
Table of contents
1. Overview of cloud computing operating model
2. Cloud computing service role
3. Cloud Computing Responsibility Model
3.1 Cloud computing service model and responsibility relationship diagram
3.2 Analysis of cloud computing service model and responsibility relationship
3.2.1 Assessment of cloud service responsibility capabilities
3.2.2 Assessment of cloud service security usage capabilities
3.3 Cloud computing responsibility sharing model diagram
3.4 Description of security responsibilities of IaaS, PaaS and SaaS models
4. Delivery of cloud computing services
4.1 Cloud computing delivery model
4.1.1 Mode 1: Enterprise-owned and self-operated
4.1.2 Model 2: Enterprise-owned, operation and maintenance outsourcing
4.1.3 Model 3: Enterprise-owned, operation and maintenance outsourcing, external operation
4.1.4 Mode 4: Enterprise leasing, external operation, exclusive resource
4.1.5 Mode 5: Enterprise leasing, external operation, resource sharing and scheduling
4.1.6 Mode 6: Public cloud services
1. Overview of cloud computing operating model
1.1 Overview
Cloud computing provides three service models : IaaS, PaaS and SaaS . In specific operations, cloud service providers and users share security responsibilities. The security responsibilities of the two are different under different service models.
2. Cloud computing service role
As cloud computing applications continue to deepen and expand, the market size of the entire cloud industry is growing rapidly . Cloud computing policies continue to be favorable, and national and local governments are actively encouraging the development of government cloud, industrial cloud, and financial cloud . The cloud computing market in these sub-sectors will become key investment and construction areas in the next few years. As important participants in the cloud computing industry chain, operators have promoted the rapid development of cloud computing services by actively penetrating into the enterprise market and subdivided industries.
2.1 Role division
In the general cloud computing architecture defined by NIST, five cloud computing-related roles are included, as follows.
2.1.1 Cloud service provider
That is, manufacturers that provide cloud services (cloud computing products), such as Amazon providing AWS cloud services, Alibaba providing Alibaba cloud services, Huawei providing Huawei cloud services, etc.
2.1.2 Cloud service consumers
That is, companies, enterprises and individual consumers who rent and use cloud service products.
2.1.3 Cloud Service Agent
That is, an agent for cloud service products. Because it is difficult for a product manufacturer to sell on its own, it usually looks for agents, who sell the products around the world. Since cloud services are products, there will naturally be agents.
2.1.4 Cloud Computing Auditor
That is, a third-party organization or individual that can independently evaluate the security, performance, and operation of cloud computing.
2.1.5 Cloud Service Carrier
That is, manufacturers that provide connection media between cloud service consumers and cloud service products. Usually cloud service consumers access and use cloud services through the Internet, so Internet service providers are the cloud service carriers here, such as China Telecom.
3. Cloud Computing Responsibility Model
3.1 Cloud computing service model and responsibility relationship diagram
Under different cloud computing service models, cloud service providers and customers have different control scopes and security responsibility scopes for computing resources. The control scope determines the boundaries of security responsibility. Responsibility for cloud security is shared between different types of roles, as shown in the diagram below.

3.2 Analysis of cloud computing service model and responsibility relationship
The division of security responsibilities is a pain point between cloud service providers and cloud service customers in cloud computing scenarios. Liability disputes often occur after security incidents occur. In the second half of 2019, the China Academy of Information and Communications Technology took the lead and collaborated with dozens of domestic cloud service providers to compile the "Cloud Computing Security Responsibility Shared Model" industry standard for public clouds . The standard standardizes cloud computing under the public cloud IaaS, PaaS, and SaaS models. A shared security responsibility model between service providers and cloud service customers .
3.2.1 Assessment of cloud service responsibility capabilities
Examine the security responsibilities of public cloud service providers (which provide at least one type of cloud service among IaaS, PaaS or SaaS) and the disclosure of security responsibilities, that is, whether they truthfully inform customers of the security responsibilities assumed by the cloud service provider.
3.2.2 Assessment of cloud service security usage capabilities
Examine the ability of public cloud service customers (who use at least one cloud service among IaaS, PaaS or SaaS) to use the cloud services securely.
