Why should we rewrite the hashcode method after rewriting equals?
1.set stores string string
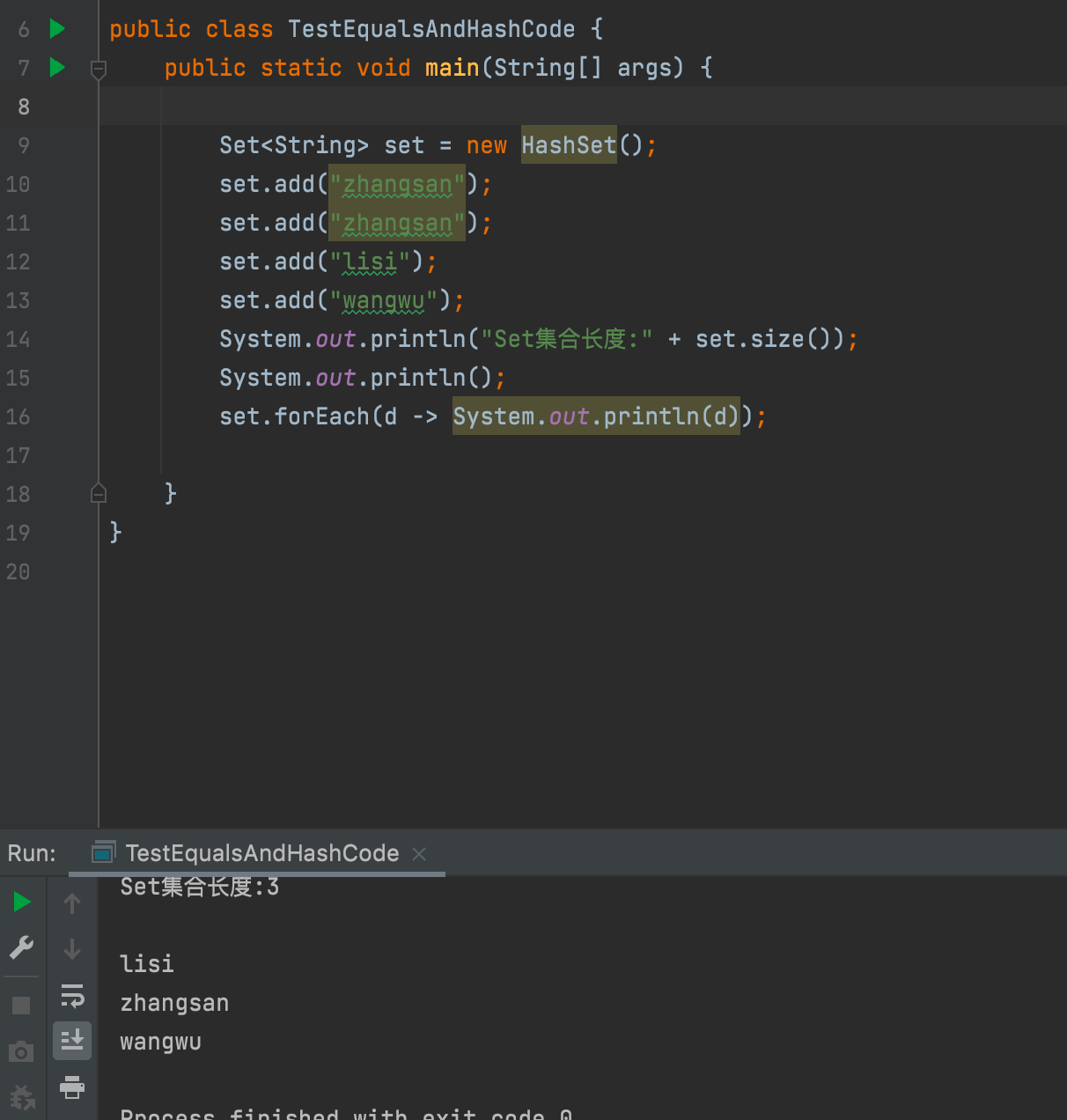
