First, the concept of EMC
EMC EMC (Electro Magnetic Compatibility): is a new comprehensive discipline is an important technical performance of electronic, electrical equipment or systems. National standard GB / T 4365-2003 "Electromagnetic Compatibility term" "capability of the device or the system to work in its electromagnetic environment without electromagnetic interference to withstand the environment of anything" under the definition of the electromagnetic compatibility, That electrical and electronic equipment or system to perform their functions well in the same electromagnetic environment coexist in such a state, simply put, is a variety of equipment and be able to work without disturbing each other, to achieve "compatibility" status. Pay attention to electromagnetic compatibility required two basic ways: in a common electromagnetic environment without interference and do not interfere with other devices.

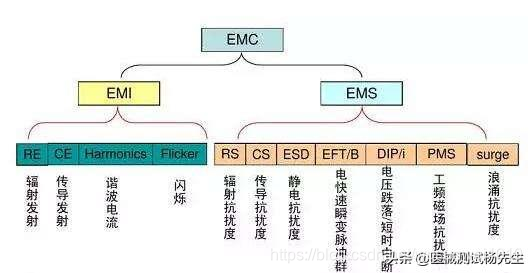
So understand more than what we know, EMC requirements include two aspects: on the one hand refers to electromagnetic interference electronics, electrical equipment or systems during normal operation of the host environment can not exceed a certain limit, namely EMI (Electro Magnetic interference) electromagnetic interference.
Refers to an electronic hand, electrical equipment or systems have a degree of immunity to electromagnetic interference present in the environment where, i.e. EMS (Electro Magnetic Susceptibility) electromagnetic immunity.
EMC (electromagnetic compatibility) = EMI (electromagnetic interference) + EMS (electromagnetic immunity)
If so abstract that we still feel it, let's give a few examples to illustrate:
Whether we live to see such a phenomenon

If the figures for the two devices if they both EMC have failed, it explains the interference of the socks off the cheese 1 and 2 clearly affected the cheese so that it does not work, on the other hand it illustrates anti-jamming capability cheese 2 that affect less than 1 by cheese, ha ha ......
Well, here to say a few normal points
Example 1: When you turn on the TV, the room will be dark momentarily fluorescent phenomenon, which is due to open TV moments large amount of current flowing to the TV, resulting in a sudden drop in voltage from the same source fluorescent affected.

Example 2: When the phone call, the microphone will be accompanied by harsh distortion "creak" sound or television / computer screen flicker, because these are the waves from your cell phone communications space coupled to the microphone, TV / computer the receiving antenna it is disturbed.

像例子1中由一个设备中产生的电压/电流变化通过电源线、信号线传导并影响其他设备时,将这个电压/电流的变化称为传导干扰;而像例子2中通过空间传播并对其他设备产生无用电压/电流,造成危害的干扰称为辐射干扰。
了解了电磁兼容的概念,我们再一起来看看电磁兼容由何组成~
二、电磁兼容三要素
任何产生电磁兼容问题都必须具备以下三个条件:骚扰源(干扰源)、耦合途径、敏感设备,我们称之为电磁兼容三要素,缺少任何一个都构不成电磁兼容问题。骚扰源即产生骚扰的电子、电气设备或系统,说明骚扰从哪里来;耦合途径是将骚扰源产生的骚扰传输到敏感设备的途径,说明骚扰如何传输;敏感设备是受到骚扰影响的电子、电气设备或系统,说明了骚扰到哪里去。
电磁干扰源通常分为自然干扰源和人为干扰源。
自然干扰源包括:
(1)大气噪声干扰:如雷电产生的火花放电,属于脉冲干扰,其频率从几Hz到100MHz以上。

(2)太阳噪声干扰:指太阳黑子的辐射噪声。在太阳黑子活动期.黑子的爆发产生的强烈噪声可致使通信中断。
(3)宁宙噪声:指来自宇宙天体的噪声。
(4)静电放电:人体、设备上所积累的静电电压可高达几万伏乃至几十万伏.常以电晕或火花方式放掉,称为静电放电。静电放电产生强大的瞬间电流和电磁脉冲,会导致静电敏感器件及设备的损坏。
人为干扰源指而电气电子设备和其他人工装置产生的电磁干扰。这里所说的人为干扰源都是指无意识的干扰,至于为了达到某种目的而有意施放的干扰,如军事上或者比赛等的电子对抗则不属于本文讨论范围。
常见的人为干扰源包括:
(1)无线电发射设备:包括移动通信系统、广播、电视、雷达、导航及无线电接力通信系统.

