May 31 task
1.13 single-user mode
1.14 rescue mode
1.15 clone virtual machines and modify the hostname
1.16 Linux machine to log each other
1.13 single-user mode (Example: If you forget your root password):
First, restart the machine can be used init 6 reboot
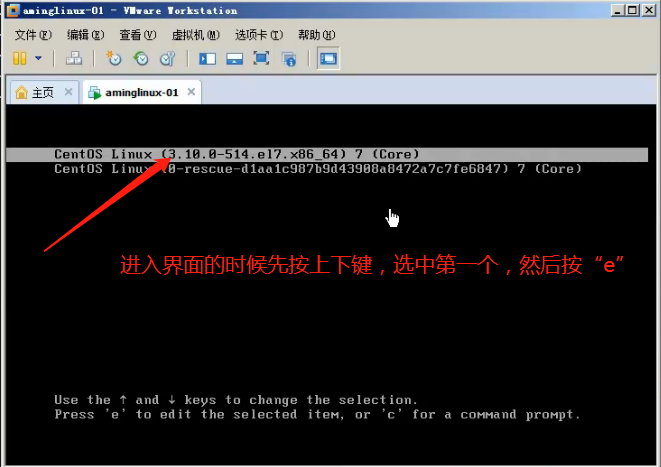
ro (read only) to RW (read) and written init = / sysroot / bin / sh, then press Ctrl + x
That is, into single-user mode (similar to Windows in Safe Mode)
First enter chroot / sysroot / (i.e., switch to the original system, available with the original command to change the password)
Enter passwd root (ie change the password)
Prompted, press Ctrl + c (cancel) Enter LANG = en (Definition Language non-Chinese)
And then re-enter passwd root
Enter the new password twice (not before a few times, then changed the complex password, not too simple)
Finally, input touch /.autorelabel (very important, be sure to enter)
Restart the machine
1.14 Rescue Mode:
