Real-time risk control solution for Apache Flink and rules engine
A product of the Internet, the typical risk control scenarios include: registration risk control, risk control landing, transaction risk control, risk control and other activities, and risk control is the best preventive measures, so things in advance and after the event three implementation scenarios, again prior warning and control things best. This requires that the wind must have real-time control system. This paper presents a real-time risk control solutions. Risk control is a product of business scenarios, risk control system directly serve the business systems, as well as the associated system of penalties and analysis system, the system of relationships and roles as follows:
Business system, usually APP + background or web, is the carrier of Internet business, the risk of triggering from business systems;
- Wind control system to support business systems, to determine whether the current user or event risk according to data from the operational systems or buried point information;
- Punishment system , business system to call the results of risk control system for risk control user or event or punishment, such as adding code, landing restrictions prohibit orders and so on;
- Analysis system , the system to support wind control system to measure the performance of risk control system based on the data, such as a sudden drop in catch rate policy, it may mean that the strategy has failed, and activities such as finished goods robbed of time suddenly short, indicating that the overall campaign strategy may be a problem, etc. the system also should support operational / analysis found that the new policy;
Where the wind control system and analysis system is the focus of this article, but the sake of discussion, we assume that the business scenario is as follows:
Wind control system has rules and models two techniques, the advantage rule is simple and intuitive, strong interpretive, flexible, so long active in the wind control system, but the drawback is easy to break, but was black production guess it will fail, then the actual wind control system, often combined with the need to increase the robustness of the model based on the air control part. But space is limited, this article, we only focus on risk control rules based system architecture, of course, if there is risk control model demands, the architecture is also fully supported. The rule is to determine the conditions for things, we focused on registration, login, trading activities are assumed to few rules, such as:
- IP the last hour of a number of registered accounts over 10;
- An account group recently purchased one hour Offer more than 100;
Rules can be combined into a set of rules, for simplicity, we only discuss the rules.
- Fact , i.e. determination of the body and attributes, such as the account number and login, IP and registration number etc. The above rule;
- Index threshold , according to the judge, such as landing a critical threshold number, such as a critical threshold number of registered accounts;
Rules can be empirically fill operations experts, but also by the data analysts based on historical data mining, but because the rules in offense and defense with the black production be guessed lead to failure, so invariably need to be adjusted dynamically.
- Real-time control of wind data stream , identified by a red line, synchronous call control core wind call link;
- Index near real-time data streams , asynchronous writes by the blue line identification, the index data portion of preparing for real-time control of the wind;
- Near real-time / off-line analysis of data streams , asynchronous writes by the green line identification, to provide data for the performance of the air control system analysis;
Real-time risk control is the core of the system, the system is operational synchronous call, complete the corresponding risk control judgment. The aforementioned rules are often written by people and need to dynamically adjust, so we'll wind control judging section and rule management section apart. Rules for the operation service management background, by the operations personnel to carry out related operations:
- Scene management , to decide whether a scene implement risk control, such as the active scene, after the event can turn off the scene;
- Black and white lists , manual / program finds black and white list system, direct filtration;
- Rule management , management rules, including additions, deletions or modifications, such as the IP address of the new landing judgment, such as single new frequency check and the like;
- Threshold management , management indicators of threshold values, such as IP rules for a number of hours last registered account can not be more than 10, 1 and 10 that belong to a threshold value;
Finished management background, that part of the judgment logical rules also very clear, include pre-filter, the fact that the data required for the rule to determine the three links.
