The computer-based test interface is as follows (single-choice questions). The top is the question status, the bottom is the questions, and 1/5/1 is the number of questions completed, the total number of questions, and the number of correct questions.

Take another look at the multiple-choice question interface.

Interface for judgment questions.

Feedback when the answer is correct will include the time taken.

Feedback when answering incorrectly will show the correct answer and the time taken.
The overall score will be given at the end of the answer.

Question.java question bank
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.List;
class SingleChoice {
public String question, optionA, optionB, optionC, optionD, correctAnswer;
public SingleChoice(String question, String optionA, String optionB, String optionC, String optionD, String correctAnswer) {
this.question = question;
this.optionA = optionA;
this.optionB = optionB;
this.optionC = optionC;
this.optionD = optionD;
this.correctAnswer = correctAnswer;
}
}
class MultipleChoice {
public String question, optionA, optionB, optionC, optionD, correctAnswer;
public MultipleChoice(String question, String optionA, String optionB, String optionC, String optionD, String correctAnswer) {
this.question = question;
this.optionA = optionA;
this.optionB = optionB;
this.optionC = optionC;
this.optionD = optionD;
this.correctAnswer = correctAnswer;
}
}
class TrueOrFalse {
public String question;
public boolean correctAnswer;
public TrueOrFalse(String question, boolean correctAnswer) {
this.question = question;
this.correctAnswer = correctAnswer;
}
}
public class Questions {
public List<SingleChoice> singleChoices = new ArrayList<>();
public List<MultipleChoice> multipleChoices = new ArrayList<>();
public List<TrueOrFalse> trueOrFalse = new ArrayList<>();
public Questions() {
// 添加单选题
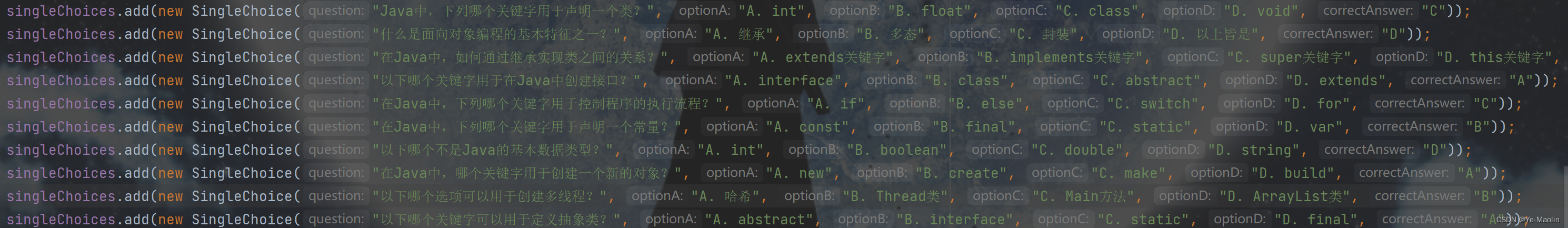
singleChoices.add(new SingleChoice("Java中,下列哪个关键字用于声明一个类?", "A. int", "B. float", "C. class", "D. void", "C"));
singleChoices.add(new SingleChoice("什么是面向对象编程的基本特征之一?", "A. 继承", "B. 多态", "C. 封装", "D. 以上皆是", "D"));
singleChoices.add(new SingleChoice("在Java中,如何通过继承实现类之间的关系?", "A. extends关键字", "B. implements关键字", "C. super关键字", "D. this关键字", "A"));
singleChoices.add(new SingleChoice("以下哪个关键字用于在Java中创建接口?", "A. interface", "B. class", "C. abstract", "D. extends", "A"));
singleChoices.add(new SingleChoice("在Java中,下列哪个关键字用于控制程序的执行流程?", "A. if", "B. else", "C. switch", "D. for", "C"));
singleChoices.add(new SingleChoice("在Java中,下列哪个关键字用于声明一个常量?", "A. const", "B. final", "C. static", "D. var", "B"));
