A, inode to go from real practice
1.ls -i inode can see the name of the file, stat 123.txt command can be seen permissions, inode number, hard links, three times the access time can be seen. 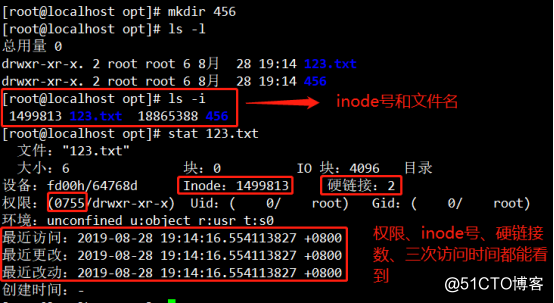
2. New Link to 123 text abc text, see the command with the stat 123.txt, number of hard links immediately changed to 2 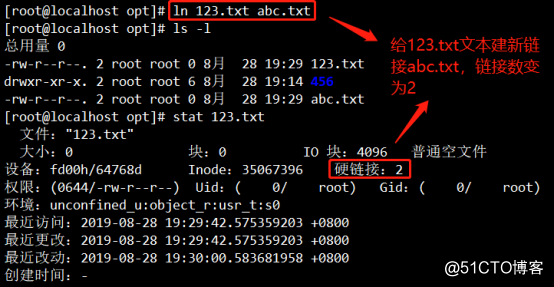
consistent inode number 3. Text and hard links, namely hard link aliases (soft link text inode number two That is different) 
4. View details 456 files, use the file command to see the text format, the directory form 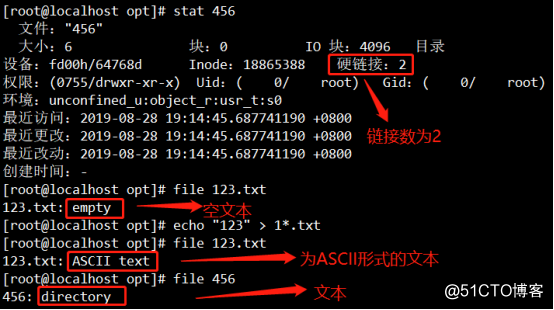
5.df -i command to see all file system has a total of inode numbers, and inode numbers are available 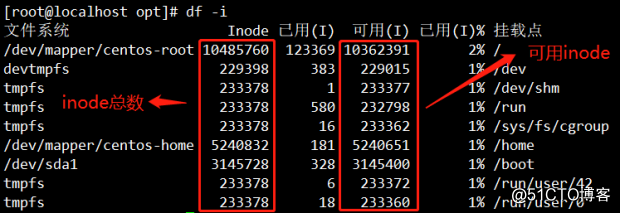
6. Add a new sdb disk, giving it a partition sdb1 (20G all).
7. formatted disk 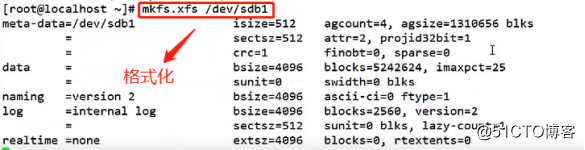
8. The new directory abc, abc next sdb1 mount 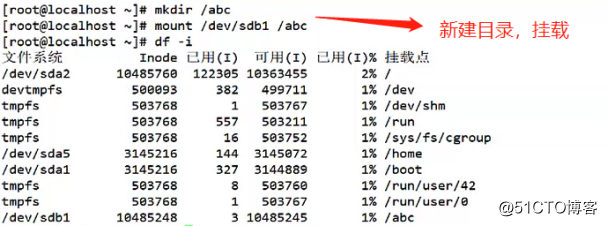
9. 10,485 new empty text at abc directory, which accounted for 10,485 empty text inode number 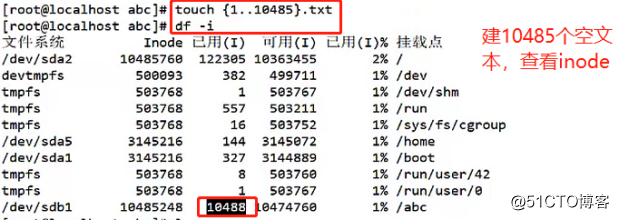
10. Check with df -hT, which accounts for empty text the 38M space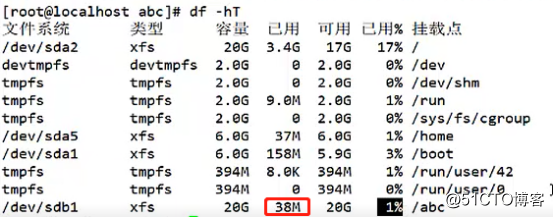
Second, restore accidentally deleted files
1. Screening rpm package, if not you need to install via yum 
2.xfs file recovery, disk file system for backup 
3. Enter interactive interface, has an input address backup and backup file or device name. 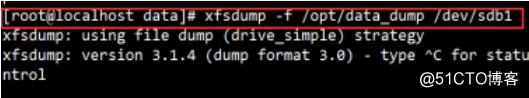
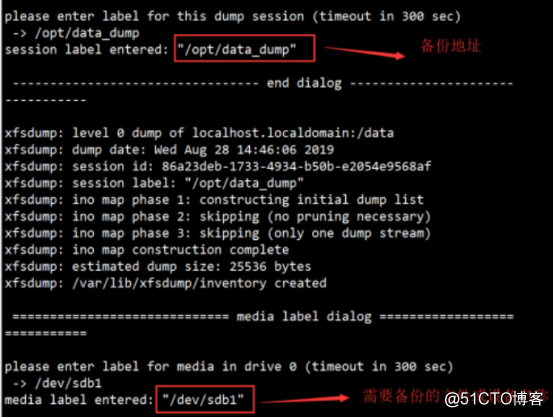
4. Analog delete files, text 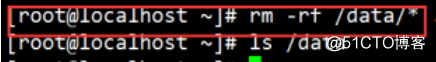
5. restore runs
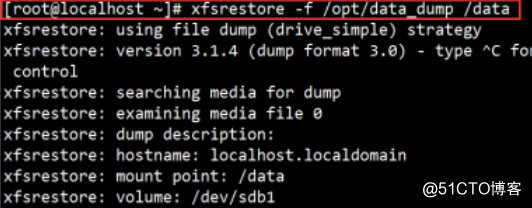
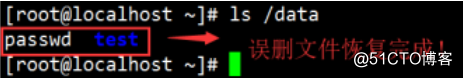
Conclusion: xfsdump backup tool also has a lot of restrictions
1. Only backup mounted file systems
2. You must use root privileges to operate
3. XFS file system can only back up
data after the backup only 4. Let xfsrestore analytical
the two file systems can not back up with the same UUID