Reprint: traditional target detection algorithm of DPM
Introduced earlier about HOG, HOG has a drawback: difficult to handle the occlusion problem, human pose excessive range of motion or change the direction of an object can be readily detected .
Following the 2005 HOG proposed, DPM model after draws HOG has also been put forward but also achieved good results.
DPM Overview
The DPM ( Deformable the Model Part ), as the name of the component model can be deformed, a detection algorithm based component, i.e., it is intended that seen. The model consists of the Great God Felzenszwalb in 2008 proposed and published a series of cvpr, NIPS. And also won in 2010, PASCAL VOC 's "Lifetime Achievement Award."
DPM algorithm uses the HOG feature improved, SVM classifier and the sliding window (Sliding Windows) detect thoughts, for multi-viewing angle objective, using a strategy multi-component (Component), and for the deformation problem target itself, adopted on FIG structure (Pictorial structure) component modeling strategy. Further, the sample belongs to the category of the model, the position or the like member as a latent variable model (Latent Variable), multi-instance learning (Multiple-instance Learning) be automatically determined.
DPM features
DPM detection model
DPM detection process
latent SVM
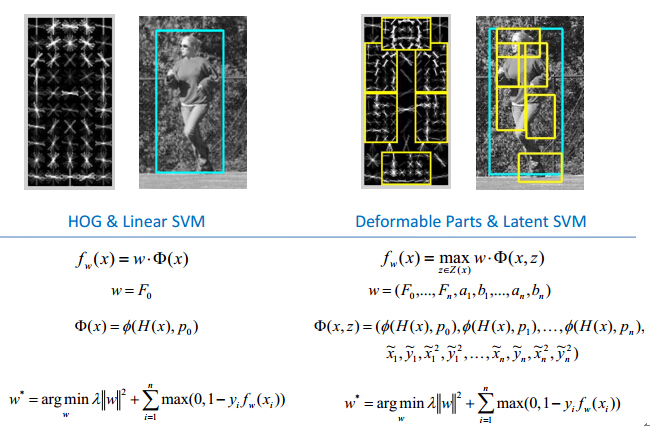
Traditional Hog + DPM + LatentSVM difference SVM and as shown in the above formula.
