I. Overview:
- Used to describe a series of string or match a statement in line with the rules
Second, a single symbol
. "" 1, English dot notation: matches any single character.
- Expression "to" match: tno, t # o, teo and so on. May not match: tnno, to, Tno, t o n the like.
2, in brackets "[]": only specified character inside the square brackets to be involved in matches, only matches a single character.
- Expression: t [abcd] n can only be matched: tan, tbn, tcn, tdn. Can not match: thn, tabn, tn and so on.
3, "|" symbol. Comparable "or" can match the specified character, but can only choose one to match.
- Expression: t (a | b | c | dd) n can only be matched: tan, tbn, tcn, tddn. You can not match taan, tn, tabcn
4, the number of matching symbols representing
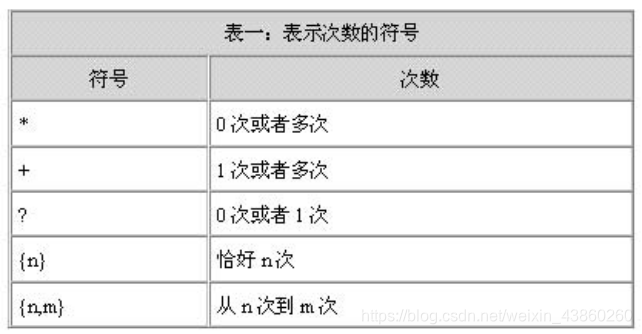
- Expression: [0-9] 3} {\ - [0-9]} 2 {\ - [0-9] {3} match the format: 999-99-999
because the "-" symbol in the regular expression It has a special meaning, representing a range, preceded by the escape character "\."
5, "^" symbol: Indicates whether, if in square brackets, "^" represents the characters do not want to match.
- Expression: [^ x] is not the first character x
6, "\ S" symbol: non-null character
7, "\ s" symbols: empty string, a match can only spaces, tabs, carriage returns, page break, may not match their input a plurality of spaces.
8, "\ r" symbol: space character, and "\ n", "\ tab " same
Third, fast sign
1, \ d represents [0-9]
2, \ D represents [^ 0-9]
. 3, \ W represents [0-9A-Z_a-Z]
. 4, \ W is [^ 0-9A-Z_a-Z] represents
5, \ s represents [\ T \ n-\ R & lt \ F]
. 6, \ S represents [^ \ t \ n \ r \ f]
Fourth, the common regular expressions
1, Java: (([a-z]|_)(\\w*)){6,20}matching start with a letter or underscore, underlined numbers ending letter string
2, JavaScript: /^(\-?)(\d+)$/matching digits
3, JavaScript: /^\w+$/matching alphanumeric underlined.
Five, Java regular expression applications
1, determining function
public boolean matches(String regex)
Example: determining whether the input phone number beginning with 13 or 18
package Lemon;
import java.util.Scanner;
public class RegexDm {
public static void main(String[] args){
Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in);
System.out.println("请输入手机好:");
String s = sc.nextLine();
String regex = "1[38]\\d{9}";//定义手机好规则
boolean flag = s.matches(regex);//判断功能
System.out.println("flag:"+flag);
}
}
2, split function
public String[] split(String regex)
Case:
package Lemon;
import java.util.Scanner;
