Fifth, the history of the development of machine learning
1, machine learning stage of development
(1) warm period laid the foundation: the mid-1950s, early 1960s
(2) cool period of stagnation: the mid-1960s to the late 1970s
(3) to regain hope of a renaissance: the late 1970s to the mid-1980s
(4) molding machine learning modern period: the 20th century, the early 1990s to the early 21st century
(5) a boom period shine: the beginning of the 21st century so far
2, an important figure in the history of the development of machine learning

3, the structure of neurons

Let the machine like people to learn, we must first understand the structure of the brain's neurons.
A biological neuron cell bodies (Soma), dendritic (Dendrites), synapse (Synapse) and axonal (Axon) and the like.
Neuronal cell bodies in the central metabolism of the cell body has many dendrite growth generally, called dendrites, which is the main receiver neurons. The cell body further extending a tubular fibrous tissue, called axons. Dendritic biological signal input neuron is connected to other neurons; axons signal output neuron is connected to other neurons dendrites.
Biological neuron has two states: excitation and inhibition, biological neurons are usually in the inhibition of axon no input, when the biological neuron dendrites to a certain extent the input signal, exceeds a certain threshold, the biological neurons inhibiting state to the excited state, and sends a signal to the axon of a biological neuron. Axon conduction mainly information, the direction of conduction is passed from the starting point toward the end of the axon. Typically, the separation of many axon terminal endings, they are the same after a biological neuron dendrites configuration mechanism called synapses. Wherein a front tip of axons called pre-synaptic membrane, after a biological neuron dendrites called a post synaptic membrane; slit space between the two front film and the rear film called projection the contact gap, after the biological information of the previous neuron axons reached its tip, an impact on the back of each neuron through synapses.
4、机器学习巨匠及算法发展历程
(1)唐纳德·赫布(1904-1985)是加拿大著名生理心理学家。Hebb于1949年基于神经心理学的学习机制开启机器学习的第一步,此后被称为Hebb学习规则。
![]()
hebb是一种无监督学习规则。Hebb的理论认为在同一时间被激发的神经元间的联系会被强化。比如,铃声响时一个神经元被激发,在同一时间食物的出现会激发附近的另一个神经元,那么这两个神经元间的联系就会强化,从而记住这两个事物之间存在着联系。相反,如果两个神经元总是不能同步激发,那么它们间的联系将会越来越弱。
(2)1950年,阿兰·图灵创造了图灵测试来判定计算机是否智能。图灵测试认为,如果一台机器能够与人类展开对话(通过电传设备)而不能被辨别出其机器身份,那么称这台机器具有智能。这一简化使得图灵能够令人信服地说明“思考的机器”是可能的。
(3)1952年,IBM 的 Arthur Samuel(被誉为“机器学习之父”)在《Some Studies in Machine Learning Using the Game of Checkers》的论文中,定义并解释了一个新词——机器学习(Machine Learning,ML)。将机器学习非正式定义为”在不直接针对问题进行编程的情况下,赋予计算机学习能力的一个研究领域”。他还设计了一款可以学习的西洋跳棋程序。它能通过观察棋子的走位来构建新的模型,并用其提高自己的下棋技巧。Samuel 和这个程序进行多场对弈后发现,随着时间的推移程序的棋艺变得越来越好。
(4)1957年,罗森 布纳特(Rosenblatt)发明了感知机(或称感知器,Perceptron),是神经网络的雏形,同时也是支持向量机的基础,在当时引起了不小的轰动。感知机是二类分类的线性分类模型,其输入为实例的特征向量,输出为实例的类别,取+1和-1二值。感知机对应于输入空间(特征空间)中将实例划分为正负两类的分离超平面,属于判别模型。感知机学习旨在求出将训练数据进行线性划分的分离超平面。

