Basic environment:
System: CentOS 6.5
Storm: 1.1.1
the JDK: 1.8
I. Introduction
Storm is the first real-time processing system developed by the BackType, the underlying implementation of Clojure, Clojure is a JVM-based senior-oriented functional programming language.
2011 Twitter's acquisition of BackType company, will use the Storm to help enterprises solve problems in real-time processing of massive data.
Ali Baba, the Storm, based on the use of Java Clojure proxy implements the core, and optimized in terms of performance, resulting in JStorm.
Storm and currently has Jstrom Apache organization and management Foundation.
Storm is a distributed, secure, fault-tolerant data stream processing system. It will delegate tasks to different types of components, each responsible for a specific task simple. Storm input stream is called a cluster by the component management spout,
spout to pass data to the bolt, bolt or save data to some memory, or transmitting data to the other bolt. You can imagine a Storm cluster is converted spout pass over the series of data between the bolt.
It is a real-time data analysis framework
- storm streaming data processing framework: true real-time processing framework for processing data on a time, up to milliseconds
- spark streaming real-time data analysis framework: Micro batch process frame data, processes the data in a few seconds, the time span is relatively small, close seconds.
- lot
Data analysis and processing
- Data analysis is based on a certain time period.
- Batch, real-time processing. Essentially the same time span is not the same.
- Batch: The time span is relatively large. A year, a quarter, month, week day, one hour, one minute, one second (it has come to the real-time)
- Real-time processing: time span small batch. * Per unit time (seconds) larger than the data, GB TB
Second, build environment
1. Download the official website: http://storm.apache.org
2. zookeeper cluster installation requirements, pythod2.6.6 + (analogous to cage)
The system will default install python, is recommended to check whether the installation
python --version
rpm -qa | grep python
Install python
cd /opt/software
wget https://www.python.org/ftp/python/2.7.11/Python-2.7.11.tgz
tar -zxvf Python-2.7.11.tgz
mv Python-2.7.11 /opt/module/pythonexport LANG=zh_CN.UTF-8
export LANGUAGE=zh_CN.UTF-8
./configure
make
make install
Executable file in the / usr / bin, if there is no change over, can delete the directory under the python file, and then compiled python files immediately after the last copy
3. Extract
cd /opt/software
tar -zxvf apache-storm-1.1.1.tar.gz
mv apache-storm-1.1.1 /opt/module/storm4. Modify the configuration file
storm.yaml
(1) zookeeper cluster
storm.zookeeper.servers:
- "node1.sunny.cn"
- "node2.sunny.cn"
- "node3.sunny.cn"Zookeeper if not the default port used in the cluster, you also need storm.zookeeper.port options.
(2) nimbus.seeds represents the master node configuration, can be configured to a plurality of, with between each master node "," separated.
nimbus.seeds: ["node1.sunny.cn"]5. Start
启动nimbus(主节点): nohup bin/storm nimbus &
启动supervisor(计算子节点):nohup bin/storm supervisor &
启动storm ui(监控画面): nohup bin/storm ui &
启动logviewer(在每个supervisor节点上启动):nohup bin/storm logviewer &Verify: node1.sunny.cn: 8080

Third, the architecture and various components
Storm Chart

All coordination between Nimbus and Supervisor is done by Zookeeper cluster. In addition, Nimbus and Supervisor processes are fail-fast process (fail-fast) and stateless. All state zookeeper either inside or on the local disk. This means you can use kill -9 to kill Nimbus and Supervisor process, and then restart them, as if nothing had happened. This design makes the Storm unusual stability.
Nimbus master node:
- Receiving a request submitted by the client task, the task assigned by Nimbus, zookeeper allocation information submitted to the cluster (znode on respective nodes ZK, write task allocation information, view the information on the task assigned by the Supervisor these znode, assigned to acquired task.)
- Monitor the status of the entire cluster. (Read from the corresponding cluster zookeeper znode supervisor, worker process status information data.)
- Fault Tolerance: When the task run on certain supervisor node, the task process fails, re-assign these tasks to other supervisor node operation.