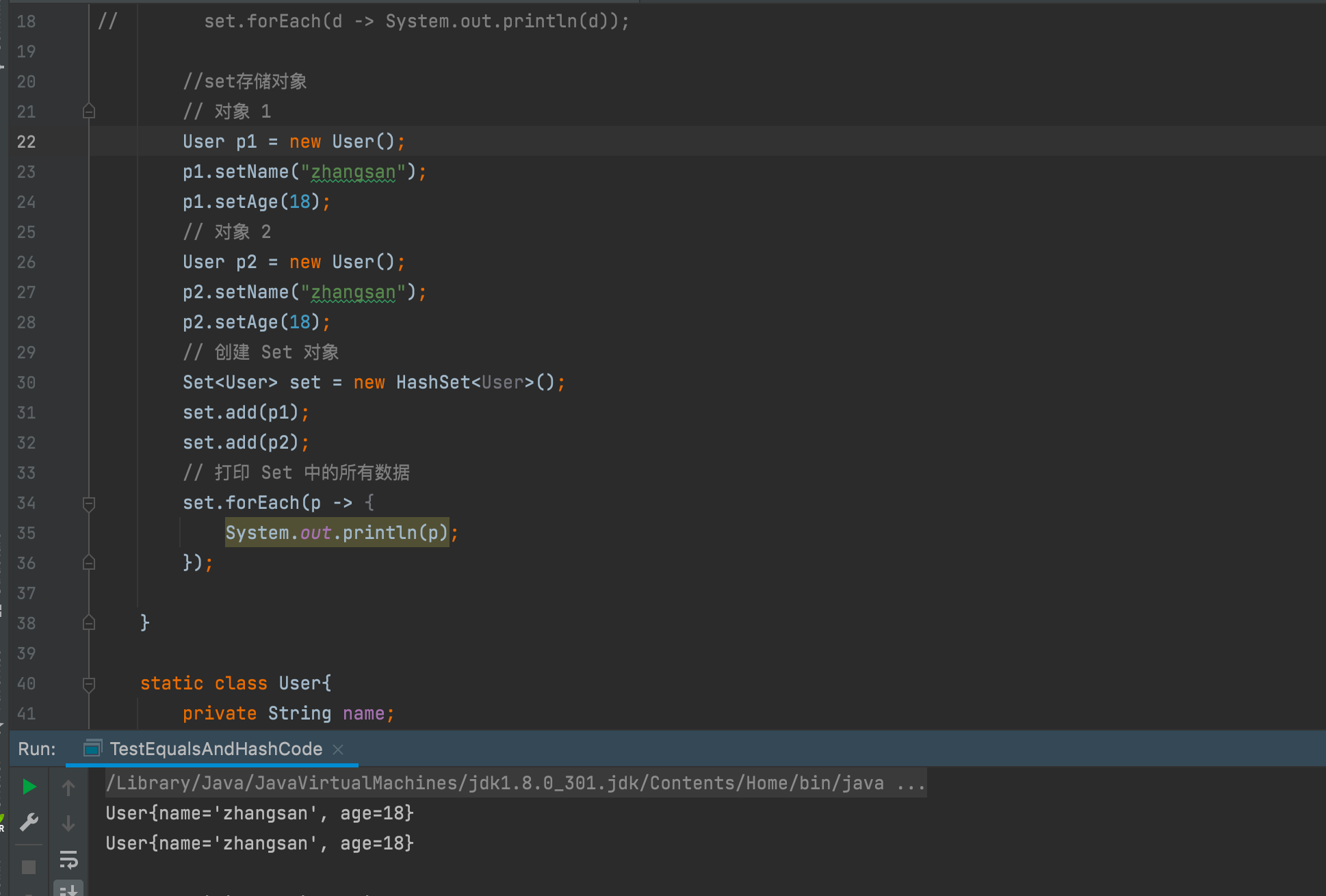
2. Only rewrite equals but not hashcode.
There are two identical ones in the set and there is no deduplication.