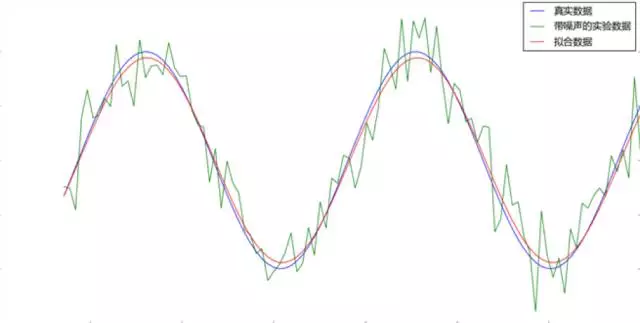
(5)1960年,Widrow(维德罗)发明了Delta学习规则,它是一种简单的有监督学习算法,即如今的最小二乘问题,该算法根据神经元的实际输出与期望输出差别来调整连接权。该算法被应用到感知机中,并且得到了一个极好的线性分类器。
![]()
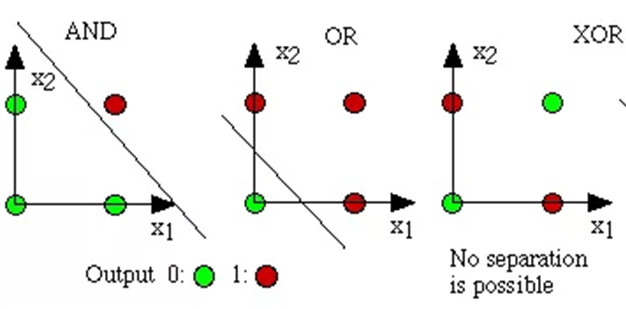
(6)1969年,马文·明斯基(Minskey)将感知机推到最高顶峰。他提出了著名的XOR问题和感知机数据线性不可分的情形,论证了感知器在类似XOR问题的线性不可分数据的无力,以至于其后十年被称为“冷静时期”,给感知机画上了一个逗号,以洪荒之力将如火如荼将的ML暂时封印了起来,Rosenblatt在这之后两年郁郁而终与此也不无关系。
(7)1970年,Seppo Linnainmaa(林纳因马)首次完整地叙述了自动链式求导方法(Automatic Differentiation,AD),是著名的反向传播算法(Back Propagation,BP)的雏形,但在当时并没有引起重视。

(8)1974年,Werbos(伟博斯)首次提出把BP算法的思想应用到神经网络,也就是多层感知机(Multilayer Perception,MLP),MLP或者称为人工神经网络(Artificial Neural Network,ANN),是一个带有单隐层的神经网络。

事实上,这个时期整个AI领域都遭遇了瓶颈。当时的计算机有限的内存和处理速度不足以解决任何实际的AI问题。要求程序对这个世界具有儿童水平的认识,研究者们很快发现这个要求太高了:1970年没人能够做出如此巨大的数据库,也没人知道一个程序怎样才能学到如此丰富的信息。
感知机也成为单个神经元结构,神经元也成为单层感知机。
(9)1980年,在美国的卡内基梅隆大学(CMU)召开了第一届机器学习国际研讨会,标志着机器学习研究已在全世界兴起。
(10)1985-1986年,Rumelhart,Hinton等许多神经网络学者成功实现了实用的BP算法来训练神经网络,并在很长一段时间内BP都作为神经网络训练的专用算法。

