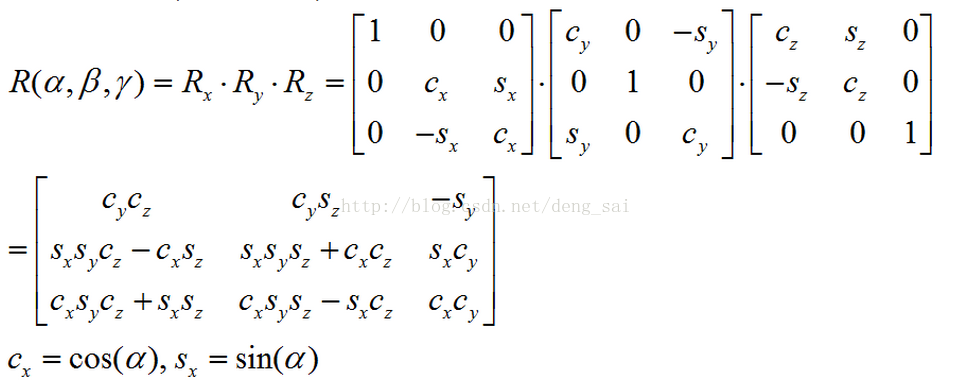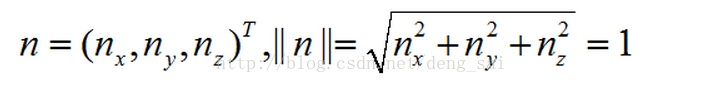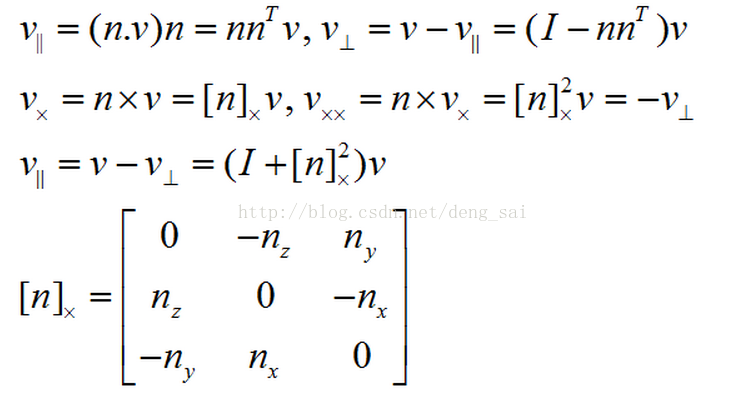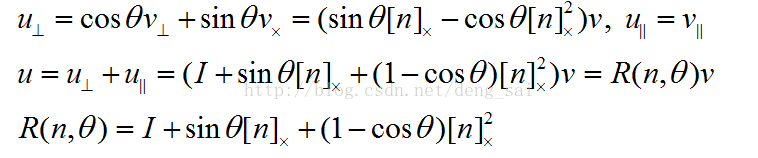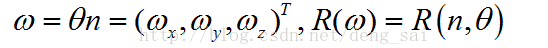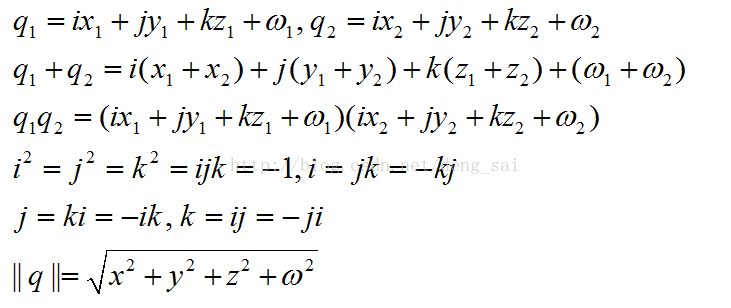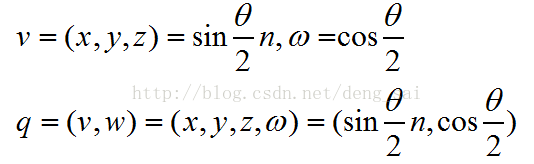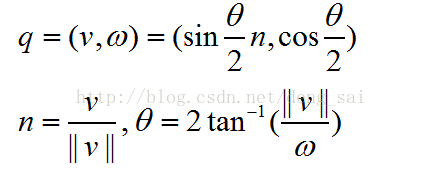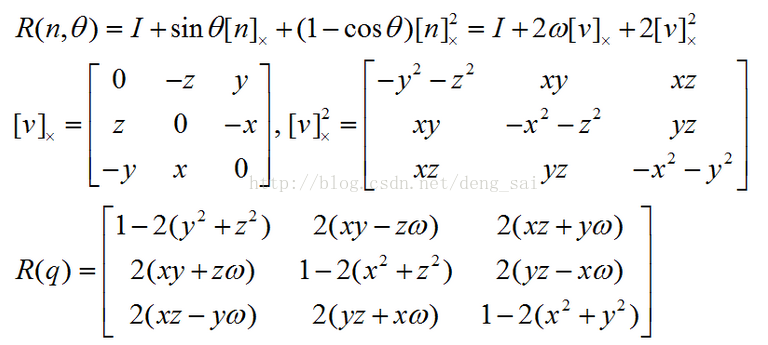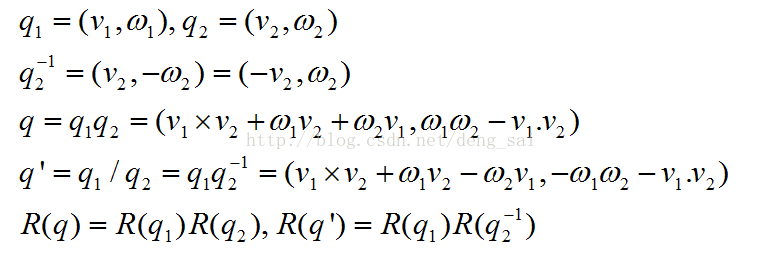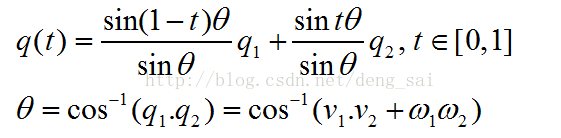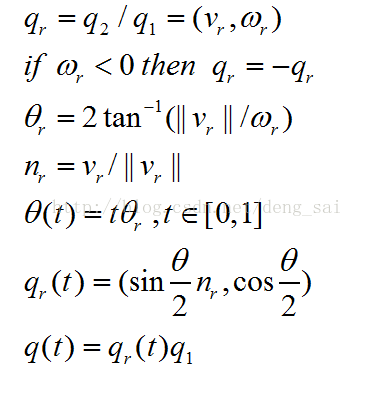Transfer: https://blog.csdn.net/deng_sai/article/details/21169997
Transfer: http://hi.baidu.com/herohbc/item/4d20780de7726697a2df437f
Calculating three-dimensional rotation matrix
In three dimensions, the rotational transform is one of the basic transform type, described in a variety of ways, such as Euler angles, rotation matrix, the rotation shaft / rotation angle quaternion and the like. This article describes the various ways described and transitions between them.
1. The rotation matrix
With a third-order orthogonal transform matrix represents the rotation, it is the most common representation. Easy to show that the degree of freedom for the 3 3 matrix quadrature. Note that, its determinant must equal 1, when the time is equal to -1 corresponds to a mirroring also made.
2. Euler angles
According to Euler theorem in three dimensions, any rotation conversion can be attributed to a combination of rotation around a plurality of axes, the number of combinations of two and no more than three adjacent must rotate along different axes . Thus, the angle can be used along the three axes of