Step 1: Install cnpm install vue-router --save
The basic syntax routing configuration
index.js introduced next router
import Vue from "vue"; import Router from "vue-router"; import HelloWorld from "@/components/HelloWorld"; The introduction of demand will be written under the routing lazy load
export default new Router({ routers: [{ path: "router", component: '', meta: {} children: [{ path: 'router1', component: Router1 }, { path: 'router2', component: Router2 } ] }] })
In the main.js
Router from Import './router' // introduced // use the new new Vue ({ el: '#app', router, store, components: { App }, template: '<App/>' })
The formal aspects of the code -
Components:
<template>
<div class="router">
<H3> route using substantially </ h3>
</div>
</template>
<script>
export default {
name: "router",
data() {
return {};
}
};
</script>
<style scoped>
</style>
Route index.js:
import Vue from "vue"; import Router from "vue-router"; //组件 import router from "@/components/router"; Vue.use(Router); export default new Router({ routes: [{ path: "/router", component: router, }] });
Jump route
Using the label bound to the router-link through to top
<Router-link to = "/ lifeCycle"> life cycle </ router-link> direct replication <Router-link: to = "vuex"> vuex </ router-link> to the variable data() { return { vuex: "/vuex", }; }
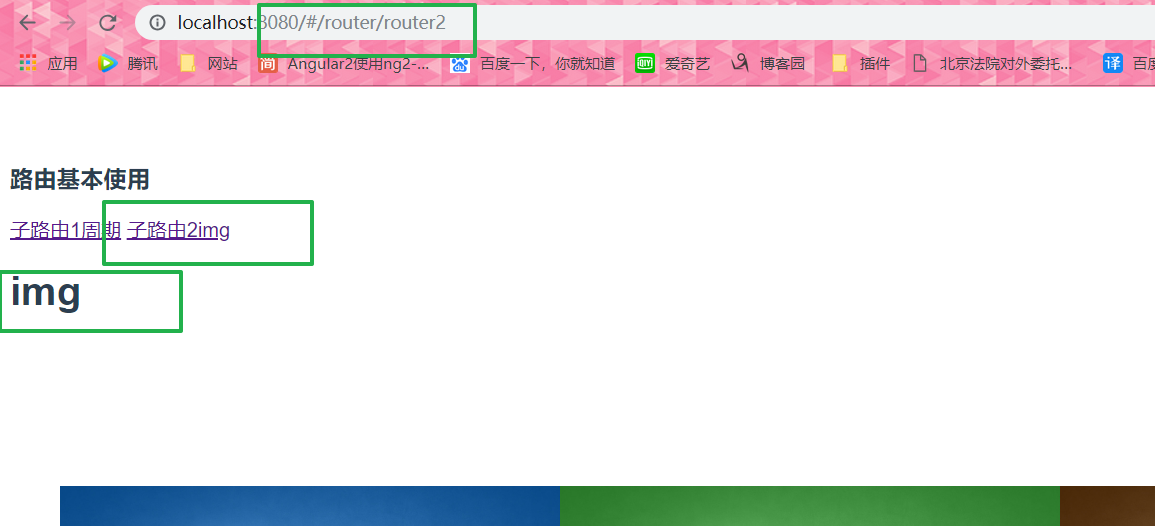
Defined sub-routes
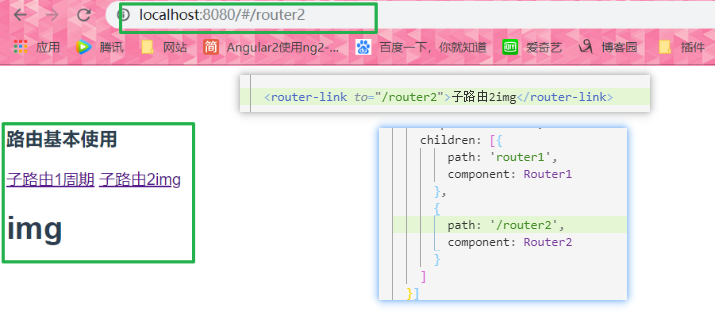
<Router-link to = "/ router / router1"> Route 1 sub cycle </ router-link> <router-link to="/router2">子路由2img</router-link> <router-view></router-view>
routes: [{ path: "/router", component: router, children: [{ path: 'router1', component: Router1 }, { path: 'router2', component: Router2 } ] }]
