Article directory
Integer array merging
Merge two integer arrays in ascending order and filter outrepeatArray elements.
There is no space between two adjacent numbers when outputting.
Input description:
1 Enter the number of the first array
2 Enter all the values of the first array
3 Enter the number of the second array
4 Enter all the values of the second array
Output description:
Output the merged numerical string
Example 1
input:
3
1 2 5
4
-1 0 3 2
Output:
-101235
python implementation:
def merge_arr():
s0,s1,s3,s2 = input(), input().split(), input(), input().split()
s = map(str,sorted(map(int, set(s1+s2))))
print(''.join(s))
merge_arr()
prime factors
Input a positive integer and output all its prime factors in order from small to large (repeated ones must also be listed) (for example, the prime factors of 180 are 2 2 3 3 5)
Example 1
input:
180
Output:
2 2 3 3 5
python code:
- What is normally reduced is the prime factor
- 180/2 90/2 45/3 15/3 5/5
import math
def prime_factor():
n = int(input().strip())
for i in range(2, int(math.sqrt(n)) + 1):
while n % i == 0:
print(i, end=" ")
n = n // i
# 不能约掉的
if n > 2:
print(n)
lowest common denominator
Input two positive integers a, b;
find their lowest common divisor.
Input:
4 6
Output:
2
least common multiple
The least common multiple of positive integer A and positive integer B refers to the smallest positive integer value that can be divided by A and B. Design an algorithm to find the least common multiple of A and B.
Input description:
Enter two positive integers A and B.
Output description:
Output the least common multiple of A and B.
Example 1
Input:
5 7
Output:
35
Example 2
input:
2 4
output:
4
python implementation:
def min_bei(a, b):
if a > b:
a, b = b, a
if b % a == 0:
print(b)
return b
temp = b
while True:
temp += b # +1 只是增加了复杂度
if temp % a == 0 and temp % b == 0:
print(temp)
return temp
a, b = input().strip().split()
a = int(a)
b = int(b)
min_bei(a, b)
- short division
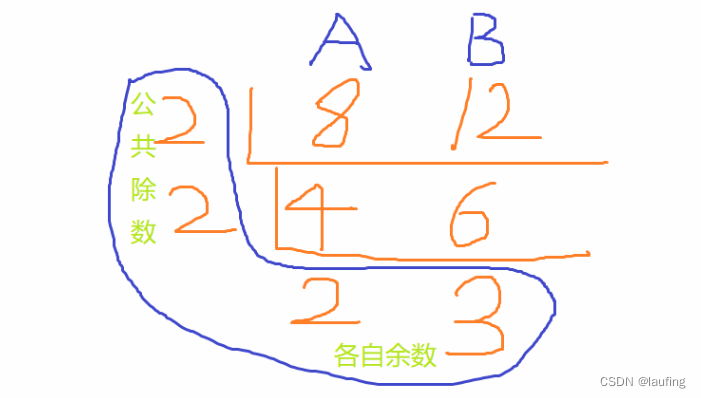
A, B = map(int, input().split())
T = 1 # 初始1便于不影响乘数结果
for i in range(2, min(A, B) + 1): # 只需遍历到最小的一个数
while A % i == 0 and B % i == 0: # 逐一找公共除数
T = T * i # 每找到一个公共除数就累乘
A = A // i
B = B // i
print(T * A * B)
Solving Cube Roots
Computes the cube root of a floating point number without using library functions.
Round off to one decimal place.
Input description:
a double type (real number)
Output description:
Output its cube root to one decimal place.
Example 1
Input:
19.9
Output:
2.7
Example 2
Input:
2.7
Output:
1.4
python implementation
- Two points
def binary_split():
a = float(input().strip())
epsilon = 0.0001
low = min(-1.0, a)
high = max(1.0, a)
ans = (low + high)/2
while abs(ans**3 - a) >= epsilon:
if ans**3 < a:
low = ans
else:
high = ans
ans = (low + high)/2.0
print('%.1f' % ans)
binary_split()
Arithmetic
Enter an expression (represented as a string) and evaluate the expression.
Valid characters in the string are guaranteed to include ['0'-'9'],'+','-', '*','/','(', ')','[', ']', '{','}'. And the expression must be legal.
Enter description:
Enter an arithmetic expression
Output description:
Get calculation results
Example 1
input:
3+2*{1+2*[-4/(8-6)+7]}
output:
25 Note the data type
python, stack implementation.
# 将输入的表达式中的数字和符号区分开,并保存到列表中
def group(s):
num, res = '', []
for i, c in enumerate(s):
if c.isdigit():
num += c # 数字可能有很多位数
else:
if num:
res.append(num)
num = ''
if c == '-': # 负数的判断
if (i == 0) or (s[i-1] in '+-*/([{'):
num += c
continue
res.append(c)
if num:
res.append(num)
return res
while True:
try:
s = input()
lst = group(s)
stack_n, stack_op = [], []
'''
遍历数字和符号列表lst:
1.如果遇到数字,添加到数字栈stack_n中;
2.如果遇到*/([{这些符号,直接添加到符号栈stack_op中;
3.如果遇到+-号:
(1).如果符号栈stack_op为空或栈顶元素是左括号([{的话,直接入栈;
(2).如果符号栈stack_op不为空,则不断从符号栈stack_op中弹出一个符号,
同时从数字栈stack_n中弹出两个数字进行运算,并将运算结果保存到数字栈stack_n中。
期间若遇到(不弹栈)左括号([{,则跳出循环,最后再将加号+或者减号-添加到符号栈中。
4.如果遇到右括号)]},在栈顶元素不是左括号([{之前,不断地取出数字和符号进行运算,
同时将结果保存到数字栈stack_n中,最后删除左括号。
'''
for i in lst:
if i not in '+-*/()[]{}': # 数字
stack_n.append(i)
elif i in '*/([{':
stack_op.append(i)
elif i in '+-':
if len(stack_op) == 0 or stack_op[-1] in '([{':
stack_op.append(i)
else:
while stack_op:
if stack_op[-1] in '([{':
break
op = stack_op.pop()
n2, n1 = stack_n.pop(), stack_n.pop()
stack_n.append(str(eval(n1 + op + n2)))
stack_op.append(i)
elif i in ')]}':
while stack_op[-1] not in '([{':
op = stack_op.pop()
n2, n1 = stack_n.pop(), stack_n.pop()
stack_n.append(str(int(eval(n1 + op + n2))))
stack_op.pop()
# 对数字栈和符号栈中剩余元素进行运算
while stack_op:
op = stack_op.pop()
n2, n1 = stack_n.pop(), stack_n.pop()
stack_n.append(str(int(eval(n1 + op + n2))))
# 弹出并打印数字栈中最后一个数字,即运算结果
print(stack_n.pop())
except:
break