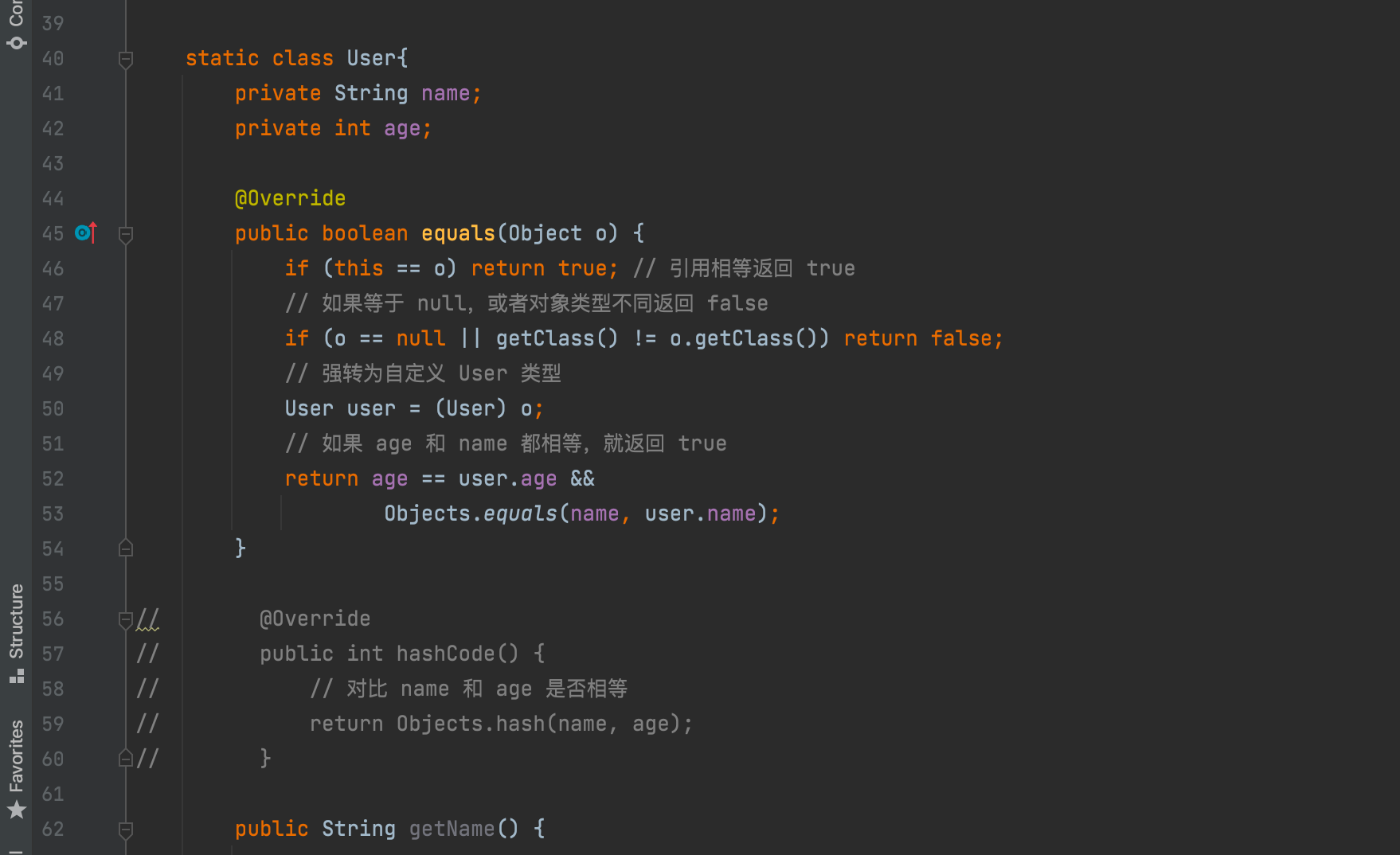
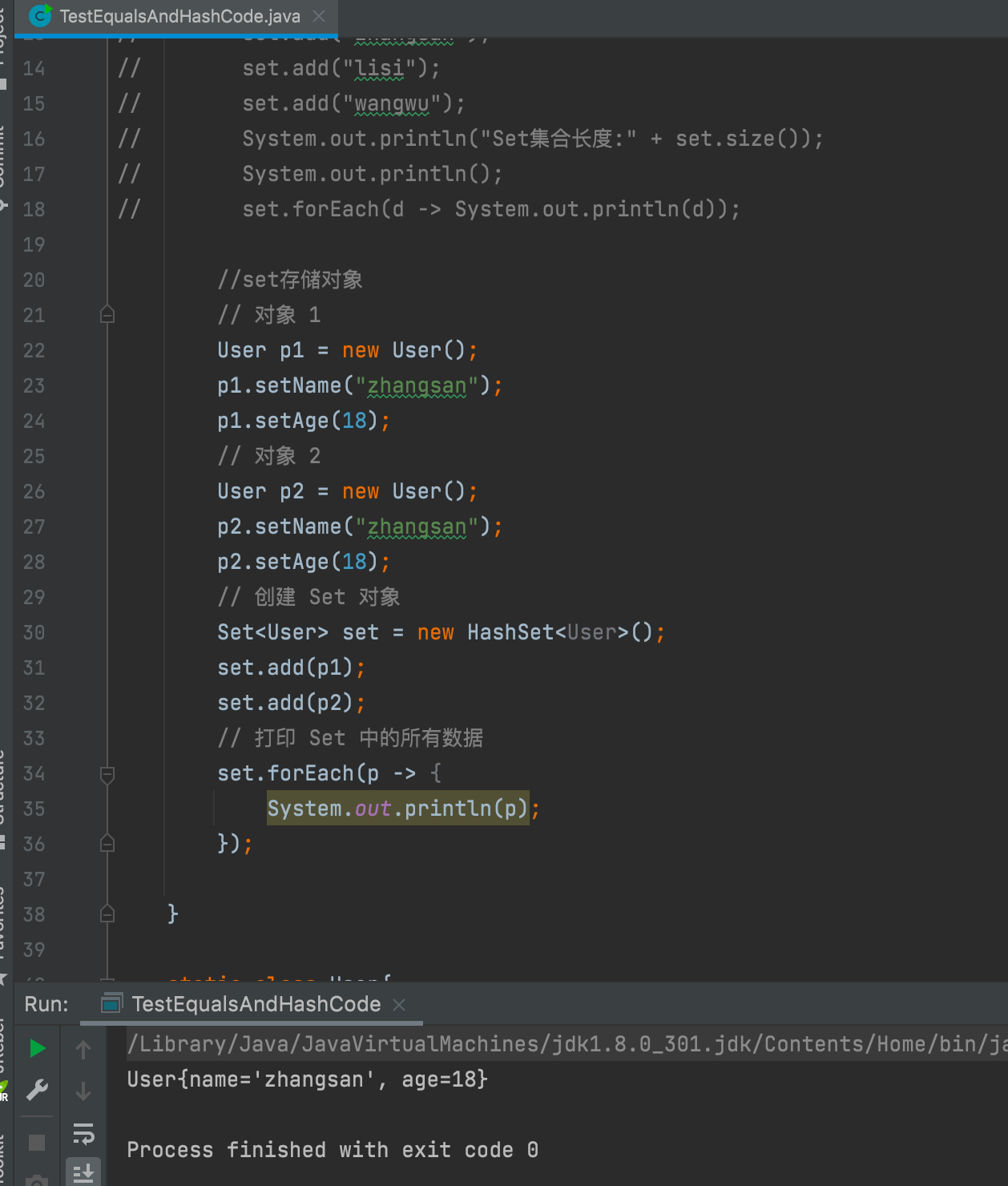
3. Rewrite equals and also rewrite hashcode

There is only one object in set
in conclusion
When deduplicating Set, it will first determine whether the hashcode is the same and then determine whether the equals method is the same.
import java.util.HashSet;
import java.util.Objects;
import java.util.Set;
public class TestEqualsAndHashCode {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//set保存string
// Set<String> set = new HashSet();
// set.add("zhangsan");
// set.add("zhangsan");
// set.add("lisi");
// set.add("wangwu");
// System.out.println("Set集合长度:" + set.size());
// System.out.println();
// set.forEach(d -> System.out.println(d));
//set存储对象
// 对象 1
User p1 = new User();
p1.setName("zhangsan");
p1.setAge(18);
// 对象 2
User p2 = new User();
p2.setName("zhangsan");
p2.setAge(18);
// 创建 Set 对象
Set<User> set = new HashSet<User>();
set.add(p1);
set.add(p2);
// 打印 Set 中的所有数据
set.forEach(p -> {
System.out.println(p);
});
}
static class User{
private String name;
private int age;
@Override
public boolean equals(Object o) {
if (this == o) return true; // 引用相等返回 true
// 如果等于 null,或者对象类型不同返回 false
if (o == null || getClass() != o.getClass()) return false;
// 强转为自定义 User 类型
User user = (User) o;
// 如果 age 和 name 都相等,就返回 true
return age == user.age &&
Objects.equals(name, user.name);
}
@Override
public int hashCode() {
// 对比 name 和 age 是否相等
return Objects.hash(name, age);
}
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public int getAge() {
return age;
}
public void setAge(int age) {
this.age = age;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "User{" +
"name='" + name + '\'' +
", age=" + age +
'}';
}
}
}