rotation to represent a transformation, called Euler angles. Rotational transformation are not interchangeable, depending on the rotation sequence, there are 12 kinds of representation, namely: XYZ, XZY, XYX, XZX, YXZ, YZX, YXY, YZY, ZXY, ZYX, ZXZ, ZYZ, can freely choose where a. For the same conversion, different rotation sequence, Euler angles are different, when specifying the Euler angles conventions should first rotation sequence.
2.1 Euler angle is converted to a rotation matrix
You may wish to set gamma] around the Z axis, then the rotation β around the Y-axis, and finally the rotation α around the X axis, i.e., the XYZ rotation order, the rotation matrix
3. The rotating shaft / rotation angle
θ is represented by a vector n and the rotation angle of the rotation direction of the rotary shaft, wherein
θ> 0 counterclockwise rotation.
3.1 rotating shaft / the rotational angle is converted to a rotation matrix
Let v be any vector, defined
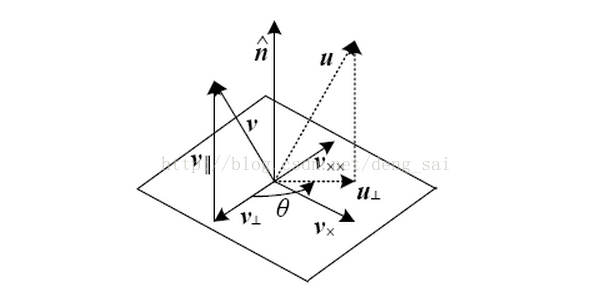
As shown below
In this way, we have established a Cartesian coordinate system 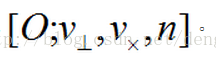
Let u is a vector v obtained after the rotation about the axis, there is
R is the rotation matrix. Further it can be expressed as
4. 单位四元数(Unit quaternions)
四元数由Hamilton于1843年提出,实际上是在四维向量集合上定义了通常的向量加法和新的乘法运算,从而形成了一个环。
q称为单位四元数,如果||q||=1。一个单位四元数可以表示三维旋转。用单位四元数表示旋转可以保持一个光滑移动的相机的轨迹,适合动画生成。
4.1 旋转轴/旋转角度 转化为 单位四元数
根据旋转轴n和旋转角度θ,得到单位四元数q
4.2 单位四元数 转化为 旋转轴/旋转角度
4.3 单位四元数 转化为 旋转矩阵
4.4 四元数的性质
定义四元数的逆、乘法和除法,如下所示
根据该性质,我们可以对两个旋转变换q1和q2作线性插值,这相当于在四维空间中的超球面上对点q1和q2作球面线性插值。
也可以按下面的方法计算