public class RegexDm {
public static void main(String[] args){
String age = "18-24";//定义年龄范围
String regex = "-";
String[] strArr = age.split(regex);//分割成字符串数组
int startAge = Integer.parseInt(strArr[0]);
int endAge = Integer.parseInt(strArr[1]);
Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in);
System.out.println("请输入您的年龄:");
int a = sc.nextInt();
if (a >= startAge && a <= endAge){
System.out.println("你就是我想找的");
}else{
System.out.println("滚");
}
}
}
3. Replace function
public String replaceAll(String regex,String replacement)
Case:
package Lemon;
public class RegexDm {
public static void main(String[] args){
String s = "12342jasfkgnas234";
//把字符串里面的数字替换成*
String regex = "\\d";
String ss = "*";
String result = s.replaceAll(regex,ss);
System.out.println(result);
}
}
4, acquisition function
Pattern和Matcher类的使用
Six commonly used regular expressions
(1)"^\d+$" //非负整数(正整数 + 0)
(2)"^[0-9]*[1-9][0-9]*$" //正整数
(3)"^((-\d+)|(0+))$" //非正整数(负整数 + 0)
(4)"^-[0-9]*[1-9][0-9]*$" //负整数
(5)"^-?\d+$" //整数
(6)"^\d+(\.\d+)?$" //非负浮点数(正浮点数 + 0)
(7)"^(([0-9]+\.[0-9]*[1-9][0-9]*)|([0-9]*[1-9][0-9]*\.[0-9]+)|([0-9]*[1-9][0-9]*))$" //正浮点数
(8)"^((-\d+(\.\d+)?)|(0+(\.0+)?))$" //非正浮点数(负浮点数 + 0)
(9)"^(-(([0-9]+\.[0-9]*[1-9][0-9]*)|([0-9]*[1-9][0-9]*\.[0-9]+)|([0-9]*[1-9][0-9]*)))$" //负浮点数
(10)"^(-?\d+)(\.\d+)?$" //浮点数
(11)"^[A-Za-z]+$" //由26个英文字母组成的字符串
(12)"^[A-Z]+$" //由26个英文字母的大写组成的字符串
(13)"^[a-z]+$" //由26个英文字母的小写组成的字符串
(14)"^[A-Za-z0-9]+$" //由数字和26个英文字母组成的字符串
(15)"^\w+$" //由数字、26个英文字母或者下划线组成的字符串
(16)"^[\w-]+(\.[\w-]+)*@[\w-]+(\.[\w-]+)+$" //email地址
(17)"^[a-zA-z]+://(\w+(-\w+)*)(\.(\w+(-\w+)*))*(\?\S*)?$" //url
(18)/^(d{2}|d{4})-((0([1-9]{1}))|(1[1|2]))-(([0-2]([1-9]{1}))|(3[0|1]))$/ // 年-月-日
(19)/^((0([1-9]{1}))|(1[1|2]))/(([0-2]([1-9]{1}))|(3[0|1]))/(d{2}|d{4})$/ // 月/日/年
(20)"^([w-.]+)@(([[0-9]{1,3}.[0-9]{1,3}.[0-9]{1,3}.)|(([w-]+.)+))([a-zA-Z]{2,4}|[0-9]{1,3})(]?)$" //Emil
(21)/^((\+?[0-9]{2,4}\-[0-9]{3,4}\-)|([0-9]{3,4}\-))?([0-9]{7,8})(\-[0-9]+)?$/ //电话号码
(22)"^(d{1,2}|1dd|2[0-4]d|25[0-5]).(d{1,2}|1dd|2[0-4]d|25[0-5]).(d{1,2}|1dd|2[0-4]d|25[0-5]).(d{1,2}|1dd|2[0-4]d|25[0-5])$" //IP地址
(23)
(24)匹配中文字符的正则表达式: [\u4e00-\u9fa5]
(25)匹配双字节字符(包括汉字在内):[^\x00-\xff]
(26)匹配空行的正则表达式:\n[\s| ]*\r
(27)匹配HTML标记的正则表达式:/<(.*)>.*<\/\1>|<(.*) \/>/
(28)匹配首尾空格的正则表达式:(^\s*)|(\s*$)
(29)匹配Email地址的正则表达式:\w+([-+.]\w+)*@\w+([-.]\w+)*\.\w+([-.]\w+)*
(30)匹配网址URL的正则表达式:^[a-zA-z]+://(\\w+(-\\w+)*)(\\.(\\w+(-\\w+)*))*(\\?\\S*)?$
(31)匹配帐号是否合法(字母开头,允许5-16字节,允许字母数字下划线):^[a-zA-Z][a-zA-Z0-9_]{4,15}$
(32)匹配国内电话号码:(\d{3}-|\d{4}-)?(\d{8}|\d{7})?
