I. Overview

Second, class hero
1 class HeroNode { 2 //值域 3 public int id; 4 public String name; 5 public String nickName; 6 //指针域 7 public HeroNode next; 8 public HeroNode prev; 9 10 HeroNode(int id, String name, String nickName) { 11 this.id = id; 12 this.name = name; 13 this.nickName = nickName; 14 } 15 }
Third, the main method
. 1 @Test 2 public void Test () { . 3 // Create the first node . 4 HeroNode head = new new HeroNode (-1, null , null ); . 5 insertNode (head, new new HeroNode (. 1, "Matsue", "timely" ) ); . 6 insertNode (head, new new HeroNode (2, "Wu", "Walker" )); . 7 insertNode (head, new new HeroNode (. 3, "Lin", "leopard head" )); . 8 printLinked (head); . 9 }
4. Operation
Doubly-linked list with a single operation is almost the same, so just write and insert printing operations
1, insert
1 // Insert a new node 2 public void insertNode (HeroNode head, HeroNode the newNode) { . 3 IF (head == null ) { . 4 System.out.println ( "head node can not be empty" ); . 5 return ; . 6 } . 7 HN = HeroNode head; . 8 // recycled to the last node, its next = null, i.e. == null hn.next . 9 the while (hn.next =! null ) { 10 HN = hn.next; . 11 } 12 is // the hn.next point to the new node 13 = hn.next the newNode; 14 // PREV new node to the hn, that is, before a new node 15 newNode.prev = HN; 16 }
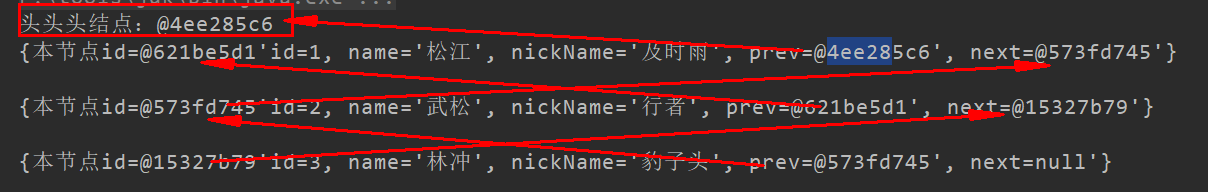
2, print
1 // print doubly linked list 2 public void printLinked (HeroNode head) { . 3 IF (head == null ) { . 4 System.out.println ( "head node can not be empty" ); . 5 return ; . 6 } . 7 IF (head == .next null ) { . 8 System.out.println ( "only the first node, no data list" ); . 9 return ; 10 } . 11 HeroNode tmp = head; 12 is System.out.println ( "head first node: "+ convertNode (tmp)); 13 is while (tmp.next != null) { 14 System.out.println(show(tmp.next)); 15 tmp = tmp.next; 16 } 17 }
3, an auxiliary method for printing
1 public String show(HeroNode h) { 2 return "{" + 3 "本节点id=" + convertNode(h) + '\'' + 4 "id=" + h.id + 5 ", name='" + h.name + '\'' + 6 ", nickName='" + h.nickName + '\'' + 7 ", prev=" + convertNode(h.prev) + '\'' + 8 ", next=" + convertNode(h.next) + '\'' + 9 '}' + "\n"; String convertNode (HeroNode H) { public13 isformatted HeroNode, directly outputs the address value//12 is. 11 } 10 14 return h == null ? null : h.toString().substring(h.toString().lastIndexOf('@')); 15 }
Fifth, the results show