In single-user mode if there is no access to the encrypted time set, we can enter Rescue Mode root password to modify or change the configuration file on knocking wrong in Linux (Correction important configuration files resulting from system error)
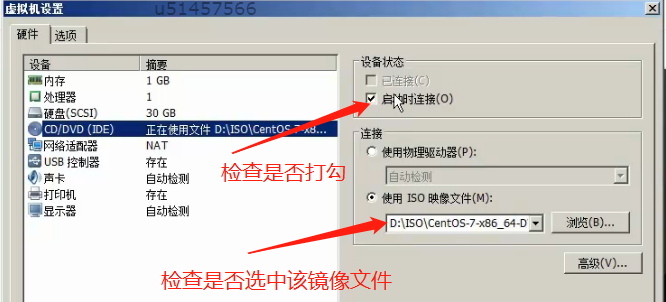
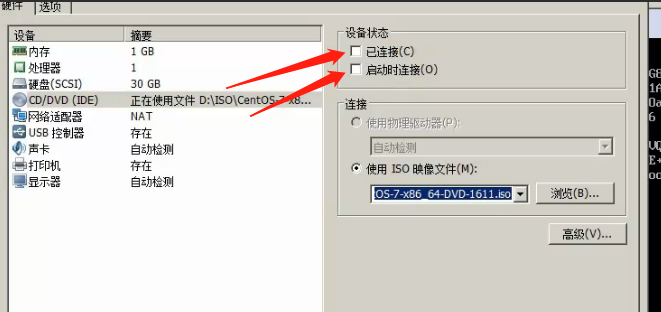
Using an optical drive or U disk into the next interface that installed the system (that is, CD / DVD)
First, CD view the virtual machine settings / DVD
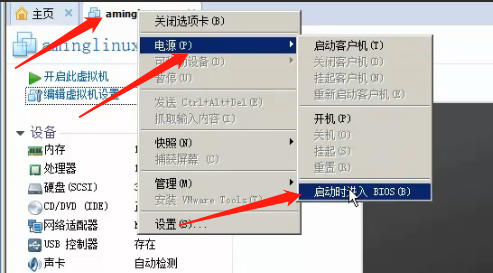
When select boot into the BIOS
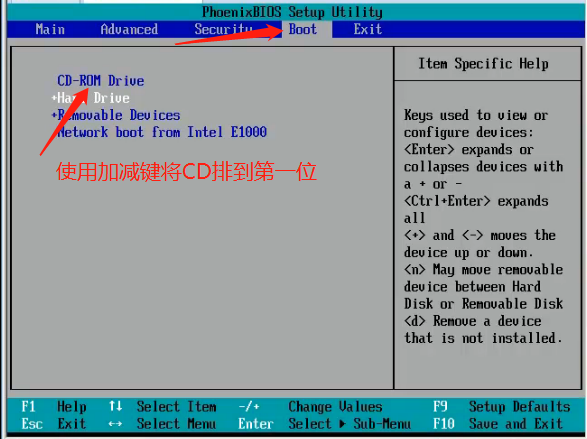
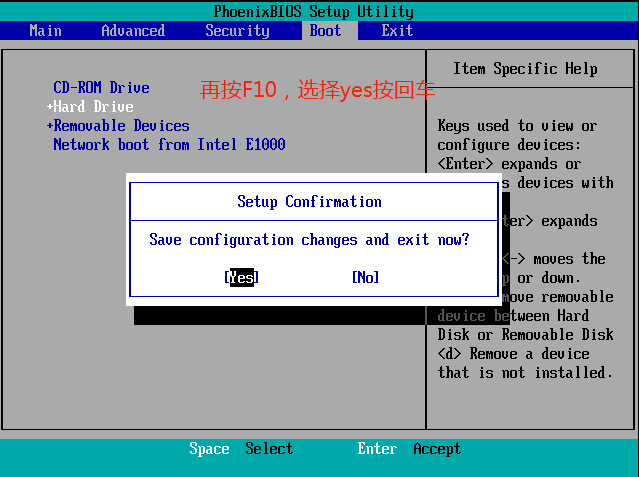
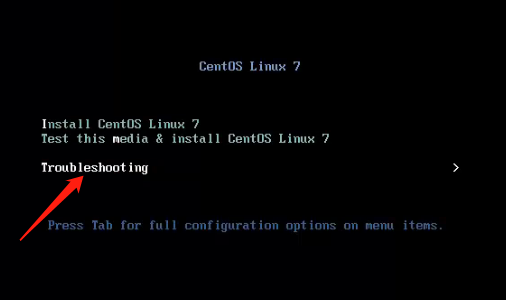
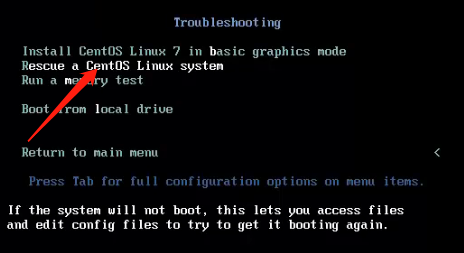
Press 1 then Enter

The following characters, press Enter
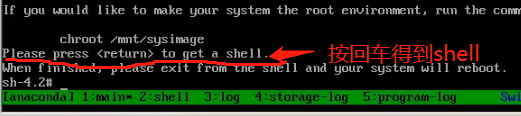
The above command will prompt written below
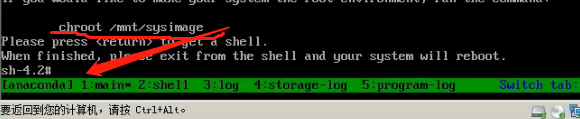
Then you can modify the password (passwd root)
Finally, the CD / DVD before removing the hook (that is, after the restart no longer enter the BIOS)
Restart the virtual machine on it
1.15 clone virtual machines and modify the host name:
1. After Shutdown
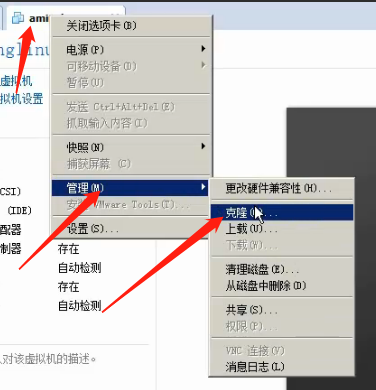
2.
