Outline
NLP basic concepts
Development and application of NLP
Introduction of common terms and extended NLP
1.1 What is NLP
- The basic classification
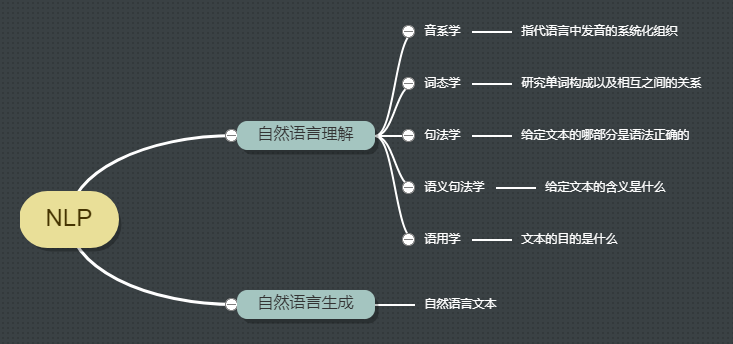
Natural Language Generation (Natural Language Generation, NLG)
It refers to the structured data generated automatically reads the text consists of three phases:
- Text planning: planning to complete the basics of structured data;
- Programming statements: Statement composition expressed stream from the structured data;
- Implementation: produce a grammatical sentence to express the text;
Research Task
- machine translation
- emotion analysis
- Smart Answers
- Abstracts generation
- Text Categorization
- Public opinion analysis
- Knowledge Mapping
Development of 1.2 NLP
Infancy (before 1956)
Bayesian methods, hidden Markov, maximum entropy, support vector machine ......, the mainstream is still a rule-based rationalist approach;
The rapid development period (1980 to 1999)
Based on statistics, corpus-based examples of technologies and rule-based flourish during this period;
Rapid period (2000 to date)
Neural networks and deep learning;
1.3 NLP knowledge of the constitution
Basic terms
- Participle (segment)
- Speech tagging (part-of-speech tagging)
Named entity recognition (NER, Named Entity Recognition)
Identification means, such as place names, organization names, proper nouns with the specific class target entity (usually a noun) from the text and the like;
Parsing (syntax parsing)
Analytical object component dependencies of each sentence;
- Anaphora resolution (anaphora resolution)
- Emotion Recognition (emotion recognition)
- Error correction (correction)
- Q system (QA system)
knowledge structure
NLP is an interdisciplinary scientific, systematic and specialized co-exist, that knowledge is as follows:
- Syntactic and semantic analysis : target sentence, various syntactic analysis;
- Keyword extraction : extracting main information in the target text;
- Text Mining : mainly includes the text clustering, classification, information extraction, summary, sentiment analysis and visualization of information and knowledge mining, interactive presentation interface;
- Information retrieval : large-scale document indexing;
- Machine Translation : source language text inputted by automated translation into another language text;
- Q system : for a natural language question, is given by a question and answer system accurate answer;
- Dialogue system : the system through multi-round dialogue, chat with users, questions and answers, to complete a task;

1.4 Corpus
1.5 explore several levels of NLP
The first level: lexical analysis
Participle
Speech tagging
The purpose is to give a category for each word;
The second level: Parsing
The text of the input sentence as a unit, for analysis processing to obtain the syntactic structure of the sentence;
Third level: semantic analysis
Semantic Role Labeling (semantic role labeling) is currently more mature shallow semantic analysis techniques;