singleChoices.add(new SingleChoice("以下哪个不是Java的基本数据类型?", "A. int", "B. boolean", "C. double", "D. string", "D"));
singleChoices.add(new SingleChoice("在Java中,哪个关键字用于创建一个新的对象?", "A. new", "B. create", "C. make", "D. build", "A"));
singleChoices.add(new SingleChoice("以下哪个选项可以用于创建多线程?", "A. 哈希", "B. Thread类", "C. Main方法", "D. ArrayList类", "B"));
singleChoices.add(new SingleChoice("以下哪个关键字可以用于定义抽象类?", "A. abstract", "B. interface", "C. static", "D. final", "A"));
// 添加多选题
multipleChoices.add(new MultipleChoice("下列哪些选项是Java的基本数据类型?", "A. boolean", "B. string", "C. integer", "D. double", "AD"));
multipleChoices.add(new MultipleChoice("下列哪些选项是Java中的流控制语句?", "A. if-else", "B. for", "C. while", "D. function", "ABC"));
multipleChoices.add(new MultipleChoice("下列哪些选项是Java中的包装类?", "A. Integer", "B. Float", "C. Long", "D. Char", "ABC"));
multipleChoices.add(new MultipleChoice("下列哪些选项是Java中的集合类?", "A. ArrayList", "B. LinkedList", "C. HashSet", "D. Map", "ABCD"));
multipleChoices.add(new MultipleChoice("下列哪些选项是Java中的线程状态?", "A. NEW", "B. RUNNING", "C. WAITING", "D. DEAD", "ABCD"));
multipleChoices.add(new MultipleChoice("下列哪些选项是Java中的线程同步方法?", "A. wait()", "B. notify()", "C. synchronized()", "D. interrupt()", "ABC"));
multipleChoices.add(new MultipleChoice("下列哪些选项是Java中的异常类型?", "A. Checked Exception", "B. Unchecked Exception", "C. Error", "D. Throwable", "ABCD"));
multipleChoices.add(new MultipleChoice("下列哪些选项是Java中的注解类型?", "A. @Override", "B. @Deprecated", "C. @SuppressWarnings", "D. @Inject", "ABCD"));
multipleChoices.add(new MultipleChoice("下列哪些选项是Java中的IO流类型?", "A. FileInputStream", "B. InputStreamReader", "C. OutputStream", "D. Socket", "ABCD"));
multipleChoices.add(new MultipleChoice("下列哪些选项是Java中的网络通信协议?", "A. TCP", "B. UDP", "C. FTP", "D. HTTP", "ABCD"));
//添加判断题
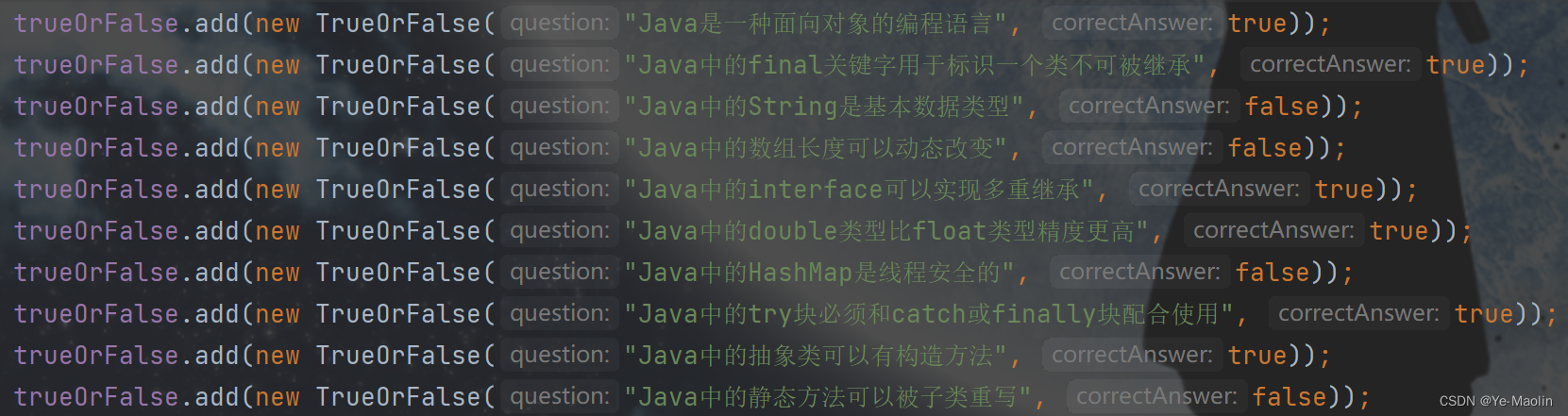
trueOrFalse.add(new TrueOrFalse("Java是一种面向对象的编程语言", true));
trueOrFalse.add(new TrueOrFalse("Java中的final关键字用于标识一个类不可被继承", true));
trueOrFalse.add(new TrueOrFalse("Java中的String是基本数据类型", false));
trueOrFalse.add(new TrueOrFalse("Java中的数组长度可以动态改变", false));
trueOrFalse.add(new TrueOrFalse("Java中的interface可以实现多重继承", true));
trueOrFalse.add(new TrueOrFalse("Java中的double类型比float类型精度更高", true));
trueOrFalse.add(new TrueOrFalse("Java中的HashMap是线程安全的", false));
trueOrFalse.add(new TrueOrFalse("Java中的try块必须和catch或finally块配合使用", true));
trueOrFalse.add(new TrueOrFalse("Java中的抽象类可以有构造方法", true));
trueOrFalse.add(new TrueOrFalse("Java中的静态方法可以被子类重写", false));
}
}JavaExam.java main interface
import javax.swing.*;
import javax.swing.border.EmptyBorder;
import java.awt.*;