When purchasing cloud services, you need to pay attention to signing relevant agreements with cloud service providers to clarify matters such as service levels, security responsibilities and obligations.
The infrastructure, physical hardware, resource abstraction and control layer of cloud computing are all under the full control of the cloud service provider, and all security responsibilities are borne by the cloud service provider. The security responsibilities of the application software layer, software platform layer, and virtualized computing resource layer are shared by both parties. The closer to the underlying cloud computing service (i.e., IaaS), the greater the customer's management and security responsibilities; conversely, the cloud service provider's Greater management and security responsibilities.
3.3 Cloud computing responsibility sharing model diagram
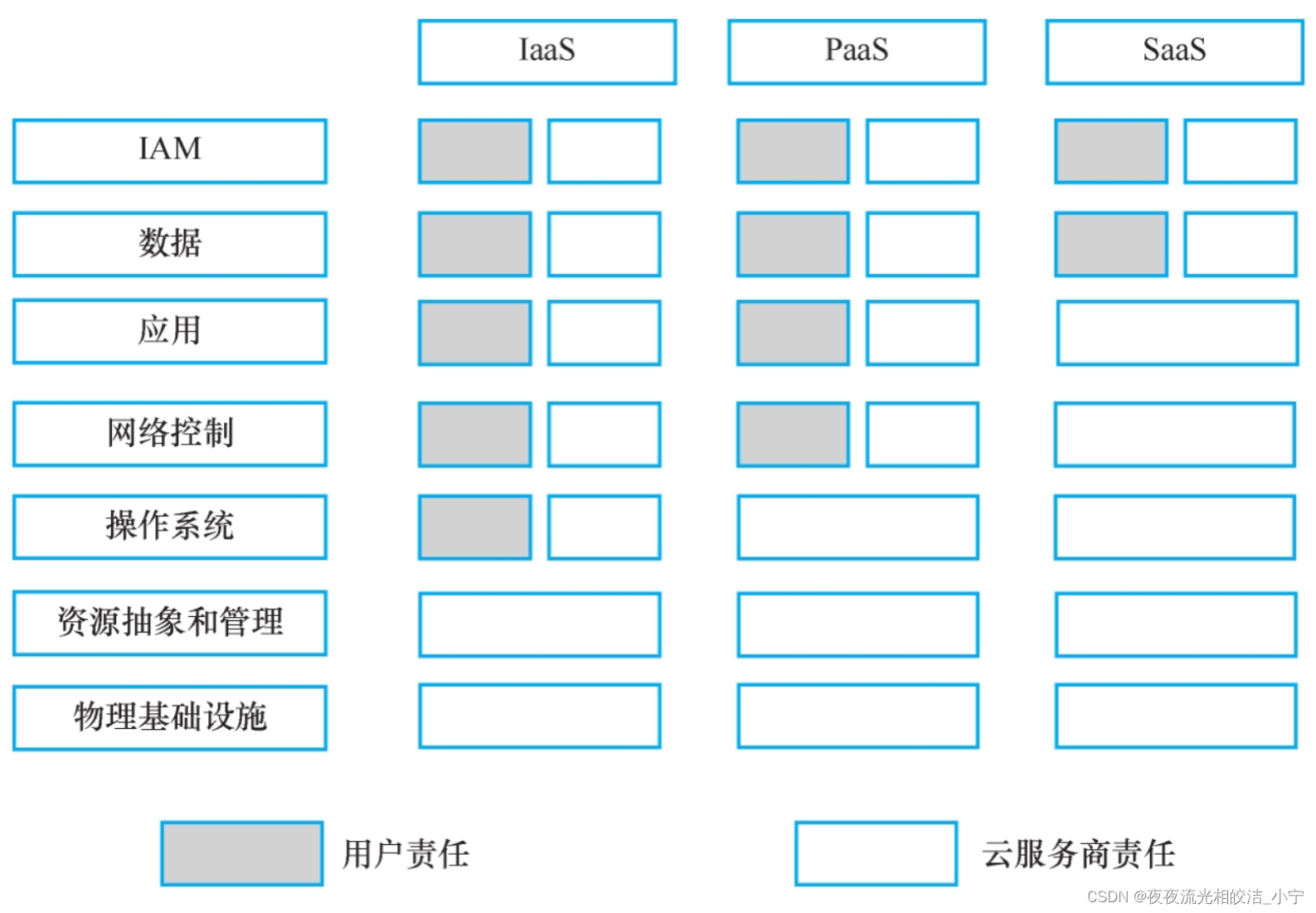
3.4 Description of security responsibilities of IaaS, PaaS and SaaS models
In IaaS, the customer's responsibility is the greatest, in SaaS the customer's responsibility is the least, and in PaaS the customer's responsibility is between IaaS and SaaS.