2.1.1 pre-filter
业务系统在特定事件(如注册、登陆、下单、参加活动等)被触发后同步调用风控系统,附带相关上下文,比如 IP 地址,事件标识等,规则判断部分会根据管理后台的配置决定是否进行判断,如果是,接着进行黑白名单过滤,都通过后进入下一个环节。
2.1.2 实时数据准备
在进行判断之前,系统必须要准备一些事实数据,比如:
- 注册场景,假如规则为单一 IP 最近 1 小时注册账号数不超过 10 个,那系统需要根据 IP 地址去 Redis/Hbase 找到该 IP 最近 1 小时注册账号的数目,比如 15;
- 登陆场景,假如规则为单一账号最近 3 分钟登陆次数不超过 5 次,那系统需要根据账号去 Redis/Hbase 找到该账号最近 3 分钟登陆的次数,比如 8;
Redis/Hbase 的数据产出我们会在第 2.2 节准实时数据流中进行介绍。
2.2.3 规则判断
在得到事实数据之后,系统会根据规则和阈值进行判断,然后返回结果,整个过程便结束了。整个过程逻辑上是清晰的,我们常说的规则引擎主要在这部分起作用,一般来说这个过程有两种实现方式:
- 借助成熟的规则引擎,比如 Drools,Drools 和 Java 环境结合的非常好,本身也非常完善,支持很多特性,不过使用比较繁琐,有较高门槛,可参考文章【1】;
- 基于 Groovy 等动态语言自己完成,这里不做赘述。可参考文章【2】;
这部分属于后台逻辑,为风控系统服务,准备事实数据。把数据准备与逻辑判断拆分,是出于系统的性能/可扩展性的角度考虑的。前边提到,做规则判断需要事实的相关指标,比如最近一小时登陆次数,最近一小时注册账号数等等,这些指标通常有一段时间跨度,是某种状态或聚合,很难在实时风控过程中根据原始数据进行计算,因为风控的规则引擎往往是无状态的,不会记录前面的结果。