import java.util.Collections;
import java.util.List;
public class JavaExam extends JFrame {
private final JLabel labelQuestion;
private final JRadioButton radioButtonA, radioButtonB, radioButtonC, radioButtonD;
private final JCheckBox checkBoxA, checkBoxB, checkBoxC, checkBoxD;
private final ButtonGroup buttonGroup;
private final JButton buttonSubmit;
private final JLabel labelSingleChoiceNum, labelMultipleChoiceNum, labelTrueOrFalseNum, labelScore, labelTime;
private int singleChoiceCount = 0, multipleChoiceCount = 0, trueOrFalseCount = 0;
private int singleChoiceCorrectCount = 0, multipleChoiceCorrectCount = 0, trueOrFalseCorrectCount = 0;
private int score = 0, seconds = 0, questionIndex = 0;
private boolean isSingleChoice, isMultipleChoice, isTrueOrFalse, submit = false;
private final List<SingleChoice> singleChoices;
private final List<MultipleChoice> multipleChoices;
private final List<TrueOrFalse> trueOrFalse;
private final Timer timer;
private final JPanel panelQuestion = new JPanel();
class GiveQuestion implements Runnable {
@Override
public void run() {
Collections.shuffle(singleChoices);
Collections.shuffle(multipleChoices);
Collections.shuffle(trueOrFalse);
while (questionIndex < 15) {
submit = false;
if (questionIndex % 3 == 0) {
isSingleChoice = true;
showSingleChoiceQuestion(singleChoices.get(singleChoiceCount));
singleChoiceCount++;
} else if (questionIndex % 3 == 1) {
isMultipleChoice = true;
showMultipleChoiceQuestion(multipleChoices.get(multipleChoiceCount));
multipleChoiceCount++;
} else {
isTrueOrFalse = true;
showTrueOrFalseQuestion(trueOrFalse.get(trueOrFalseCount));
trueOrFalseCount++;
}
timer.start();
while (!submit) {
}
questionIndex++;
}
endExam();
}
}
public JavaExam() {
super("Java机考 By YeMaolin");
singleChoices = new Questions().singleChoices;
multipleChoices = new Questions().multipleChoices;
trueOrFalse = new Questions().trueOrFalse;
setDefaultCloseOperation(JFrame.EXIT_ON_CLOSE);
setSize(400, 250);
setLocationRelativeTo(null);
setLayout(new BorderLayout());
panelQuestion.setLayout(new GridLayout(5,1));
panelQuestion.setBorder(new EmptyBorder(0,15,0,0)); // 设置组件的外边距
labelQuestion = new JLabel("", SwingConstants.CENTER);
radioButtonA = new JRadioButton("A");
radioButtonB = new JRadioButton("B");
radioButtonC = new JRadioButton("C");
radioButtonD = new JRadioButton("D");
checkBoxA = new JCheckBox("A");
checkBoxB = new JCheckBox("B");
checkBoxC = new JCheckBox("C");
checkBoxD = new JCheckBox("D");
buttonGroup = new ButtonGroup();
buttonGroup.add(radioButtonA);
buttonGroup.add(radioButtonB);
buttonGroup.add(radioButtonC);