Zi Chinese and do not add '/' if the increase is a jump from the root path
Route passing parameters
1. The routing configuration acquisition: . The this $ route.params.id
Direct write:
<-Link to Router = "/ Router / Router2 / 11111"> sub-route 2img </ router-link> must not forget the routing path: 'router2 /: Name',
Or script:
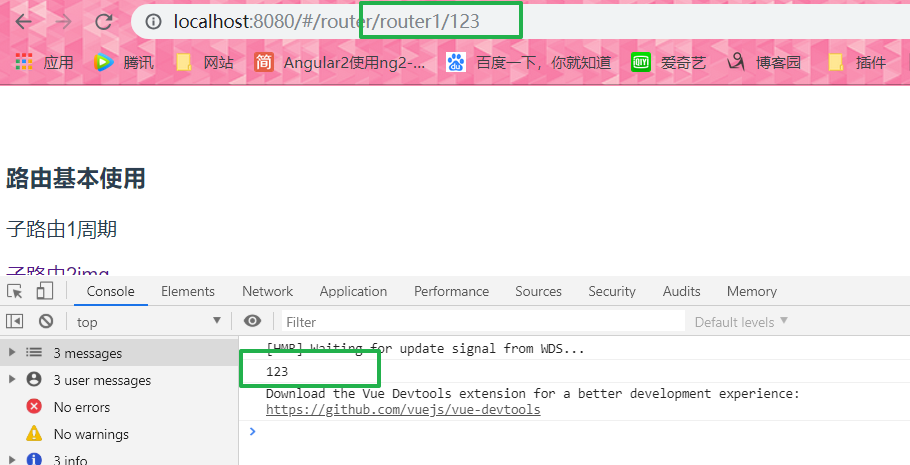
<p @ click = "getDescribe ( '123')"> Route 1 sub cycle </ P> Methods: { getDescribe(id) { this.$router.push({ path: `/router/router1/${id}` }); } }, mounted() { console.log(this.$route.params.id); }
2.params 获取: this.$route.params.id
<p @click="getDescribe('222222')">子路由1周期</p>
methods: {
getDescribe(id) {
this.$router.push({
name: "router1",
params: {
id: id
}
});
}
},
mounted() {
console.log(this.$route.params.id);
}
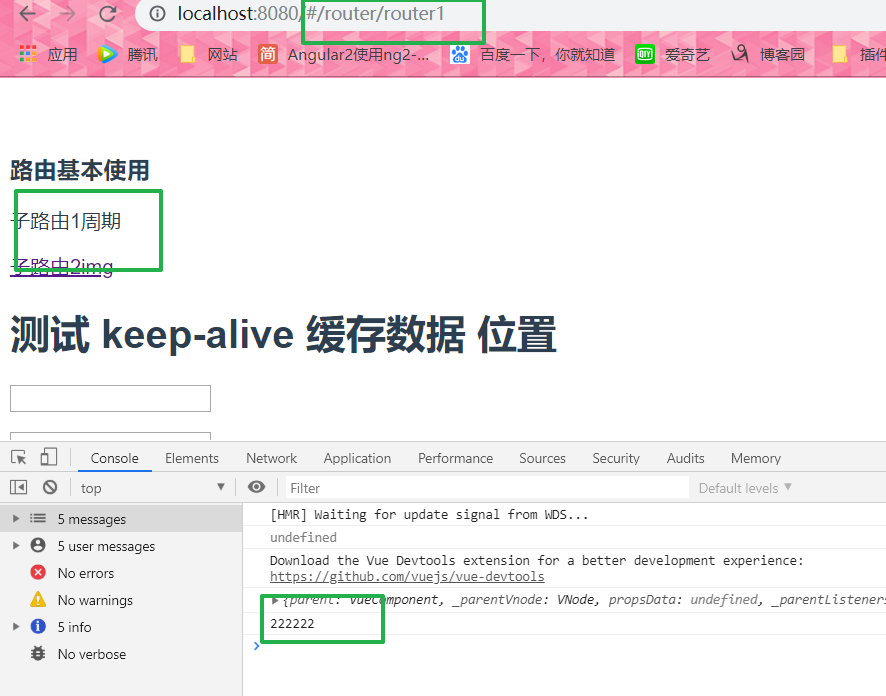 可以看见 地址栏参数不显示 与query相反
可以看见 地址栏参数不显示 与query相反children: [{ path: 'router1/:id', name: "router1", //通过name值 params component: Router1 }, { path: 'router2', component: Router2 } ]
3.query 获取: this.$route.query.id
直接写:
<router-link :to="{path:'/router/router1',query:{id:'000'}}">子路由1周期</router-link>
或者脚本:
<p @click="getDescribe('6666')">子路由1周期</p>
methods: {
getDescribe(id) {
this.$router.push({
path: "/router/router1",
query: {
id: id
}
});
}
}
//子组件
mounted: function() {
console.log(this.$route.query.id);
}
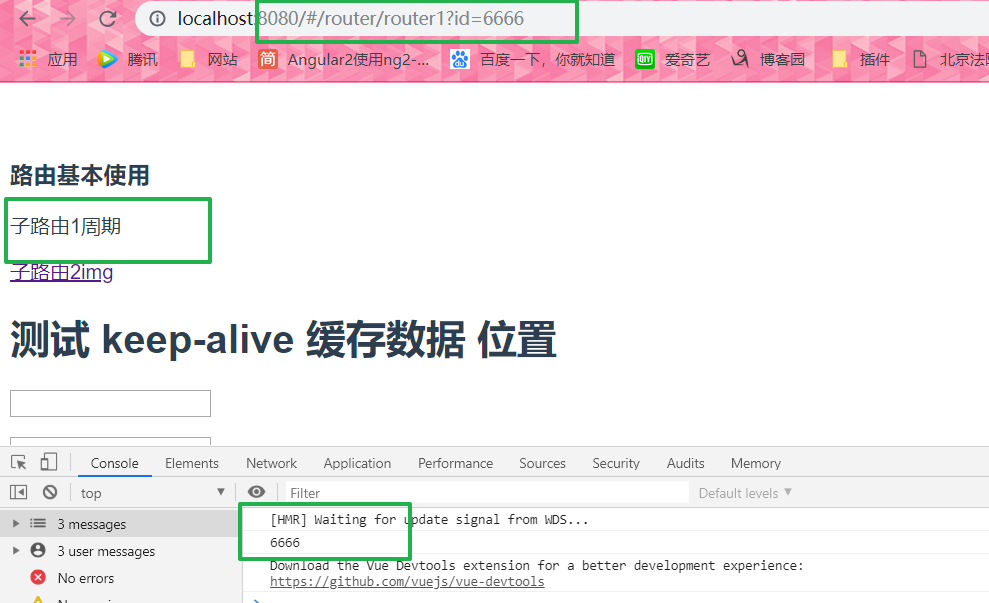 注意看 现在的地址栏和上面两种方式不同 ?=
注意看 现在的地址栏和上面两种方式不同 ?=
上面例举了三种跳转传参 第一路由配置 第二params 第三query 注意获取的时候是$route 没有 r
下面三种跳转的方法与区别:push replace go
router.go(n)
这个方法的参数是一个整数, 意思是在 history 记录中向前或者后退多少步, 类似 window.history.go(n)