Supervisor:
- 需要定时将自己的运行状态信息(心跳信息)汇报给zookeeper(在zk相应的znode节点上写入心跳信息)
- 接受nimbus分配给它的任务,负责启动工作进程,停止工作进程。 其本身并不是执行任务的工作进程。worker的容错也是由supervisor负责。
- 后台启动:nohup bin/storm supervisor
Worker:并不是常驻进程,不能通过手动启动,是真正执行任务的进程。
Excuter 线程:worker进程来启动,executor负责执行客户提交到storm集群上的task(spout/bolt)
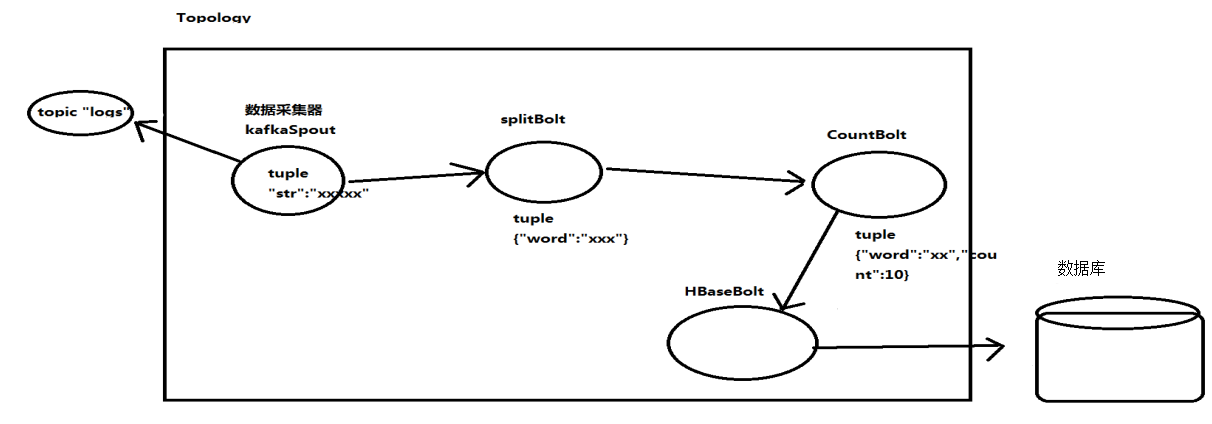
1、Topologies
一个topology是spouts和bolts组成的图, 通过stream groupings将图中的spouts和bolts连接起来,如下图:
一个topology会一直运行直到你手动kill掉,Storm自动重新分配执行失败的任务, 并且Storm可以保证你不会有数据丢失(如果开启了高可靠性的话)。如果一些机器意外停机它上面的所有任务会被转移到其他机器上。
运行一个topology很简单。首先,把你所有的代码以及所依赖的jar打进一个jar包。然后运行类似下面的这个命令:
storm jar all-my-code.jar backtype.storm.MyTopology arg1 arg2
这个命令会运行主类: backtype.strom.MyTopology, 参数是arg1, arg2。这个类的main函数定义这个topology并且把它提交给Nimbus。storm jar负责连接到Nimbus并且上传jar包。
Topology的定义是一个Thrift结构,并且Nimbus就是一个Thrift服务, 你可以提交由任何语言创建的topology。上面的方面是用JVM-based语言提交的最简单的方法。
杀掉任务:bin/storm kill wordcount
每个提交到storm集群上的任务就是Topology。
Topology就是一个有向无环图。 (拓扑图,DAG)
Topology:由spout和bolt两个组件组成。
- spout数据采集器,由它负责从数据源上获取数据,转发给后面的bolt进行处理。
- bolt数据处理器,在bolt里面实现数据的处理逻辑。
2、Streams
消息流stream是storm里的关键抽象。一个消息流是一个没有边界的tuple序列, 而这些tuple序列会以一种分布式的方式并行地创建和处理。通过对stream中tuple序列中每个字段命名来定义stream。在默认的情况下,tuple的字段类型可以是:integer,long,short, byte,string,double,float,boolean和byte array。你也可以自定义类型(只要实现相应的序列化器)。
每个消息流在定义的时候会被分配给一个id,因为单向消息流使用的相当普遍, OutputFieldsDeclarer定义了一些方法让你可以定义一个stream而不用指定这个id。在这种情况下这个stream会分配个值为‘default’默认的id 。
Storm提供的最基本的处理stream的原语是spout和bolt。你可以实现spout和bolt提供的接口来处理你的业务逻辑。
3、Spouts
消息源spout是Storm里面一个topology里面的消息生产者。一般来说消息源会从一个外部源读取数据并且向topology里面发出消息:tuple。Spout可以是可靠的也可以是不可靠的。如果这个tuple没有被storm成功处理,可靠的消息源spouts可以重新发射一个tuple, 但是不可靠的消息源spouts一旦发出一个tuple就不能重发了。
消息源可以发射多条消息流stream。使用OutputFieldsDeclarer.declareStream来定义多个stream,然后使用SpoutOutputCollector来发射指定的stream。
Spout类里面最重要的方法是nextTuple。要么发射一个新的tuple到topology里面或者简单的返回如果已经没有新的tuple。要注意的是nextTuple方法不能阻塞,因为storm在同一个线程上面调用所有消息源spout的方法。
另外两个比较重要的spout方法是ack和fail。storm在检测到一个tuple被整个topology成功处理的时候调用ack,否则调用fail。storm只对可靠的spout调用ack和fail。
4、Bolts
所有的消息处理逻辑被封装在bolts里面。Bolts可以做很多事情:过滤,聚合,查询数据库等等。
Bolts可以简单的做消息流的传递。复杂的消息流处理往往需要很多步骤,从而也就需要经过很多bolts。比如算出一堆图片里面被转发最多的图片就至少需要两步:第一步算出每个图片的转发数量。第二步找出转发最多的前10个图片。(如果要把这个过程做得更具有扩展性那么可能需要更多的步骤)。