buttonGroup.add(radioButtonD);
JPanel panelInfo = new JPanel();
labelSingleChoiceNum = new JLabel("单选题:0/5/0", SwingConstants.CENTER);
labelMultipleChoiceNum = new JLabel("多选题:0/5/0", SwingConstants.CENTER);
labelTrueOrFalseNum = new JLabel("判断题:0/5/0", SwingConstants.CENTER);
labelScore = new JLabel("成绩:0分", SwingConstants.CENTER);
labelTime = new JLabel("用时:0秒", SwingConstants.CENTER);
panelInfo.add(labelSingleChoiceNum);
panelInfo.add(labelMultipleChoiceNum);
panelInfo.add(labelTrueOrFalseNum);
panelInfo.add(labelScore);
panelInfo.add(labelTime);
add(panelInfo,BorderLayout.NORTH);
add(panelQuestion,BorderLayout.WEST);
setVisible(true);
buttonSubmit = new JButton("提交");
add(buttonSubmit,BorderLayout.SOUTH);
buttonSubmit.addActionListener(e -> submitAnswer());
timer = new Timer(1000, e -> {
seconds++;
labelTime.setText("用时:" + seconds + "秒");
if (seconds >= 20) {
submitAnswer();
}
});
Thread giveQuestion = new Thread(new GiveQuestion());
giveQuestion.start();
}
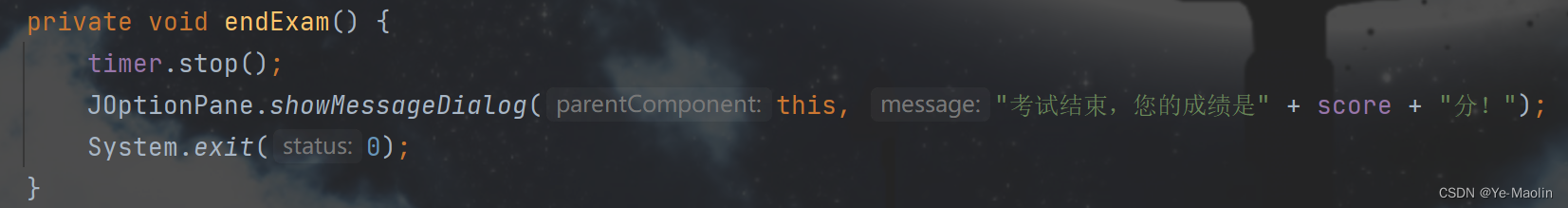
private void endExam() {
timer.stop();
JOptionPane.showMessageDialog(this, "考试结束,您的成绩是" + score + "分!");
System.exit(0);
}
private void showSingleChoiceQuestion(SingleChoice singleChoice) {
panelQuestion.removeAll();
labelQuestion.setText(questionIndex + 1 + "/15[单选题]" + singleChoice.question);
radioButtonA.setText(singleChoice.optionA);
radioButtonB.setText(singleChoice.optionB);
radioButtonC.setText(singleChoice.optionC);
radioButtonD.setText(singleChoice.optionD);
panelQuestion.add(labelQuestion);
panelQuestion.add(radioButtonA);
panelQuestion.add(radioButtonB);
panelQuestion.add(radioButtonC);
panelQuestion.add(radioButtonD);
}
private void showMultipleChoiceQuestion(MultipleChoice multipleChoice) {
panelQuestion.removeAll();
labelQuestion.setText(questionIndex + 1 + "/15[多选题]" + multipleChoice.question);
checkBoxA.setText(multipleChoice.optionA);
checkBoxB.setText(multipleChoice.optionB);
checkBoxC.setText(multipleChoice.optionC);
checkBoxD.setText(multipleChoice.optionD);
panelQuestion.add(labelQuestion);
panelQuestion.add(checkBoxA);
panelQuestion.add(checkBoxB);
panelQuestion.add(checkBoxC);
panelQuestion.add(checkBoxD);
}
private void showTrueOrFalseQuestion(TrueOrFalse trueOrFalse) {
panelQuestion.removeAll();
labelQuestion.setText(questionIndex + 1 + "/15[判断题]" + trueOrFalse.question);
radioButtonA.setText("正确");
radioButtonB.setText("错误");
panelQuestion.add(labelQuestion);
panelQuestion.add(radioButtonA);
panelQuestion.add(radioButtonB);
}
private void submitAnswer() {
timer.stop();
String correctAnswer = "";
boolean right = false;
if (isSingleChoice) {