同时,这部分原始数据量很大,因为用户活动的原始数据都要传过来进行计算,所以这部分往往由一个流式大数据系统来完成。在这里我们选择 Flink,Flink 是当今流计算领域无可争议的 No.1,不管是性能还是功能,都能很好的完成这部分工作。
-
业务系统把埋点数据发送到 Kafka;
-
Flink 订阅 Kafka,完成原子粒度的聚合;
注:Flink 仅完成原子粒度的聚合是和规则的动态变更逻辑相关的。举例来说,在注册场景中,运营同学会根据效果一会要判断某 IP 最近 1 小时的注册账号数,一会要判断最近 3 小时的注册账号数,一会又要判断最近 5 小时的注册账号数……也就是说这个最近 N 小时的 N 是动态调整的。那 Flink 在计算时只应该计算 1 小时的账号数,在判断过程中根据规则来读取最近 3 个 1 小时还是 5 个 1 小时,然后聚合后进行判断。因为在 Flink 的运行机制中,作业提交后会持续运行,如果调整逻辑需要停止作业,修改代码,然后重启,相当麻烦;同时因为 Flink 中间状态的问题,重启还面临着中间状态能否复用的问题。所以假如直接由 Flink 完成 N 小时的聚合的话,每次 N 的变动都需要重复上面的操作,有时还需要追数据,非常繁琐。
- Flink 把汇总的指标结果写入 Redis 或 Hbase,供实时风控系统查询。两者问题都不大,根据场景选择即可。
通过把数据计算和逻辑判断拆分开来并引入 Flink,我们的风控系统可以应对极大的用户规模。前面的东西静态来看是一个完整的风控系统,但动态来看就有缺失了,这种缺失不体现在功能性上,而是体现在演进上。即如果从动态的角度来看一个风控系统的话,我们至少还需要两部分,一是衡量系统的整体效果,一是为系统提供规则/逻辑升级的依据。