3.4.1 Saa model
In the SaaS model, customers only need to bear their own data security, client security and other related responsibilities, while the cloud service provider assumes other security responsibilities;
3.4.2 PaaS model
In the PaaS model, the security responsibility of the software platform layer is shared between customers and cloud service providers. Customers are responsible for the security of the applications they develop and deploy and their operating environments, and other security is the responsibility of the cloud service provider;
3.4.3 IaaS model
In the IaaS model, the security responsibility of the virtualized computing resource layer is shared between the customer and the cloud service provider. The customer is responsible for the security of the operating system, operating environment and applications deployed by them, as well as the operation, update, configuration security and reliability of these resources. Responsible, the cloud service provider is responsible for the security of the virtual machine monitor and underlying resources.
The security of the cloud computing environment is guaranteed by both the cloud service provider and the customer. In some cases, cloud service providers also rely on other organizations to provide computing resources and services, and other organizations should also bear security responsibilities. Therefore, there are multiple entities implementing cloud computing security measures, and the security responsibilities of various entities vary depending on different cloud computing service models.
4. Delivery of cloud computing services
Cloud computing service delivery mainly includes six modes, which are as follows.
4.1 Cloud computing delivery model
4.1.1 Mode 1: Enterprise-owned and self-operated
Model 1: Enterprise-owned and self-operated. This is a typical private cloud model. The enterprise builds and uses it for itself. The basic resources are in the enterprise data center, and the operation and maintenance are also borne by the enterprise itself.
4.1.2 Model 2: Enterprise-owned, operation and maintenance outsourcing
Model 2: Enterprise-owned, operation and maintenance outsourcing. This is also a private cloud, but the enterprise only invests in construction, while the operation and maintenance of the cloud computing architecture is outsourced to service providers (or SPs), and the basic resources are still in the enterprise data center.
4.1.3 Model 3: Enterprise-owned, operation and maintenance outsourcing, external operation
Model 3: Enterprise-owned, operation and maintenance outsourcing, external operation. Enterprises invest in building private clouds, but the cloud computing architecture is located in the service provider's data center, and enterprises access cloud resources through the network. This is a physical form of hosting.
4.1.4 Mode 4: Enterprise leasing, external operation, exclusive resource
Model 4: Enterprise leasing, external operation, and resource exclusive ownership. The SP builds the basic cloud computing resources, and the enterprise only rents the basic resources to form a virtual cloud computing for its own business, but the relevant physical resources are completely used exclusively by the enterprise. This is a virtual hosting type service (data hosting).
4.1.5 Mode 5: Enterprise leasing, external operation, resource sharing and scheduling
Mode 5: Enterprise leasing, external operation, resource sharing and scheduling. Built by SP, multiple enterprises rent SP's cloud computing resources at the same time. The isolation and scheduling of resources are managed by SP. Enterprises only focus on their own business. Different enterprises are virtualized and isolated within the cloud architecture, forming a shared private cloud model.
4.1.6 Mode 6: Public cloud services
Mode 6: Public cloud services. The SP provides Internet-oriented public services (such as email, instant messaging, shared disaster recovery, etc.) to enterprises or individuals. The cloud architecture is connected to the public network, and the SP ensures the data security of different enterprises and users.
From a longer-term perspective, the form of the cloud will continue to evolve, gradually developing from an isolated cloud to an interconnected cloud.
Okay, that’s all for sharing this content. Welcome everyone to pay attention to the " Cloud Computing Security " column. We will continue to output related content articles in the future. If it is helpful to you, you are welcome to like + follow + collect. If you have any questions, you are welcome to leave a comment!