In the previous blog, " to talk about the configuration and optimization of NGINX " in Section 2.5, which mentioned location module is the most used in the nginx, and most important module, load balancing, reverse proxy, virtual domains and so on and it related.
First, we can first look at a co-worker sent me a message
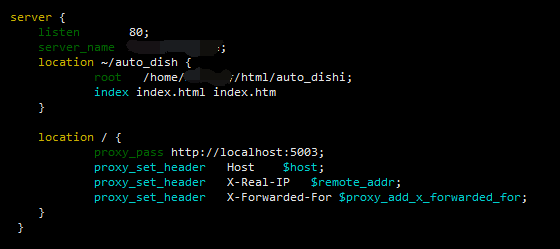
Direct access to dynamic resources in the common case where you want to match the "/", and when access to "auto_dish" when matching static files. At first glance look ignorant force, feeling nothing issue, a closer look at or slightly inkling of. On the one hand and match the order of about two location, on the other hand is the cause of the directory path.
After only want to achieve longitudinal adjustment of the position of location, change the path to the root directory on the OK auto_dish superior (below showing the effect of another configuration used).
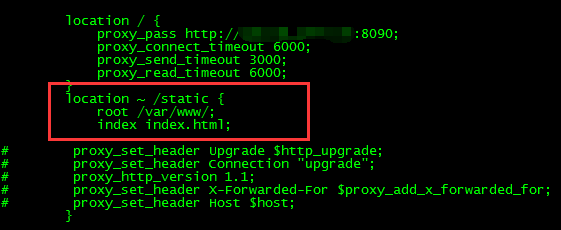
So then we can perform static access static resources under the server_name by adding static.
(Ah, this is very basic, and embarrassment)
Here we begin a comprehensive understanding of the rules under the location match.
1) location syntax rules
location [=|~|~*|^~] /uri/ {
·····
}Then after location matching rules meaning
= 开头表示精确匹配
^~ 开头表示uri以某个常规字符串开头,理解为匹配 url路径即可。nginx不对url做编码,因此请求为/static/20%/aa,可以被规则^~ /static/ /aa匹配到(注意是空格)
~ 开头表示区分大小写的正则匹配
~* 开头表示不区分大小写的正则匹配
!~ 区分大小写不匹配的正则
!~* 不区分大小写不匹配的正则
/ 通用匹配,任何请求都会匹配到When we have a plurality of location-provisioning, which matches the order of:
First matching "=", followed by the matching "^ ~", followed by the order file is a positive match, and finally to "/" generic matches.
When there is a match success when stopped matching, processing requests by the current rule matches.
Now there is a matching rule such as shown below at the same time
location = / {
#规则A
}
location = /login {
#规则B
}
location ^~ /static/ {
#规则C
}
location ~ \.(gif|jpg|png|js|css)$ {
#规则D
}
location ~* \.png$ {
#规则E } location !~ \.xhtml$ { #规则F } location !~* \.xhtml$ { #规则G } location / { #规则H }So the effect is as follows
访问根目录/ 比如 http://localhost/ 将匹配规则A
访问 http://localhost/login 将匹配规则B,http://localhost/register 则匹配规则H
访问 http://localhost/static/a.html 将匹配规则C
访问 http://localhost/a.gif, http://localhost/b.jpg 将匹配规则D和规则E,但是规则D顺序优先,规则E不起作用,而 http://localhost/static/c.png 则优先匹配到规则C
访问 http://localhost/a.PNG 则匹配规则E,而不会匹配规则D,因为规则E不区分大小写
访问 http://localhost/a.xhtml 不会匹配规则F和规则G,http://localhost/a.XHTML不会匹配规则G,因为不区分大小写。规则F,规则G属于排除法,符合匹配规则但是不会匹配到,所以想想看实际应用中哪里会用到
访问 http://localhost/category/id/1111 则最终匹配到规则H,因为以上规则都不匹配,这个时候应该是nginx转发请求给后端应用服务器,比如FastCGI(php),tomcat(jsp),nginx作为方向代理服务器存在Therefore, in practical applications, the need for at least three matching rules are defined as follows:
# 直接匹配网站根,通过域名访问网站首页比较频繁,使用这个会加速处理,官网如是说。
# 这里是直接转发给后端应用服务器了,也可以是一个静态首页
# 第一个必选规则
location = / {
proxy_pass http://localhost:8080/index } # 第二个必选规则是处理静态文件请求,这是 nginx 作为 http 服务器的强项 # 有两种配置模式,目录匹配或后缀匹配,任选其一或搭配使用 location ^~ /static/ { root /webroot/static/; } location ~* \.(gif|jpg|jpeg|png|css|js|ico)$ { root /webroot/res/; } # 第三个规则就是通用规则,用来转发动态请求到后端应用服务器 # 非静态文件请求就默认是动态请求,自己根据实际把握 # 毕竟目前的一些框架的流行,带 .php, .jsp 后缀的情况很少了 location / { proxy_pass http://localhost:8080/ }
2) rewrite grammar
last – 基本上都用这个 Flag
break – 中止 Rewirte,不在继续匹配
redirect – 返回临时重定向的HTTP状态302
permanent – 返回永久重定向的HTTP状态3012.1 can be used to determine the expression
-f 和 !-f 用来判断是否存在文件
-d 和 !-d 用来判断是否存在目录
-e 和 !-e 用来判断是否存在文件或目录
-x 和 !-x 用来判断文件是否可执行2.2 may be used as the global variable is determined
例:http://localhost:88/test1/test2/test.php
$host:localhost
$server_port:88
$request_uri:http://localhost:88/test1/test2/test.php $document_uri:/test1/test2/test.php $document_root:D:\nginx/html $request_filename:D:\nginx/html/test1/test2/test.php
3) Redirect grammar
server {
listen 80;
server_name start.igrow.cn;
index index.html index.php; root html; if ($http_host !~ “^star\.igrow\.cn$" { rewrite ^(.*) http://star.igrow.cn$1 redirect; } }
4) anti-hotlinking
location ~* \.(gif|jpg|swf)$ {
valid_referers none blocked start.igrow.cn sta.igrow.cn; if ($invalid_referer) { rewrite ^/ http://$host/logo.png; } }
5) set the expiration time depending on the file type
location ~* \.(js|css|jpg|jpeg|gif|png|swf)$ {
if (-f $request_filename) {
expires 1h; break; } }
6) prohibit access to a directory
location ~* \.(txt|doc)${
root /data/www/wwwroot/linuxtone/test;
deny all;
}
Report: Global variables are available
$args
$content_length
$content_type
$document_root
$document_uri $host $http_user_agent $http_cookie $limit_rate $request_body_file $request_method $remote_addr $remote_port $remote_user $request_filename $request_uri $query_string $scheme $server_protocol $server_addr $server_name $server_port $uri
Reference material
1. Static and dynamic resource access entry of Nginx separation
2. the Nginx Detailed Configuration of Location (Location matching order)
3. The use of static and dynamic resource separation do Nginx, were treated static and dynamic resources
4. the Nginx Examples of - processing the static and dynamic files
Transfer from
nginx configuration of static resources with dynamic access isolated - blackfoxya personal space - OSCHINA https://my.oschina.net/u/3314358/blog/1920380