- 判断规则是否多余,比如某规则从来没拦截过任何事件;
- 判断规则是否有漏洞,比如在举办某个促销活动或发放代金券后,福利被领完了,但没有达到预期效果;
- 发现全局规则,比如某人在电子产品的花费突然增长了 100 倍,单独来看是有问题的,但整体来看,可能很多人都出现了这个现象,原来是苹果发新品了……
- 识别某种行为的组合,单次行为是正常的,但组合是异常的,比如用户买菜刀是正常的,买车票是正常的,买绳子也是正常的,去加油站加油也是正常的,但短时间内同时做这些事情就不是正常的。
- 群体识别,比如通过图分析技术,发现某个群体,然后给给这个群体的所有账号都打上群体标签,防止出现那种每个账号表现都正常,但整个群体却在集中薅羊毛的情况。
这便是分析系统的角色定位,在他的工作中有部分是确定性的,也有部分是探索性的,为了完成这种工作,该系统需要尽可能多的数据支持,如:
- 业务系统的数据,业务的埋点数据,记录详细的用户、交易或活动数据;
- 风控拦截数据,风控系统的埋点数据,比如某个用户在具有某些特征的状态下因为某条规则而被拦截,这条拦截本身就是一个事件数据;
这是一个典型的大数据分析场景,架构也比较灵活,我仅仅给出一种建议的方式。
相对来说这个系统是最开放的,既有固定的指标分析,也可以使用机器学习/数据分析技术发现更多新的规则或模式,限于篇幅,这里就不详细展开了。http://archive.keyllo.com/L-编程/drools-从Drools规则引擎到风控反洗钱系统v0.3.2.pdfhttps://www.jianshu.com/p/d6f45f91bedehttps://jinfei21.github.io/2018/09/29/基于规则的风控系统/https://sq.163yun.com/blog/article/183314611296591872https://sq.163yun.com/blog/article/213006222321659904https://github.com/sunpeak/riskcontrol
Apache Flink 及大数据领域盛会 Flink Forward Asia 2019 将于 11月28-30日在北京国家会议中心举办,大会议程已上线,点击「阅读原文」可了解大会议程详情。
(点击图片可查看 Flink Forward Asia 2019 详情)
从滴滴的Flink CEP引擎说起

CEP业务场景
复杂事件处理(Complex Event Process,简称CEP)用来检测无尽数据流中的复杂模 式,拥有从不同的数据行中辨识查找模式的能力。模式匹配是复杂事件处理的一个强 大援助。 例子包括受一系列事件驱动的各种业务流程,例如在安全应用中侦测异常行为;在金 融应用中查找价格、交易量和其他行为的模式。其他常见的用途如欺诈检测应用和传 感器数据的分析等。
说了这么多可能还是觉得比较抽象,那么我们可以看看这次滴滴分享的FlinkCEP在滴滴中的业务场景。



吐槽时刻:
虽然,业务场景ppt写的很好,但是最近几次顺风车事故,给大家留下了糟糕的印象。大数据没用起来,cep其实应该也可以用在顺风车安全检测上吧。
Flink CEP
Flink的CEP是基于Flink Runtime构建的实时数据规则引擎,擅长解决跨事件的匹配问题。
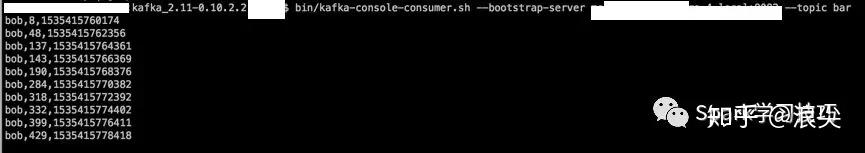