String userAnswer = "";
correctAnswer = singleChoices.get(singleChoiceCount - 1).correctAnswer;
if (radioButtonA.isSelected()) {
userAnswer = "A";
} else if (radioButtonB.isSelected()) {
userAnswer = "B";
} else if (radioButtonC.isSelected()) {
userAnswer = "C";
} else if(radioButtonD.isSelected()) {
userAnswer = "D";
}
if (userAnswer.equals(correctAnswer)) {
singleChoiceCorrectCount++;
score++;
right = true;
}
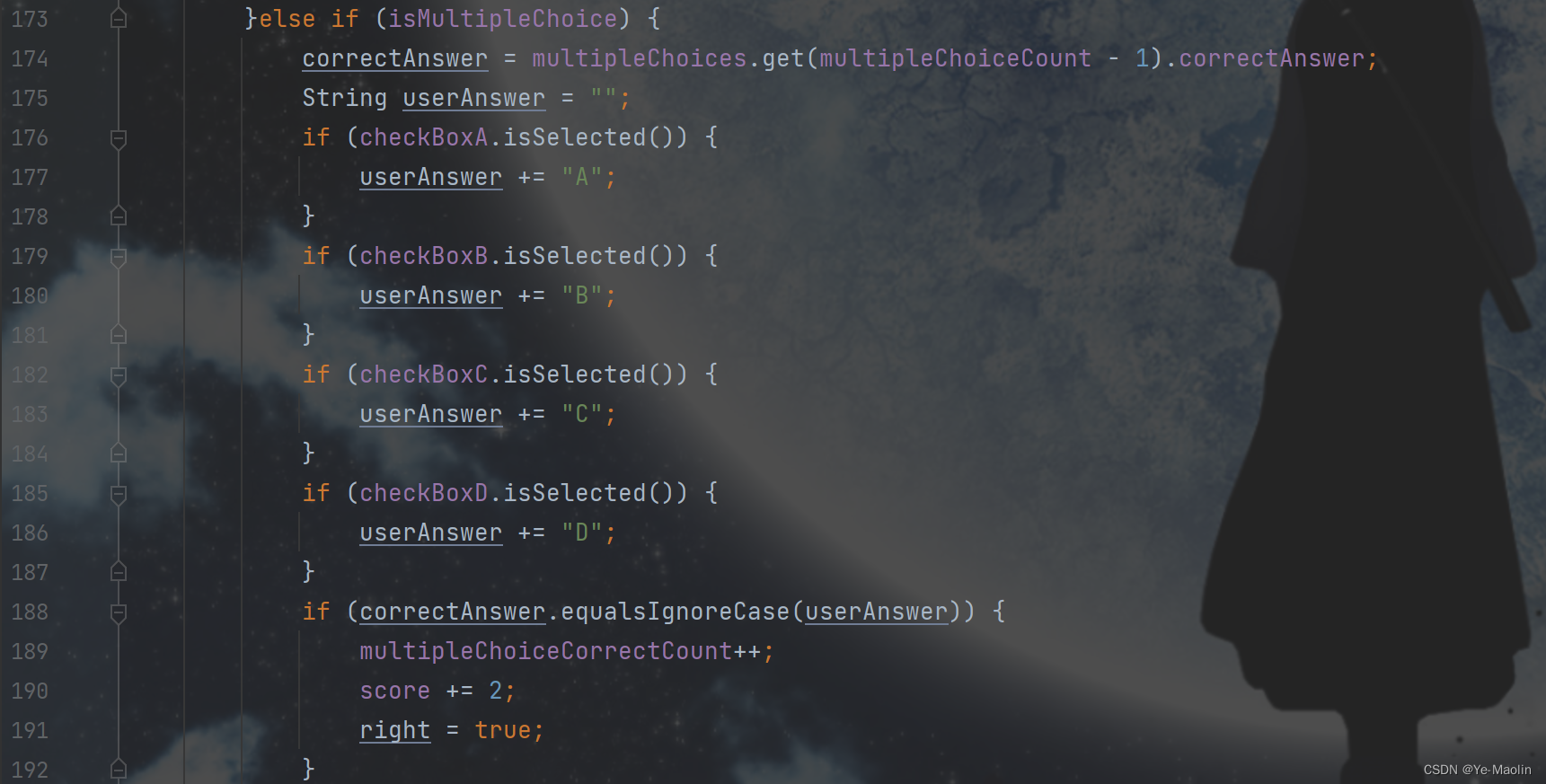
}else if (isMultipleChoice) {
correctAnswer = multipleChoices.get(multipleChoiceCount - 1).correctAnswer;
String userAnswer = "";
if (checkBoxA.isSelected()) {
userAnswer += "A";
}
if (checkBoxB.isSelected()) {
userAnswer += "B";
}
if (checkBoxC.isSelected()) {
userAnswer += "C";
}
if (checkBoxD.isSelected()) {
userAnswer += "D";
}
if (correctAnswer.equalsIgnoreCase(userAnswer)) {
multipleChoiceCorrectCount++;
score += 2;
right = true;
}
}else if (isTrueOrFalse) {
boolean correct = trueOrFalse.get(trueOrFalseCount - 1).correctAnswer;
correctAnswer = String.valueOf(correct);
if (radioButtonA.isSelected()&&correct||radioButtonB.isSelected()&&!correct) {
trueOrFalseCorrectCount++;
score++;
right = true;
}
}
if (right)
JOptionPane.showMessageDialog(this, "回答正确,用时" + seconds + "秒");
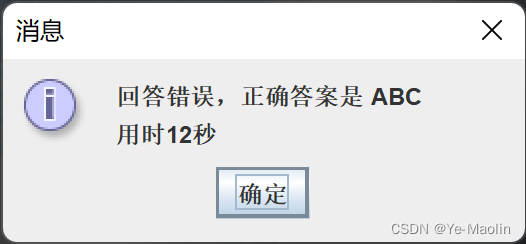
else JOptionPane.showMessageDialog(this, "回答错误,正确答案是 " + correctAnswer + "\n用时" + seconds + "秒");
update();
submit = true;
}
private void update() {
labelScore.setText("成绩:" + score + "分");
labelSingleChoiceNum.setText("单选题:" + singleChoiceCount + "/5/" + singleChoiceCorrectCount);
labelMultipleChoiceNum.setText("多选题:" + multipleChoiceCount + "/5/" + multipleChoiceCorrectCount);
labelTrueOrFalseNum.setText("判断题:" + trueOrFalseCount + "/5/" + trueOrFalseCorrectCount);
buttonGroup.clearSelection();
checkBoxA.setSelected(false);
checkBoxB.setSelected(false);
checkBoxC.setSelected(false);
checkBoxD.setSelected(false);
radioButtonA.setSelected(false);
radioButtonB.setSelected(false);
radioButtonC.setSelected(false);
radioButtonD.setSelected(false);
seconds = 0;
isSingleChoice = isMultipleChoice = isTrueOrFalse = false;
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
SwingUtilities.invokeLater(JavaExam::new);
}
}
First of all, the most important function is to display questions. We first designed the structure of three question types, and then established a question bank. The first is the single-choice question. Define a single-choice question class. The question content, four options, and the correct answer are all represented by strings, and a constructor with parameters is set for it.