Bolts可以发射多条消息流, 使用OutputFieldsDeclarer.declareStream定义stream,使用OutputCollector.emit来选择要发射的stream。
Bolts的主要方法是execute, 它以一个tuple作为输入,bolts使用OutputCollector来发射tuple,bolts必须要为它处理的每一个tuple调用OutputCollector的ack方法,以通知Storm这个tuple被处理完成了,从而通知这个tuple的发射者spouts。 一般的流程是: bolts处理一个输入tuple, 发射0个或者多个tuple, 然后调用ack通知storm自己已经处理过这个tuple了。storm提供了一个IBasicBolt会自动调用ack。
5、Stream groupings
定义一个topology的其中一步是定义每个bolt接收什么样的流作为输入。stream grouping就是用来定义一个stream应该如果分配数据给bolts上面的多个tasks。
Storm里面有7种类型的stream grouping
- Shuffle Grouping: 随机分组, 随机派发stream里面的tuple,保证每个bolt接收到的tuple数目大致相同。
- Fields Grouping:按字段分组, 比如按userid来分组, 具有同样userid的tuple会被分到相同的Bolts里的一个task, 而不同的userid则会被分配到不同的bolts里的task。
- All Grouping:广播发送,对于每一个tuple,所有的bolts都会收到。
- Global Grouping:全局分组, 这个tuple被分配到storm中的一个bolt的其中一个task。再具体一点就是分配给id值最低的那个task。
- Non Grouping:不分组,这个分组的意思是说stream不关心到底谁会收到它的tuple。目前这种分组和Shuffle grouping是一样的效果, 有一点不同的是storm会把这个bolt放到这个bolt的订阅者同一个线程里面去执行。
- Direct Grouping: 直接分组, 这是一种比较特别的分组方法,用这种分组意味着消息的发送者指定由消息接收者的哪个task处理这个消息。 只有被声明为Direct Stream的消息流可以声明这种分组方法。而且这种消息tuple必须使用emitDirect方法来发射。消息处理者可以通过TopologyContext来获取处理它的消息的task的id (OutputCollector.emit方法也会返回task的id)。
- Local or shuffle grouping:如果目标bolt有一个或者多个task在同一个工作进程中,tuple将会被随机发生给这些tasks。否则,和普通的Shuffle Grouping行为一致。
6、Reliability
Storm保证每个tuple会被topology完整的执行。Storm会追踪由每个spout tuple所产生的tuple树(一个bolt处理一个tuple之后可能会发射别的tuple从而形成树状结构),并且跟踪这棵tuple树什么时候成功处理完。每个topology都有一个消息超时的设置,如果storm在这个超时的时间内检测不到某个tuple树到底有没有执行成功, 那么topology会把这个tuple标记为执行失败,并且过一会儿重新发射这个tuple。
为了利用Storm的可靠性特性,在你发出一个新的tuple以及你完成处理一个tuple的时候你必须要通知storm。这一切是由OutputCollector来完成的。通过emit方法来通知一个新的tuple产生了,通过ack方法通知一个tuple处理完成了。
Storm的可靠性我们在第四章会深入介绍。
7、Tasks
每一个spout和bolt会被当作很多task在整个集群里执行。每一个executor对应到一个线程,在这个线程上运行多个task,而stream grouping则是定义怎么从一堆task发射tuple到另外一堆task。你可以调用TopologyBuilder类的setSpout和setBolt来设置并行度(也就是有多少个task)。
8、Workers
一个topology可能会在一个或者多个worker(工作进程)里面执行,每个worker是一个物理JVM并且执行整个topology的一部分。比如,对于并行度是300的topology来说,如果我们使用50个工作进程来执行,那么每个工作进程会处理其中的6个tasks。Storm会尽量均匀的工作分配给所有的worker。
9、Configuration
Storm里面有一堆参数可以配置来调整Nimbus, Supervisor以及正在运行的topology的行为,一些配置是系统级别的,一些配置是topology级别的。default.yaml里面有所有的默认配置。你可以通过定义个storm.yaml在你的classpath里来覆盖这些默认配置。并且你也可以在代码里面设置一些topology相关的配置信息(使用StormSubmitter)。
三、程序代码
通过计数器实现wordcount