The CI/O subset of the C++ standard library implements C-style stream input/output operations. The <cstdio> header file provides general file support and provides functions with narrow and multibyte character input/output capabilities, while the <cwchar> header file provides functions with wide character input/output capabilities.
Unformatted input/output
Get characters from file stream
std::fgetc,
std::getc| int fgetc( std::FILE* stream ); |
Reads the next character from the given input stream.
parameter
| stream | - | Read character source |
return value
The character obtained on success, and EOF on failure.
If an end-of-file condition causes failure, the end-of-filestream indicator on is additionally set (see std::feof()). If some other error caused the failure, set the error indicator on (see std::ferror()).stream
Call example
#include <cstdio>
#include <cstdlib>
int main()
{
FILE* file = std::fopen("test.txt", "r");
if (!file)
{
std::perror("File opening failed");
return EXIT_FAILURE;
}
int c; // 注意:是 int 而非 char ,要求处理 EOF
while ((c = std::fgetc(file)) != EOF) // 标准 C I/O 文件读取循环
{
std::putchar(c);
}
if (std::ferror(file))
{
std::puts("I/O error when reading");
}
else if (std::feof(file))
{
std::puts("End of file reached successfully");
}
std::fclose(file);
return 0;
}output

Get a string from a file stream
std::fgets| char* fgets( char* str, int count, std::FILE* stream ); |
Reads up to count - 1 characters from the given file stream and stores them in strthe character array pointed to by . Analysis is terminated if a newline character is present or found at the end of the file, in which case stra newline character will be included. If bytes are read and no errors occur, a null strcharacter is written immediately after the last character written to .
If countless than 1, the behavior is undefined. It also does not specify whether to write null characters, if count==1.
parameter
| str | - | pointer to an element of the char array |
| count | - | The maximum number of characters to write (typically strthe length of ) |
| stream | - | read file stream from data source |
return value
On success str, a null pointer on failure.
If an end-of-file condition causes failure, the end-of-filestream indicator on is set (see std::feof()). This only fails if it results in an unread character, in which case a null pointer is returned and the contents of the pointed to array are not changed (i.e. the first byte is not overwritten with a null character).str
If other error conditions caused the failure, set the errorstream indicator on it (see std::ferror()). The contents of the array pointed to are undefined (may not even be null-terminated).str
Call example
#include <iostream>
#include <cstdio>
#include <cstdlib>
int main()
{
std::FILE* tmpf = std::tmpfile();
std::fputs("Alan Turing\n", tmpf);
std::fputs("John von Neumann\n", tmpf);
std::fputs("Alonzo Church\n", tmpf);
std::rewind(tmpf);
char buf[8];
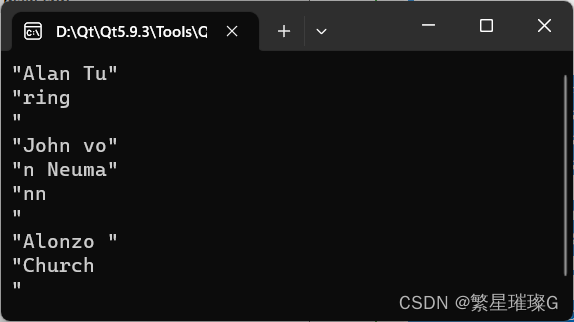
while (std::fgets(buf, sizeof buf, tmpf) != NULL)
{
std::cout << '"' << buf << '"' << '\n';
}
return 0;
}
output