Similarly, define a multiple-choice question class. The only difference between multiple-choice questions and single-choice questions is that there is more than one correct answer for a multiple-choice question, but we can both represent the correct answer through a string, so the implementation of these two classes is exactly the same. of.

For judgment questions, you only need a string to record the question content and a Boolean variable to record the correct judgment result.

Then we started to prepare the question bank, defined a question bank class, and established containers for three question types.

Then add the question in the constructor.
Add 10 multiple choice questions.
Added 10 multiple choice questions.

Add 10 true or false questions.
The next step is how to display the questions on the GUI interface and implement other functional logic.
Define a class Java Exam, inherited from JFrame, so that Java Exam is a window. We use the invokeLater method in the SwingUtilities class in the main function to execute the constructor of Java Exam on the event scheduling thread.

In the Java Exam constructor, we define some basic properties of the window and take out three types of questions from the question bank.
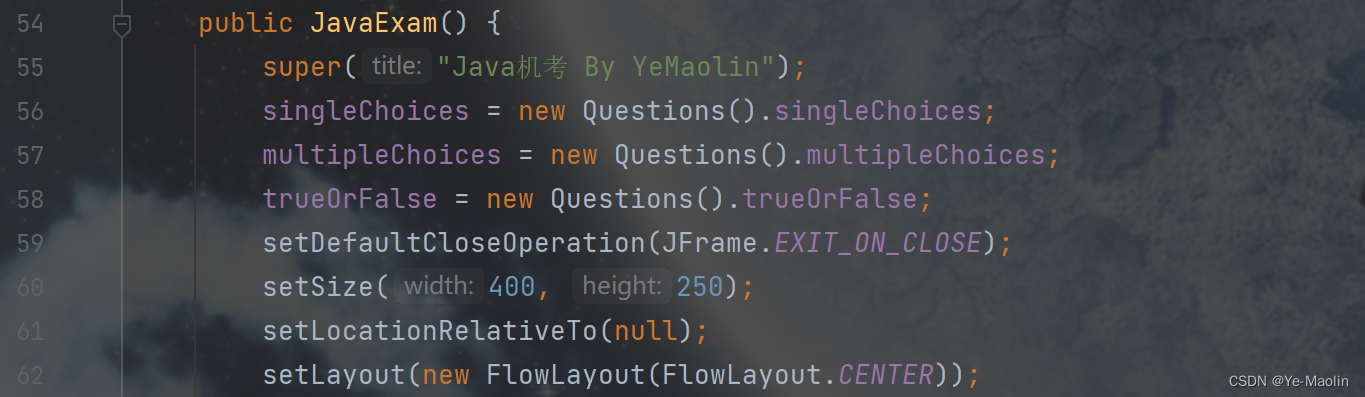
Then initialize the option component. Here, single-choice questions and true-false questions can share a set of radio buttons, and then multiple-choice questions use a check box.

