Function returns
I do not know if you noticed, in the above code, we do three times factorial, this code is actually duplicate code. Programming guru Martin Fowler Mr. once said: " Code There are many bad taste, repetition is the worst kind! ", To write high-quality code first problem to be solved is to repeat the code. For the above codes, we can calculate the factorial function call encapsulated into a "function" function modules, where needed factorial calculation, we only need to "call" the "function" it
Defined Functions
In the understanding of how to define a function, we can reconstruct the above code, the so-called reconstruction is without effect on the structure of the code to adjust the premise of code execution results.
Function parameters
Function is a code of the vast majority of programming languages are supported by the "building blocks", but the function of the Python language functions in the other there are still many not the same place, one significant difference is that Python for function parameters deal with. In Python, function parameters can have default values, but also supports the use of variable parameters, so Python does not need to support other languages like overloaded functions , we can make it because there are many different definitions of a function in time use

def hs():
zhengshu = 0
fushu = 0
sum_ = 0
cishu = 0
data = 1
while data !=0 :
data = eval(input(">>"))
if data > 0:
zhengshu += 1
if data < 0:
fushu += 1
sum_ += data
if data != 0:
cishu += 1
print(zhengshu)
print(fushu)
print(sum_ / cishu)
def Start():
hs()
Start()

def money():
dorlla = 10000
for i in range (14):
dorlla = dorlla * 0.05 + dorlla
if i == 9:
print(dorlla)
print(dorlla)
def Start():
money()
Start()

def hs():
zhengshu = 0
fushu = 0
sum_ = 0
cishu = 0
data = 1
while data !=0 :
data = eval(input(">>"))
if data > 0:
zhengshu += 1
if data < 0:
fushu += 1
sum_ += data
if data != 0:
cishu += 1
print(zhengshu)
print(fushu)
print(sum_ / cishu)
def Start():
hs()
Start()

def zc():
count = 0
for i in range(100,1001):
if i % 5 == 0 and i % 6 == 0:
print(i,end=" ")
count =1
if count % 10 ==0:
print()
def Start():
zc()
Start()

1.def num1():
n = 0
while n ** 2 < 12000:
n +=1
print(n)
def Start():
num1()
Start()
2.def num2():
n = 0
while n ** 3 <12000:
n +=1
print(n-1)
def Start():
num2()
Start()
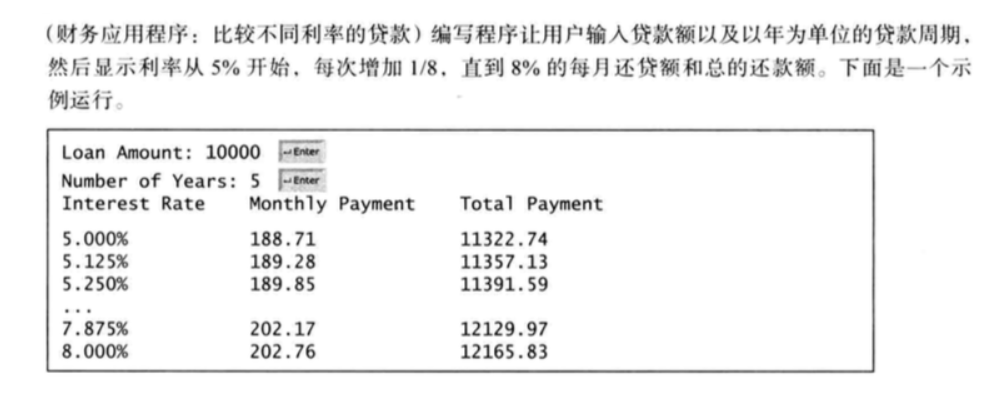
def num2():
Money = 10000
lilv = 5
nian = 5
for i in range(24):
M = Money * lilv / 100
T = 12 * M * nian
print(lilv,'%','月利率',M,'总和',T)
if lilv == 5.25:
print('.....')
lilv += 1/8
def Start():
num2()
Start()

def num2():
res = 0
for i in range(50000,0,-1):
res += 1/i
print(res)
def Start():
num2()
Start()
2.def num2():
res = 0
for i in range(1,50001,1):
res += 1/i
print(res)
def Start():
num2()
Start()

def num2():
res = 0
for i in range(1,98,2):
res += i/ (i+2)
print(res)
def Start():
num2()
Start()

def num2():
res = 0
for i in range(1,100000):
res += 4*((-1)**(i+1)/(2*i-1))
print(res)
def Start():
num2()
Start()