP message format is as follows:
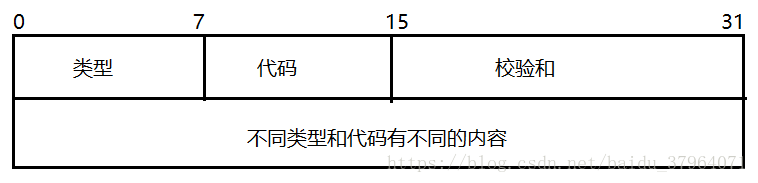
8-bit type field and a 8-bit code field together determine one kind of ICMP packet type, packet checksum for checking whether an error has occurred during transmission.
3.4 Common ICMP packets - the corresponding request
Echo Reply Type field is 0, the echo request type field is 8. ping operations include these two types of ICMP packets. Specific process is as follows: a host sends an ICMP message type field value to a node 8, if no abnormality on the way (if not discarded route, the target does not respond to ICMP or transmission failure), the target returns a value of type field 0 ICMP packets, indicating that host exist.
4 Unicast, Multicast difference (multicast) and broadcast
- Unicast: the popular talk is one to one. Receiving and transmission of information is performed between only two nodes. Unicast has been widely used in the network, most of the data on the network are unicast form of transmission.
- Multicast: the popular talk is one to many. Not only can be achieved once all target nodes transmit data, but also can achieve the purpose of transferring data only to a specific object. The classic example is the use of multicast online video conference, if unicast way, the number of destination node will send many times, inefficient, if broadcast way, data can not distinguish between the specific receiving objects.
- Broadcasting: the popular talk is a pair of all. Broadcast generally only spread in the same subnet, the IP address is 255.255.255.255, the IP address on behalf of all the addresses within the same subnet.
Reference: 1-the ARP protocol
Network Protocol - ICMP protocol (1) message format
ICMP protocol detailed
computer network (4.1) the network layer - both services provided by the network layer