(33)匹配腾讯QQ号:^[1-9]*[1-9][0-9]*$
(34)元字符及其在正则表达式上下文中的行为:
(35)\ 将下一个字符标记为一个特殊字符、或一个原义字符、或一个后向引用、或一个八进制转义符。
(36)^ 匹配输入字符串的开始位置。如果设置了 RegExp 对象的Multiline 属性,^ 也匹配 ’\n’ 或 ’\r’ 之后的位置。
(37)$ 匹配输入字符串的结束位置。如果设置了 RegExp 对象的Multiline 属性,$ 也匹配 ’\n’ 或 ’\r’ 之前的位置。
(38)* 匹配前面的子表达式零次或多次。
(39)+ 匹配前面的子表达式一次或多次。+ 等价于 {1,}。
(40)? 匹配前面的子表达式零次或一次。? 等价于 {0,1}。
(41){n} n 是一个非负整数,匹配确定的n 次。
(42){n,} n 是一个非负整数,至少匹配n 次。
(43){n,m} m 和 n 均为非负整数,其中n <= m。最少匹配 n 次且最多匹配 m 次。在逗号和两个数之间不能有空格。
(44)? 当该字符紧跟在任何一个其他限制符 (*, +, ?, {n}, {n,}, {n,m}) 后面时,匹配模式是非贪婪的。非贪婪模式尽可能少的匹配所搜索的字符串,而默认的贪婪模式则尽可能多的匹配所搜索的字符串。
(45). 匹配除 "\n" 之外的任何单个字符。要匹配包括 ’\n’ 在内的任何字符,请使用象 ’[.\n]’ 的模式。
(46)(pattern) 匹配pattern 并获取这一匹配。
(47)(?:pattern) 匹配pattern 但不获取匹配结果,也就是说这是一个非获取匹配,不进行存储供以后使用。
(48)(?=pattern) 正向预查,在任何匹配 pattern 的字符串开始处匹配查找字符串。这是一个非获取匹配,也就是说,该匹配不需要获取供以后使用。
(49)(?!pattern) 负向预查,与(?=pattern)作用相反
(50)x|y 匹配 x 或 y。
(51)[xyz] 字符集合。
(52)[^xyz] 负值字符集合。
(53)[a-z] 字符范围,匹配指定范围内的任意字符。
(54)[^a-z] 负值字符范围,匹配任何不在指定范围内的任意字符。
(55)\b 匹配一个单词边界,也就是指单词和空格间的位置。
(56)\B 匹配非单词边界。
(57)\cx 匹配由x指明的控制字符。
(58)\d 匹配一个数字字符。等价于 [0-9]。
(59)\D 匹配一个非数字字符。等价于 [^0-9]。
(60)\f 匹配一个换页符。等价于 \x0c 和 \cL。
(61)\n 匹配一个换行符。等价于 \x0a 和 \cJ。
(62)\r 匹配一个回车符。等价于 \x0d 和 \cM。
(63)\s 匹配任何空白字符,包括空格、制表符、换页符等等。等价于[ \f\n\r\t\v]。
(64)\S 匹配任何非空白字符。等价于 [^ \f\n\r\t\v]。
(65)\t 匹配一个制表符。等价于 \x09 和 \cI。
(66)\v 匹配一个垂直制表符。等价于 \x0b 和 \cK。
(67)\w 匹配包括下划线的任何单词字符。等价于’[A-Za-z0-9_]’。
(68)\W 匹配任何非单词字符。等价于 ’[^A-Za-z0-9_]’。
(69)\xn 匹配 n,其中 n 为十六进制转义值。十六进制转义值必须为确定的两个数字长。
(70)\num 匹配 num,其中num是一个正整数。对所获取的匹配的引用。
(71)\n 标识一个八进制转义值或一个后向引用。如果 \n 之前至少 n 个获取的子表达式,则 n 为后向引用。否则,如果 n 为八进制数字 (0-7),则 n 为一个八进制转义值。