Add four buttons to a button group to ensure that only one radio button can be selected in the same button group. When the user selects one of the radio buttons, the other radio buttons will automatically become unselected to achieve Radio function.

Real-time display of the number of completed questions, the total number of questions, the number of correct answers and the current total score and time for three types of questions. This information is placed in a JPanel container.

Set up a submit button, implement an event listener, call the submit answer method when the button is clicked, and set a timer. If the answer exceeds 20 seconds, the answer will be automatically submitted to complete the answer.

Finally, create a thread giveQuestion to display the question.

Let's look at the implementation of giveQuestion. We first shuffle the order of the questions, so that the order of appearance of the questions is random every time the program is restarted.
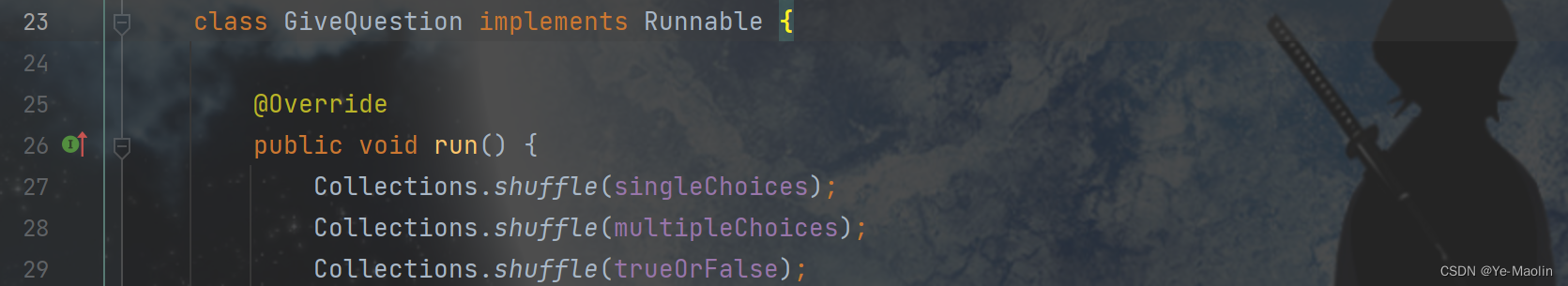
Then the first five questions of each question type, a total of fifteen questions, are displayed, and the corresponding display functions are called respectively to display the questions.
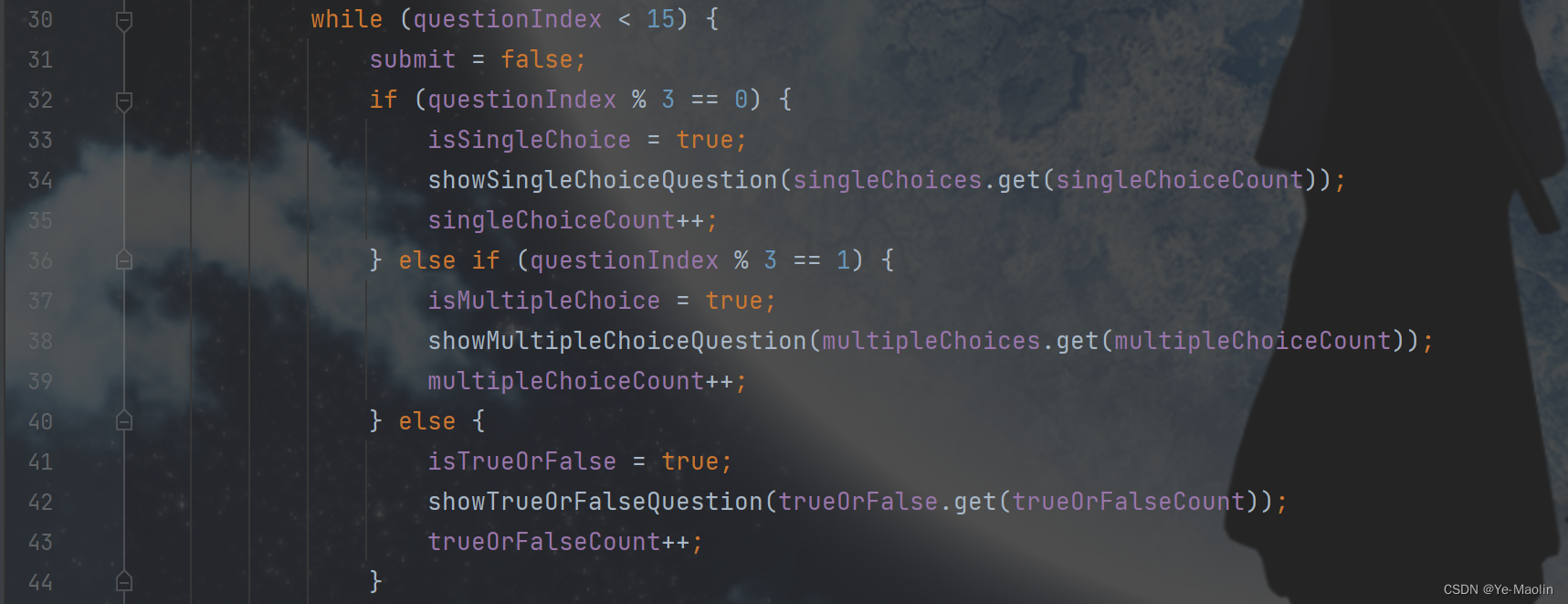
Then start the timer, wait for the answer to be submitted, and then switch to the next question. If the answer is not submitted within 20 seconds, the system will automatically call the submit function to submit and then automatically switch to the next question. When all questions are answered, the end function is called to display the results.