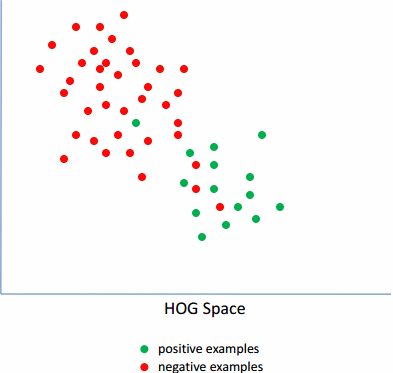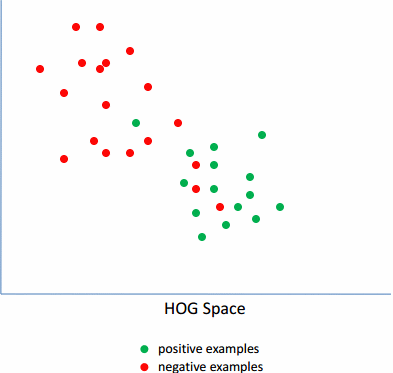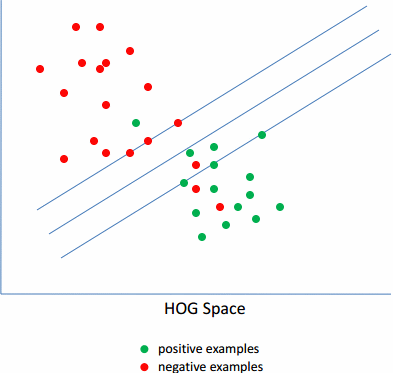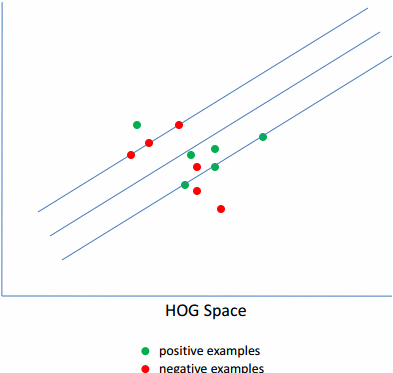
由于,训练的样本中,负样本集肯定是100%的准确的,而正样本集中就可能有噪声。因为,正样本的标注是人工进行的,人是会犯错的,标注的也肯定会有不精确的。因此,需要首先去除里面的噪声数据。而对于剩下的数据,里面由于各种角度,姿势的不一样,导致训练的模型的梯度图也比较发散,无规则。因此需要选择其中的具有相同的姿势的数据,即离正负样本的分界线最近的那些样本,将离分界线很近的样本称为Hard-examples,相反,那些距离较远的称为Easy-examples。
实际效果图如下图所示:
Latent SVM接下来有时间独立开一篇去整理学习一下。
优缺点
DPM算法的步骤:
1、产生多个模板,整体模板以及不同的局部模板;
2、拿这些不同的模板同输入图像“卷积”产生特征图;
3、将这些特征图组合形成融合特征;
4、对融合特征进行传统分类,回归得到目标位置。
DPM算法优点:
1、方法直观简单;
2、运算速度块;
2、适应动物变形;
DPM算法缺点:
1、性能一般
2、激励特征人为设计,工作量大;
这种方法不具有普适性,因为用来检测人的激励模板不能拿去检测小猫或者小狗,所以在每做一种物件的探测的时候,都需要人工来设计激励模板,为了获得比较好的探测效果,需要花大量时间去做一些设计,工作量很大。
3、无法适应大幅度的旋转,稳定性很差;
前面官方的话讲了一大堆,简单概括一下整体流程吧
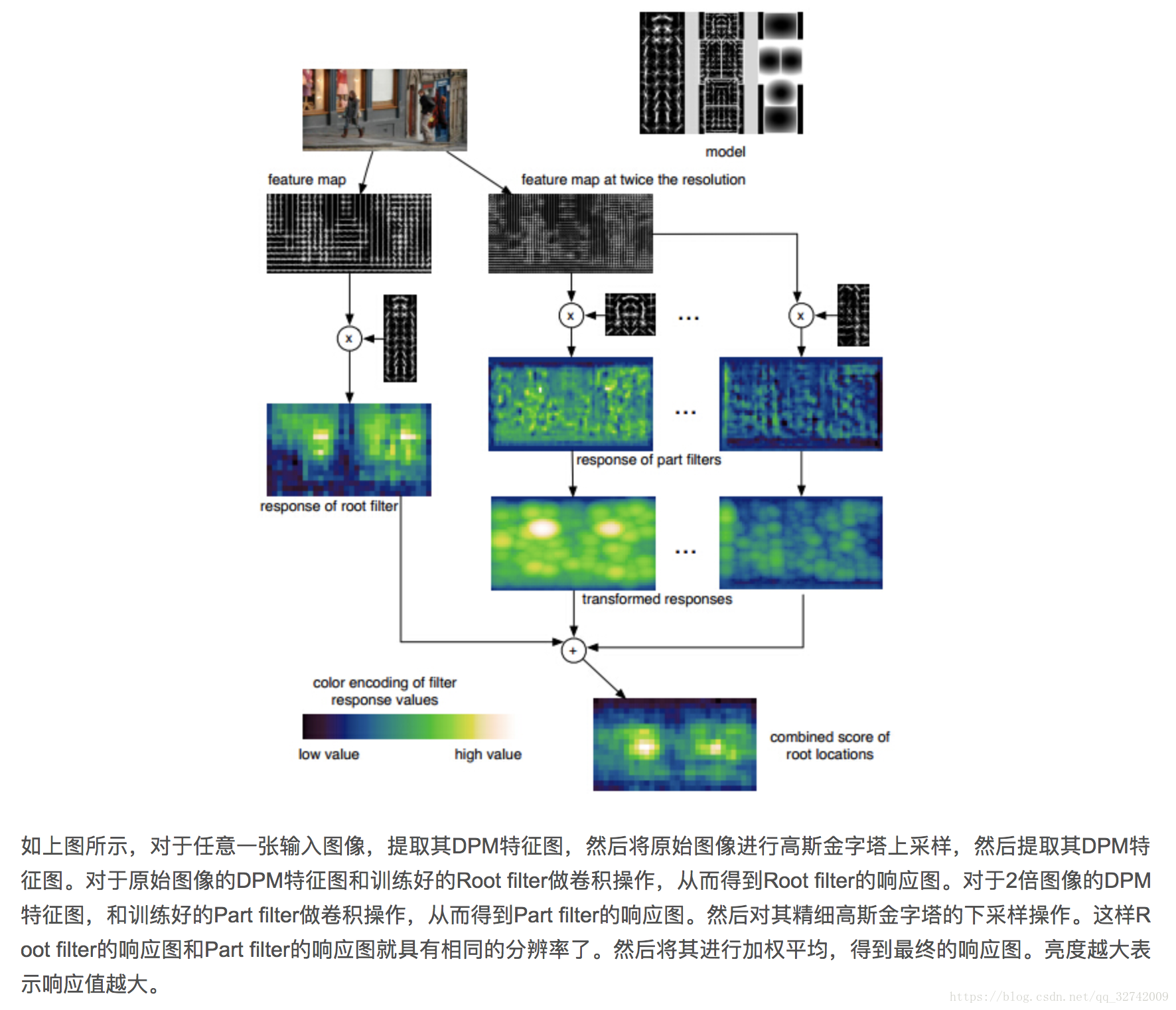
- 首先要有根模型(root filter)和若干部件模型(part filter)和部件模型的偏离损失。这些东西就是通过已有的人体,四肢等样本提取HOG特征然后经过svm训练而来的。
- 用root filter提取原始图像的DMP特征图,再对DMP特征图用root filter和part filter计算响应图。(实际上就是一个模版匹配)
- 加权平均root的和part的,得到最终的融合特征图
- 对融合特征进行传统分类,回归得到目标位置。
DPM算法思想:输入一幅图像,对图像提取图像特征,针对某个物件制作出相应的激励模板,在原始的图像中计算,得到该激励效果图,根据激励的分布,确定目标位置。
制作激励模板就相当于人为地设计一个卷积核,一个比较复杂的卷积核,拿这个卷积核与原图像进行卷积运算得到一幅特征图。比如拿一个静止站立的人的HOG特征形成的卷积核,与原图像的梯度图像进行一个卷积运算,那么目标区域就会被加密。
那么说到这里就会出现一个问题,人在图像中可能有各种的姿态,比如躺着,趴着,坐着等等,我们只用一个静止站立状态的人的激励模板去做探测就会失败。也就是说图像中的物件可能会发生形变,那么我们用固定的激励模板去探测目标物件的时候就不再适用,那么该如何解决这一问题呢,这就引出了局部模板,也就是说,我们不做一个整体的人的激励模板,转而去做人的部分组件的模板,比如头、胳膊、腿等,其实这就是DPM算法。
再概括一下,HOG的特征提取比较死板,一定要是一个人,这个人还只能是特定的姿态比如站立,动作幅度改变不能太大。而DMP就是先检测整个人,再检测四肢,然后综合两者的信息去判断。