methods:{ next(){ this.$router.go(1); //前进 }, prevent(){ this.$router.go(-1); //后退 } }
router.push(location)
想要导航到不同的 URL, 则使用 router.push 方法。 这个方法会向 history 栈添加一个新的记录, 所以, 当用户点击浏览器后退按钮时, 则回到之前的 URL。
router.replace(location)
跟 router.push 很像, 唯一的不同就是, 它不会向 history 添加新记录, 而是替换掉当前的 history 记录。是当前一次哦~
路由的别名和重定向
别名:alias
/a 的别名是 /b,意味着,当用户访问 /b 时,URL 会保持为 /b,但是路由匹配则为 /a,就像用户访问 /a 一样
export default new Router({ routes: [{ path: "/", alias: '/router', component: router, }] });
重定向:redirect
“重定向”的意思是,当用户访问 /a时,URL 将会被替换成 /b,然后匹配路由为 /b
export default new Router({ routes: [{ path: "/", alias: '/router', component: router, redirect: '/watch' }, { path: "/watch", component: watch, }] });
router懒加载
export default new Router({ routes: [{ path: "/", alias: '/router', component: (resolve) => require(['@/components/router.vue'], resolve), children: [{ path: 'router1/:id', name: "router1", component: Router1 }, { path: 'router2/:cy', component: Router2 } ] }, { path: "/watch", component: (resolve) => require(['@/components/watch.vue'], resolve), }] });
路由守卫钩子
beforeRouteEnter (to, from, next) { // 在渲染该组件的对应路由被 confirm 前调用 // 不!能!获取组件实例 `this` // 因为当守卫执行前,组件实例还没被创建
next(vm => {
// 通过 `vm` 访问组件实例 })
}
beforeRouteUpdate (to, from, next) {
// 在当前路由改变,但是该组件被复用时调用
// 举例来说,对于一个带有动态参数的路径 /foo/:id,在 /foo/1 和 /foo/2 之间跳转的时候,
// 由于会渲染同样的 Foo 组件,因此组件实例会被复用。而这个钩子就会在这个情况下被调用。
// 可以访问组件实例 `this`
next();
}
beforeRouteLeave (to, from, next) {
// 导航离开该组件的对应路由时调用
// 可以访问组件实例 `this`
next()
}
路由就告一段落了~~~~~~~~~~~~by~~~
---------------------
作者:love编程的小可爱
来源:CNBLOGS
原文:https://www.cnblogs.com/chen-yi-yi/p/11151941.html
版权声明:本文为作者原创文章,转载请附上博文链接!
内容解析By:CSDN,CNBLOG博客文章一键转载插件