(72)\nm 标识一个八进制转义值或一个后向引用。如果 \nm 之前至少有is preceded by at least nm 个获取得子表达式,则 nm 为后向引用。如果 \nm 之前至少有 n 个获取,则 n 为一个后跟文字 m 的后向引用。如果前面的条件都不满足,若 n 和 m 均为八进制数字 (0-7),则 \nm 将匹配八进制转义值 nm。
(73)\nml 如果 n 为八进制数字 (0-3),且 m 和 l 均为八进制数字 (0-7),则匹配八进制转义值 nml。
(74)\un 匹配 n,其中 n 是一个用四个十六进制数字表示的Unicode字符。
(75)匹配中文字符的正则表达式: [u4e00-u9fa5]
(76)匹配双字节字符(包括汉字在内):[^x00-xff]
(77)匹配空行的正则表达式:n[s| ]*r
(78)匹配HTML标记的正则表达式:/<(.*)>.*</1>|<(.*) />/
(79)匹配首尾空格的正则表达式:(^s*)|(s*$)
(80)匹配Email地址的正则表达式:w+([-+.]w+)*@w+([-.]w+)*.w+([-.]w+)*
(81)匹配网址URL的正则表达式:http://([w-]+.)+[w-]+(/[w- ./?%&=]*)?
(82)利用正则表达式限制网页表单里的文本框输入内容:
(83)用正则表达式限制只能输入中文:onkeyup="value=value.replace(/[^u4E00-u9FA5]/g,'')" onbeforepaste="clipboardData.setData('text',clipboardData.getData('text').replace(/[^u4E00-u9FA5]/g,''))"
(84)用正则表达式限制只能输入全角字符: onkeyup="value=value.replace(/[^uFF00-uFFFF]/g,'')" onbeforepaste="clipboardData.setData('text',clipboardData.getData('text').replace(/[^uFF00-uFFFF]/g,''))"
(85)用正则表达式限制只能输入数字:onkeyup="value=value.replace(/[^d]/g,'') "onbeforepaste="clipboardData.setData('text',clipboardData.getData('text').replace(/[^d]/g,''))"
(86)用正则表达式限制只能输入数字和英文:onkeyup="value=value.replace(/[W]/g,'') "onbeforepaste="clipboardData.setData('text',clipboardData.getData('text').replace(/[^d]/g,''))"
(87)
(88)
(89)整理:
(90)
(91)匹配中文字符的正则表达式: [\u4e00-\u9fa5]
(92)匹配双字节字符(包括汉字在内):[^\x00-\xff]
(93)匹配空行的正则表达式:\n[\s| ]*\r
(94)匹配HTML标记的正则表达式:/<(.*)>.*<\/\1>|<(.*) \/>/
(95)匹配首尾空格的正则表达式:(^\s*)|(\s*$)
(96)匹配IP地址的正则表达式:/(\d+)\.(\d+)\.(\d+)\.(\d+)/g //
(97)匹配Email地址的正则表达式:\w+([-+.]\w+)*@\w+([-.]\w+)*\.\w+([-.]\w+)*
(98)匹配网址URL的正则表达式:http://(/[\w-]+\.)+[\w-]+(/[\w- ./?%&=]*)?