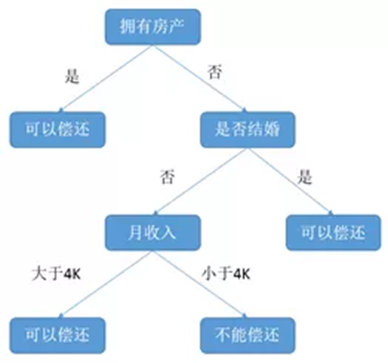
(11)1986年,昆兰提出了另一个同样著名的ML算法:决策树算法(ID3),决策树作为一个预测模型,代表的是对象属性与对象值之间的一种映射关系,而且紧随其后涌现出了很多类似或者改进算法,如ID4,回归树,CART等。
例:银行根据客户的房产情况,婚姻状况以及收入状况来评估客户偿还贷款的能力。
(12)1995年,Yan LeCun提出了卷积神经网络(CNN),受生物视觉模型的启发,通常有至少两个非线性可训练的卷积层,两个非线性的固定卷积层,模拟视觉皮层中的V1和V2中的Simple cell和Complex cell,在手写字识别等小规模问题上,取得了当时世界最好结果,但是在大规模问题上表现不佳。(V1区负责边缘检测,V2区负责形状检测。局部连接,权值共享)

(13)1995年,Vapnik和Cortes(瓦普尼克和科尔特斯)欲找到具有“最大间隔”的决策边界,提出了强大的支持向量机(SVM),主要思想是用一个分类超平面将样本分开从而达到分类效果,具有很强的理论论证和实验结果。

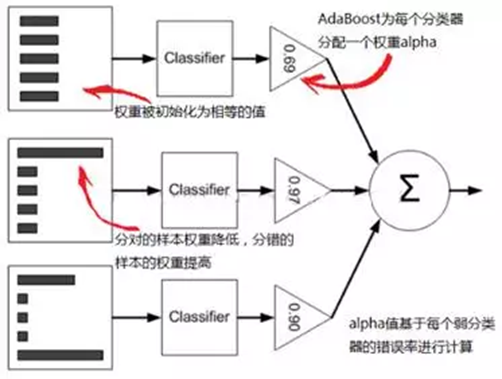
(14) 1997年,Freund和Schapire(弗洛恩德和夏皮雷)提出了另一个坚实的ML模型AdaBoost(集成学习),该算法最大的特点在于组合弱分类器形成强分类器,可以形象地表述为:“三个臭皮匠赛过诸葛亮”,分类效果比其它强分类器更好。
(15)2001年,随着核方法的提出,SVM大占上风,它的主要思想就是通过将低维数据映射到高维,从而实现线性可分。
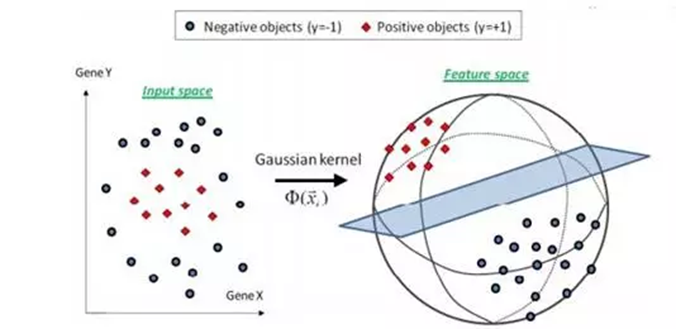
(16) 2006年,Hinton(辛顿)和他的学生在《Nature》上发表了一篇文章,提出的深度置信网络(Deep Belief Network,DBN)开启了深度学习新纪元。
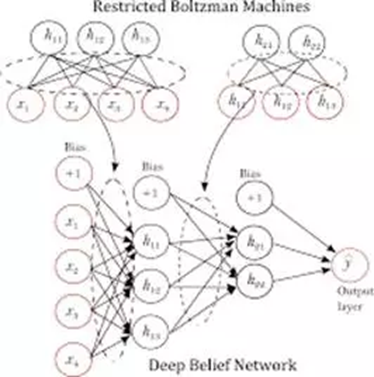
深度学习主要算法:
(1)CNN:卷积神经网络
(2)RNN:循环神经网络
(3)ResNet:残差网络
六、应用现状
机器学习中比较活跃的四大应用领域:
(1)数据挖掘,发现数据之间的关系
(2)计算机视觉,像人一样看懂世界
(3)自然语言处理,像人一样看懂文字
(4)机器人决策,像人一样具有决策能力