(2)工业、科学、医疗(ISM)设备:如高频手术刀、X光机、核磁CT、高频理疗设备等.
(3)电力设备:包括电机、继电器、电梯等设备
(4)汽车、内燃机点火系统:汽车点火系统产生宽带干扰,从几百千赫到几百兆赫。
(5)电网干扰:指由50Hz交流电网强大的电磁场和大地漏电流产生的干扰,以及高压输电线的电晕和绝缘断裂等接触不良产生的微弧和受污染导体表面的电火花。
(6)高速数字电子设备:包括计算机和相关设备。
电磁干扰的传输途径分两种方式:传导传输方式和辐射传输方式,从被干扰的敏感器角度来看,干扰的耦合可分为传导耦合和辐射耦合两类。
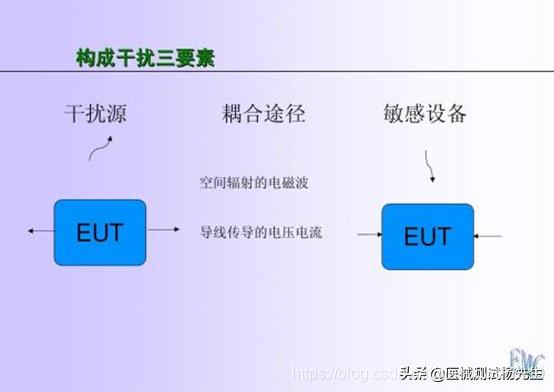
还拿例子一来说,电视就是骚扰源,电线则是耦合路径,日光灯则是敏感设备,三者一起导致了EMC问题的发生。需要强调的是:任何电子电气设备都可能是骚扰源,也可能是敏感设备;骚扰源可以是无信息的电磁噪声也可以是有用的功能性信号!
三、电磁兼容测试项目
结合医疗器械行业标准YY0505-2012简单介绍一下试验项目,后续会单独详细介绍每一个测试项目:
YY0505-2012针对EMC规定中的电磁发射测试项目(4项)如下
电源端子传导骚扰电压(传导骚扰 CE):GB4824、GB4343、GB17743;辐射骚扰(RE):GB4824、GB4343.1、GB17743;断续骚扰(喀呖声):GB4824、GB4343.1;谐波电流发射:GB17625.1;电压波动/闪烁发射:GB17625.2
辐射发射RE—通过空间以电磁波的形式发射电磁骚扰能量。
传导发射CE(其中包括功率,喀呖声)—通过导线以电压电流的形式发射电磁骚扰能量。
谐波(Harmonics) —设备工作时向交流供电电源注入的50Hz高次谐波。
电压波动和闪烁(Flicker) —设备工作时引起的交流供电电压的起伏波动。
YY0505-2012针对EMC规定中的电磁抗扰度测试项目如下:
Electrostatic discharge (ESD): GB / T17626.2 immunity radiofrequency radiation (RS): GB / T17626.3 Conducted RF immunity (CS): GB / T17626.6 Electrical Fast Transient Burst Immunity (EFT ): GB / T17626.4 power frequency magnetic field: GB / T17626.8 surge immunity (surge): GB / T17626.5 electric pressure dips, short interruptions and voltage variations: GB / T17626.11
Radiation immunity RS- space harassment immunity of electromagnetic waves.
Immunity conductive wire conducted CS- immunity to disturbance voltage and current.
ESD immunity burst disturbance ESD- electrostatic discharge.
Disturbance pulse group Electrical Fast Transient Burst Immunity EFT- certain circuit. Join harassment from the wire.
Surge (surge) - lightning impulse immunity to disturbance or some circuit. Join harassment from the wire.
Voltage dips, short interruptions and voltage variations (DIP) - immunity changes in power supply.
Frequency magnetic field (PMS) - immunity 50Hz AC magnetic field generated by the
EMC diagnosis (pre) test:
Products in the development stage, production line quality control testing, pre-tested prior to delivery accredited laboratory testing, inspection test after rectification of product failure.
Investigate whether the cause EMC problems generated by the existence and determine the exact location of generating harassment and interference, there is no improvement after taking suppression measures.
It does not require exactly as standards in the formal laboratory.
EMC conformance (compliance) test:
To test the device in accordance with the method specified in the relevant electromagnetic compatibility standards, to assess whether they meet the requirements of the proposed standard.
Products must be compliance (consistency) electromagnetic testing required in the national mandatory product certification system (3C certification) compatibility test is part of conformance testing prior to setting and enter the market.
Learn more EMC technologies come http://www.eda365.com/forum-271-1.html