(99)sql语句:^(select|drop|delete|create|update|insert).*$
(100)1、非负整数:^\d+$
(101)2、正整数:^[0-9]*[1-9][0-9]*$
(102)3、非正整数:^((-\d+)|(0+))$
(103)4、负整数:^-[0-9]*[1-9][0-9]*$
(104)
(105)5、整数:^-?\d+$
(106)
(107)6、非负浮点数:^\d+(\.\d+)?$
(108)
(109)7、正浮点数:^((0-9)+\.[0-9]*[1-9][0-9]*)|([0-9]*[1-9][0-9]*\.[0-9]+)|([0-9]*[1-9][0-9]*))$
(110)
(111)8、非正浮点数:^((-\d+\.\d+)?)|(0+(\.0+)?))$
(112)
(113)9、负浮点数:^(-((正浮点数正则式)))$
(114)
(115)10、英文字符串:^[A-Za-z]+$
(116)
(117)11、英文大写串:^[A-Z]+$
(118)
(119)12、英文小写串:^[a-z]+$
(120)
(121)13、英文字符数字串:^[A-Za-z0-9]+$
(122)
(123)14、英数字加下划线串:^\w+$
(124)
(125)15、E-mail地址:^[\w-]+(\.[\w-]+)*@[\w-]+(\.[\w-]+)+$
(126)
(127)16、URL:^[a-zA-Z]+://(\w+(-\w+)*)(\.(\w+(-\w+)*))*(\?\s*)?$
(128)或:^http:\/\/[A-Za-z0-9]+\.[A-Za-z0-9]+[\/=\?%\-&_~`@[\]\':+!]*([^<>\"\"])*$
(129)
(130)17、邮政编码:^[1-9]\d{5}$
(131)
(132)18、中文:^[\u0391-\uFFE5]+$
(133)
(134)19、电话号码:^((\(\d{2,3}\))|(\d{3}\-))?(\(0\d{2,3}\)|0\d{2,3}-)?[1-9]\d{6,7}(\-\d{1,4})?$
(135)
(136)20、手机号码:^((\(\d{2,3}\))|(\d{3}\-))?13\d{9}$
(137)
(138)21、双字节字符(包括汉字在内):^\x00-\xff
(139)
(140)22、匹配首尾空格:(^\s*)|(\s*$)(像vbscript那样的trim函数)
(141)
(142)23、匹配HTML标记:<(.*)>.*<\/\1>|<(.*) \/>
(143)
(144)24、匹配空行:\n[\s| ]*\r
(145)
(146)25、提取信息中的网络链接:(h|H)(r|R)(e|E)(f|F) *= *('|")?(\w|\\|\/|\.)+('|"| *|>)?
(147)
(148)26、提取信息中的邮件地址:\w+([-+.]\w+)*@\w+([-.]\w+)*\.\w+([-.]\w+)*
(149)
(150)27、提取信息中的图片链接:(s|S)(r|R)(c|C) *= *('|")?(\w|\\|\/|\.)+('|"| *|>)?
(151)
(152)28、提取信息中的IP地址:(\d+)\.(\d+)\.(\d+)\.(\d+)
(153)
(154)29、提取信息中的中国手机号码:(86)*0*13\d{9}
(155)
(156)30、提取信息中的中国固定电话号码:(\(\d{3,4}\)|\d{3,4}-|\s)?\d{8}
(157)
(158)31、提取信息中的中国电话号码(包括移动和固定电话):(\(\d{3,4}\)|\d{3,4}-|\s)?\d{7,14}
(159)
(160)32、提取信息中的中国邮政编码:[1-9]{1}(\d+){5}
(161)
(162)33、提取信息中的浮点数(即小数):(-?\d*)\.?\d+
(163)
(164)34、提取信息中的任何数字 :(-?\d*)(\.\d+)?
(165)
(166)35、IP:(\d+)\.(\d+)\.(\d+)\.(\d+)
(167)
(168)36、电话区号:/^0\d{2,3}$/
(169)
(170)37、腾讯QQ号:^[1-9]*[1-9][0-9]*$
(171)
(172)38、帐号(字母开头,允许5-16字节,允许字母数字下划线):^[a-zA-Z][a-zA-Z0-9_]{4,15}$
(173)
(174)39、中文、英文、数字及下划线:^[\u4e00-\u9fa5_a-zA-Z0-9]+$
Seven examples
1, efficacy QQ number (required: 5-15 digits, not begin with 0)
package Lemon; import java.util.Scanner; public class RegexDm { public static void main(String[] args){ Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in); System.out.println("请输入您的QQ号码:"); String qq = sc.nextLine(); System.out.println("checkQQ:"+checkQQ(qq)); } private static boolean checkQQ(String qq) { return qq.matches("[1-9]{1}\\d{4,14}"); } }