可以看看,滴滴的屁屁踢上给出的两个demo
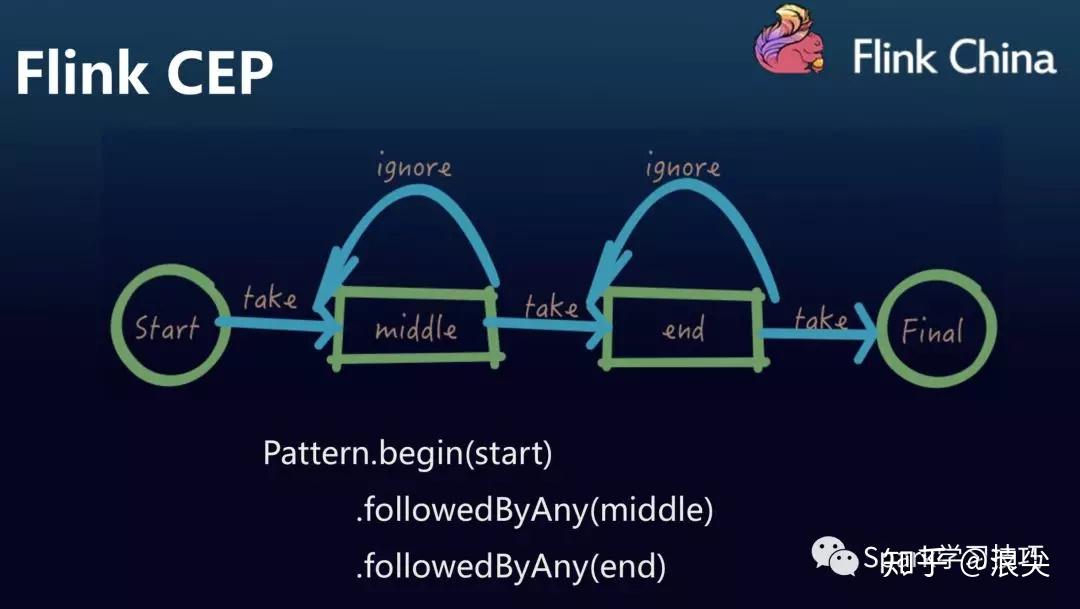
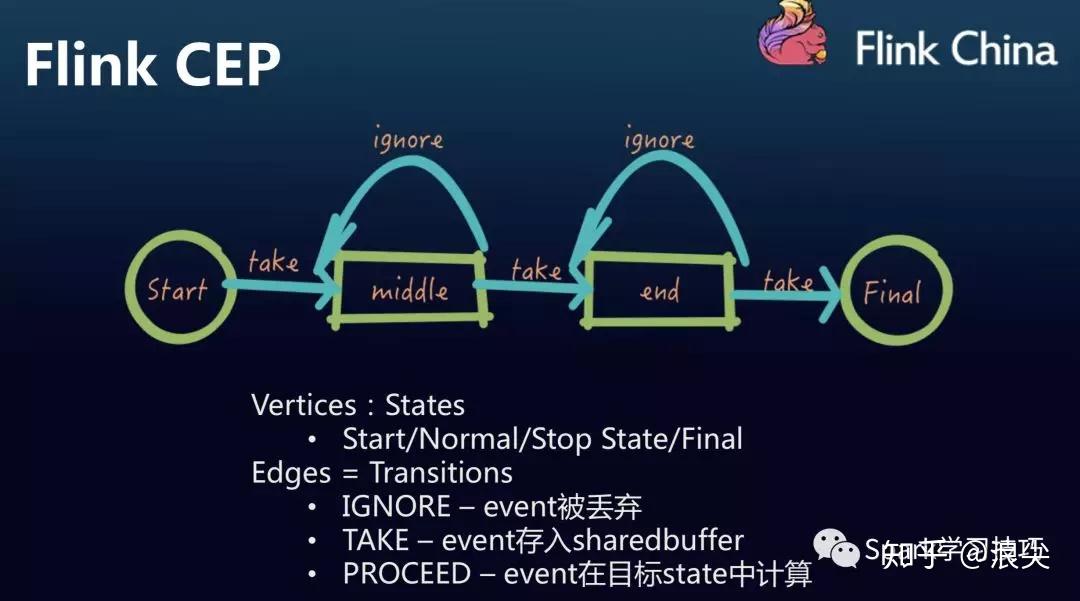
Flink CEP的特点

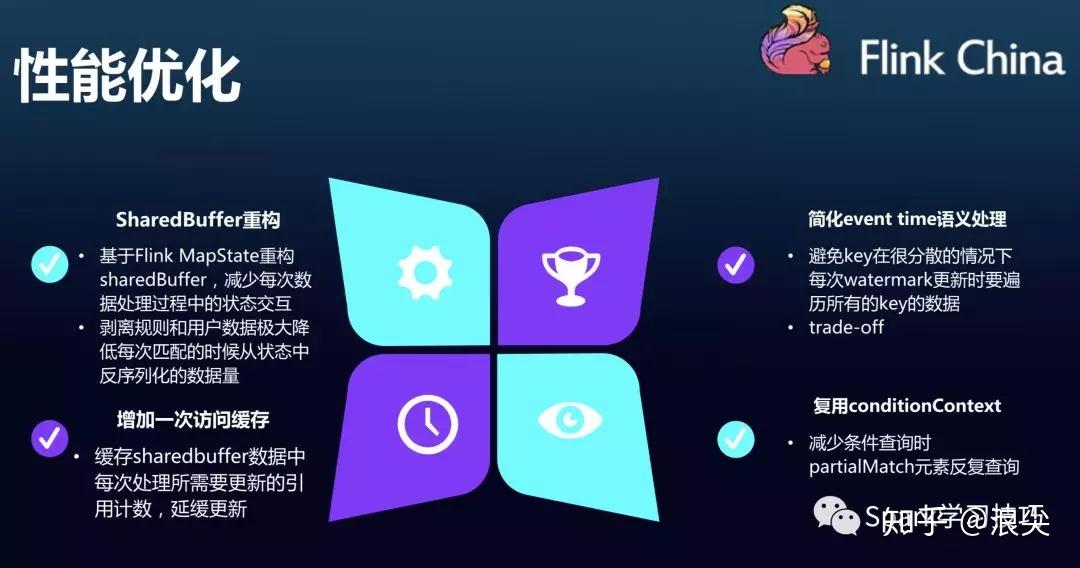
动态规则
其实,对于实时领域的规则引擎,我们不想每次修改都要打包编码,只希望简单修改一下规则就让它能执行。
当然,最好规则是sql 的形式,运营人员直接参与规则编写而不是频繁提需求,很麻烦。。。。此处,省略万字。。
要知道flink CEP官网给出的API也还是很丰富的,虽然滴滴这比也给出了他们完善的内容。

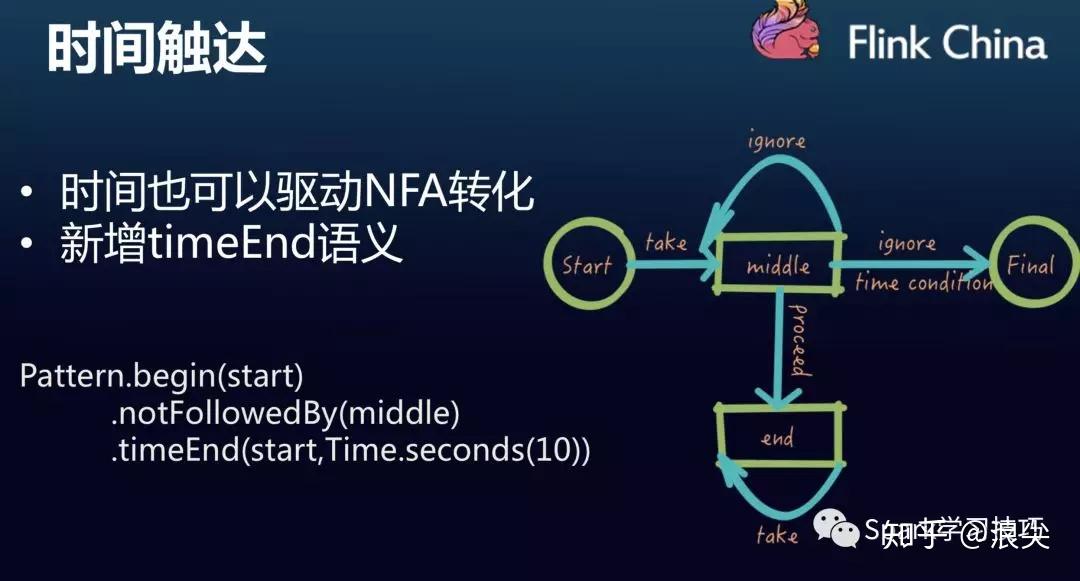
flink官方的CEP文章,浪尖及浪尖组织的flink小团队,已经翻译过了。链接如下:
https://github.com/crestofwave1/oneFlink/blob/master/doc/CEP/FlinkCEPOfficeWeb.md
那么,为了实现动态规则编写,滴滴的架构如下:
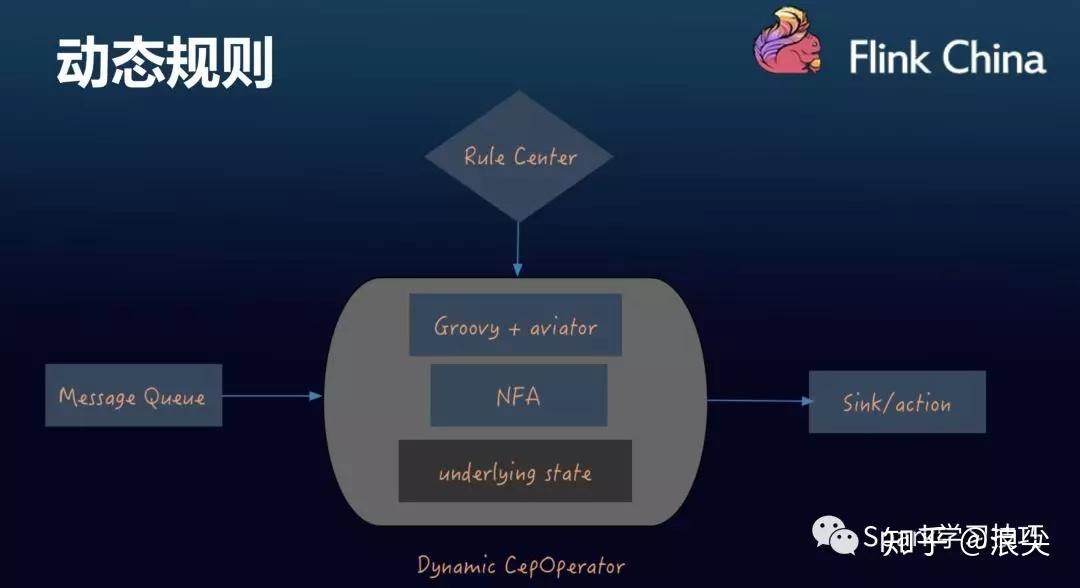
具体的规则实现如下:

可以看到,其规则还是要编码成java代码,然后再用groovy动态编译解析,不知道效率如何。。。
对于规则引擎,当然很多人想到的是drools,这个跟flink结合也很简单,但是效率不怎么苟同。
Flink CEP的SQL实现
熟悉flink的小伙伴肯定都知道Flink的SQL引擎是基于Calcite来实现的。那么细心的小伙伴,在calcite官网可以发现,calcite有个关键字MATCH_RECOGNIZE。可以在这个网页搜索,找到MATCH_RECOGNIZE关键字使用。