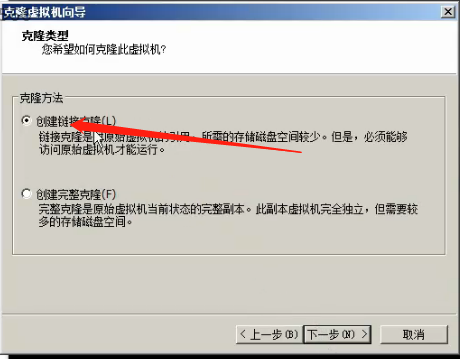
3. Modify the name and
4. Modify the IP, the number can be changed at the end (vi / etc / sysconfig / network_scripts / ifcfg-ens33)
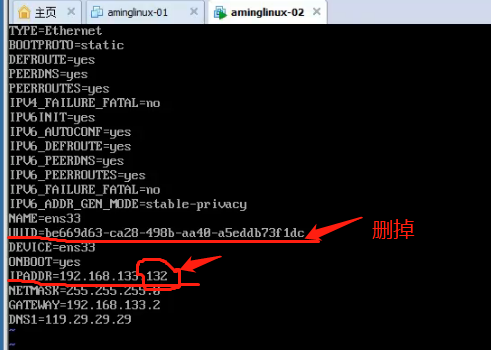
Then restart the network services (systemctl restart network.service)
Modify the host name:
Enter hostnamectl set-hostname aminglinux-02 (behind the need for the change of name)
1.16 Linux machine each visit:
1. For example, 01 even 02, with 02 behind ssh IP (you can use "W" to view the status)
Standard wording for the ssh username@ip
whoami can see who the current user, the default is the root
Therefore, under the above state standard wording should ssh [email protected] (02's IP)
2.ssh default port is a port 22, if there is a special port, the port 220 is assumed
As ssh -p 220 [email protected]
3. Key authentication connection:
If you have 01, 02, 02 and even private, there must be public on 01
Therefore, the input ssh-keygen (i.e., generate the key pair) occurs less FIG.
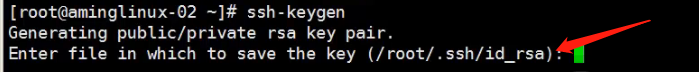
Meaning is to ask for a key to be stored where the default if you press Enter, the following figure will appear
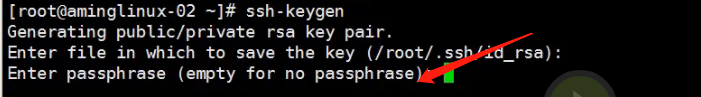
Meaning that enter the key password, enter that is empty
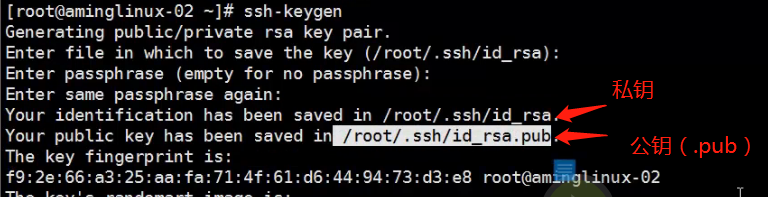
With the cat (listed) /root/.ssh/id_rsa.pub (marked above public address), and copy
01 to the (machine to be attached), vi /root/.ssh/authorizen_keys, copy down the 02 public key 01 to the paste
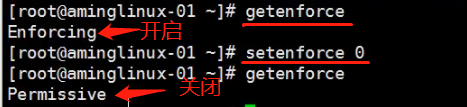
4. Check the switching state of the firewall with getenforce selinux
getenforce 0 may temporarily turn off (after the restart will open again)
Reproduced in: https: //my.oschina.net/u/3866192/blog/3059310