For the display of three types of questions, because it involves switching between questions, we use a JPanel container to install the components of the questions, and then clear all the components in this container before displaying the questions each time, and then add this Components of the topic.
Single-choice questions are displayed, with question numbers added here.

Similar display multiple choice questions.

The display of true-false questions uses the same set of components as single-choice questions, but true-false questions only require two radio buttons to indicate correctness and error.

Then look at the function that submits answers. Here we first stop the counter, and then check the answers by question type.
To check the answers to multiple-choice questions, first take out the correct answers from the question bank, then compare the answers, and add the correct answers. What needs to be noted here is that you must judge whether there is a choice among the four options, and you cannot use the else case to handle the last one. Because if there is no answer, the answer should be empty, instead of choosing D for else.

To check the answers to the multiple-choice questions, you need to concatenate the selected ABCDs in order as a string, and then directly compare them with the correct answers to see if they are equal.
Check the answers to the true-false questions and directly determine whether you have chosen the right answer.

Then give feedback to the answer. If the answer is correct, the correct prompt and time will be given. If the answer is wrong, the correct answer and time will be given, and then the update function will be called to update the status.
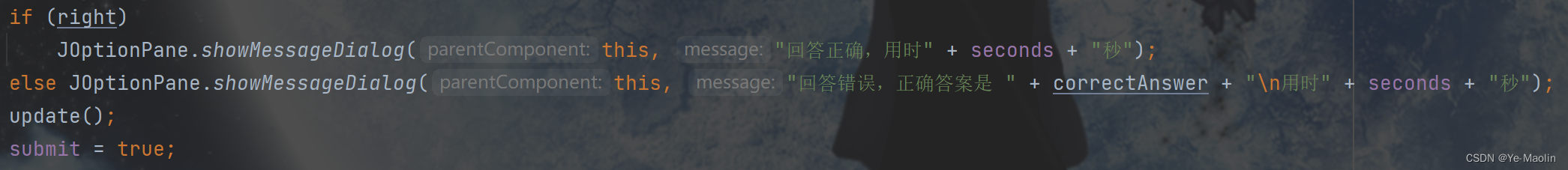
Let’s look at the update function, which is to update the scores, update the number of completed questions and the number of correct answers for the three question types, and clear the option status.

The end function called when the final answer is completed is used to stop the timing and display the results.