http://calcite.apache.org/docs/reference.html
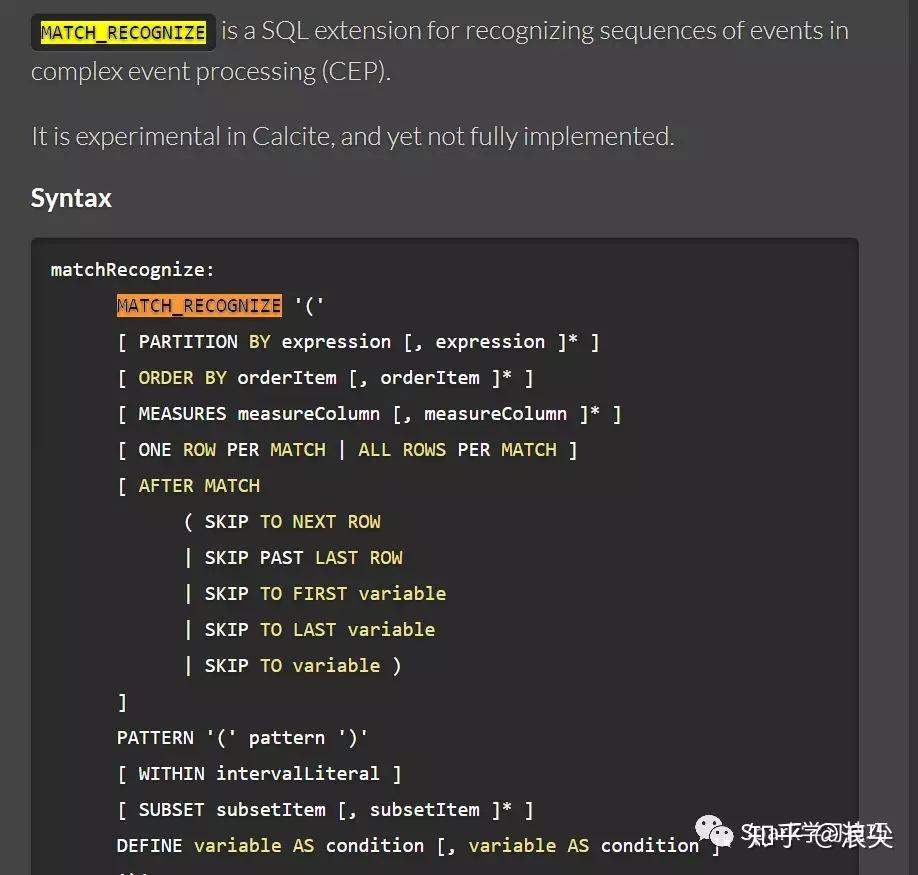
那么这时候可能会兴冲冲写个demo。
final String sql = "select frequency,word,timestamp1 "
+ " from wc match_recognize "
+ " ("
+ " order by timestamp1 "
+ " measures A.timestamp1 as timestamp1 ,"
+ " A.word as word ,"
+ " A.frequency as frequency "
+ " ONE ROW PER MATCH "
+ " pattern (A B) "
+ " within interval '5' second "
+ " define "
+ " A AS A.word = 'bob' , "
+ " B AS B.word = 'kaka' "
+ " ) mr";很扫兴的它报错了:
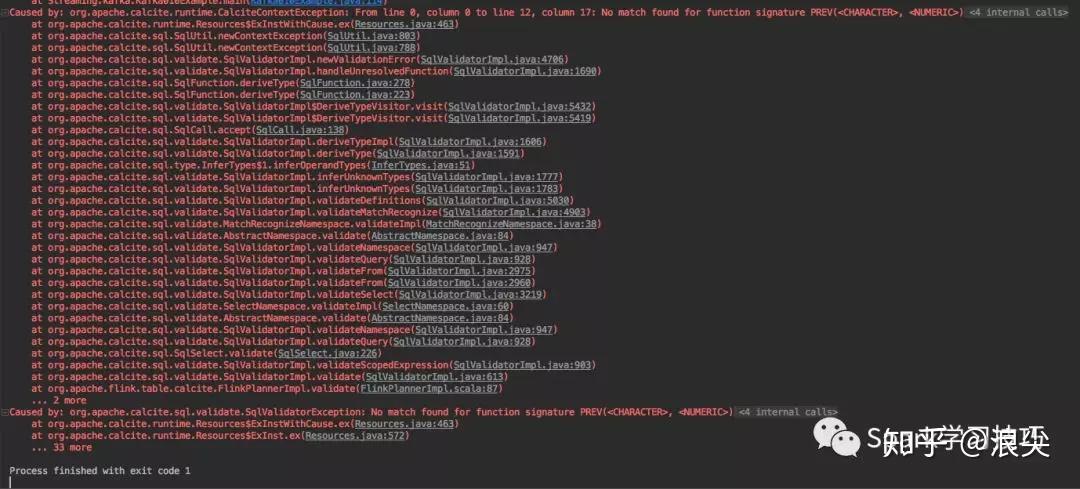
那么问题来了,calcite支持而flink不支持,为啥?
赶紧发了个issue,然后迅速得到官方回复:

但是,翻翻阿里的blink使用手册和华为的flink使用手册发现两者都支持。
好吧。其实,很不服气,周末,除了健身就是加班。
波折一番,解决了,需要修改flink-table相关的内容,执行计划,coden等。
最终,实现了。