overview
The basic principle
a) The principle of objectivity and fairness.
During the implementation of the evaluation, the evaluation party shall ensure that in accordance with the requirements of the national encryption management department and the minimum subjective judgment, according to the
secret evaluation plan jointly approved by the tested unit, based on clearly defined evaluation methods and explanations, Implement assessment activities.
b) Principle of reusability
Existing evaluation results can be reused in the evaluation work, including commercial cryptography testing and certification results and evaluation results of cryptography application security evaluation, etc. All reuse results should be based on the premise that the existing evaluation results are still applicable to the current information system under test, and can objectively reflect the current security
status of the system.
c) Principles of repeatability and reproducibility
According to the same requirements, using the same evaluation method, and under the same environment, different secret evaluators should obtain the same results when they repeatedly execute each evaluation implementation process. The difference between repeatability and reproducibility is that the former focuses on the consistency of the evaluation results of the same secret reviewer
, while the latter focuses on the consistency of the evaluation results of different secret reviewers.
d) The principle of completeness of results
On the basis of a correct understanding of the content of each requirement item of GM/T AAAA, the results of the evaluation should objectively reflect the status quo of the
cryptographic application of the information system. The assessment process and results should be based on the correct assessment methodology to ensure that it meets the requirements.
Assessment Risk Identification
a) The verification test may affect the normal operation of the information system under test.
During the on-site evaluation, certain verification tests must be carried out on the equipment and system, and some test content needs to be viewed on the computer, which may cause
unpredictable effects on the operation of the information system under test. Influence.
b) Tool testing may affect the normal operation of the tested information system
During on-site evaluation, some evaluation tools may be used for testing according to actual needs. When the evaluation tool is used, redundant data writing may occur, and at the same time, it may have a certain impact on the load of the system, and then have a certain impact or even damage on the server and network communication in the information system under test
.
c) It may lead to leakage of sensitive information of the information system under test
. During the evaluation process, sensitive information of the information system under test may be leaked, such as encryption mechanism, business process, security mechanism and relevant document information
.
d) Other possible risks
During the evaluation process, there may also be risks affecting the usability, confidentiality and integrity of the information system under test.
Assess risk aversion
a) Sign the entrusted evaluation agreement
Before the official start of the evaluation work, the evaluation party and the measured unit need to clarify the objectives, scope,
personnel composition, planning, implementation steps and requirements of the evaluation work, as well as the responsibilities and obligations of both parties in the form of an entrusted agreement Obligations, etc., so that the two sides of the evaluation can reach a consensus on the basic issues in the evaluation process.
b) Signing a confidentiality agreement
The parties involved in the evaluation should sign a non-disclosure agreement that complies with legal norms, specifying the rights, responsibilities and obligations of the parties involved in the evaluation in terms of confidentiality.
c) Sign the on-site evaluation authorization letter
. Before the on-site evaluation, the evaluation party should sign the on-site evaluation authorization letter with the unit under test, requiring the relevant evaluation parties to back up the system and data,
adopt appropriate methods to avoid risks, and formulate measures for possible events. Emergency treatment plan.
d) On-site evaluation requirements
When verification tests and tool tests are required, the peak hours of the information system under test should be avoided, and the test should be carried out when the system resources are idle,
or a simulation/simulation environment consistent with the information system under test should be configured. Carry out evaluation work in a simulation/simulation environment; when it is necessary to carry out verification tests on the machine, the secret evaluators should propose the content that needs to be verified, and the technical personnel of the unit under test will carry out the actual operation. The entire on-site evaluation process is supervised by the relevant personnel of the measured unit and the evaluation party. After the evaluation work is completed, the secret evaluation personnel should return all the privileges obtained during the evaluation process, return the relevant documents borrowed during the evaluation process, and restore the evaluation site environment to the state before the evaluation
Evaluation process
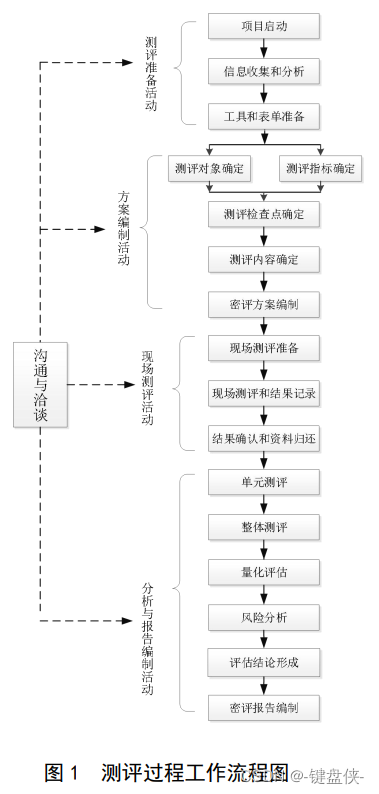
Assessment preparation activities
This activity is the premise and basis for carrying out the evaluation work. The main task is to master the details of the information system to be tested, prepare the evaluation tools, and
prepare for the preparation of the secret evaluation plan.
Project begining
In the task of starting the project, the evaluation party establishes the evaluation project team, obtains the basic situation of the measured unit and the information system to be tested, and
prepares for the implementation of the entire evaluation project in terms of basic information, personnel, and planning arrangements.
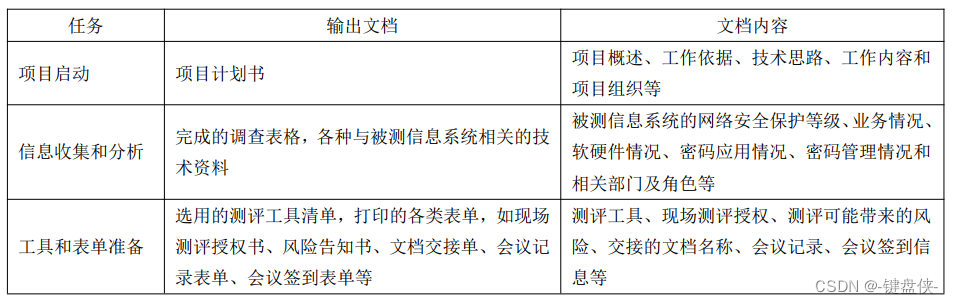
——Input: entrusted evaluation agreement, confidentiality agreement, etc.
Task description:
a) According to the entrusted evaluation agreement signed by both parties and the scale of the information system to be tested, the evaluation party establishes an evaluation project team, arranges personnel well
, and prepares a project plan. The project plan should include project overview, work basis, technical ideas, work content and project
organization.
b) The evaluation party requires the unit under test to provide basic information, and make preparations for a comprehensive and preliminary understanding of the information system under test.
- Output: Project Proposal.
Information Collection and Analysis
The evaluation party uses survey forms, consults the data of the information system under test, etc., to understand the composition of the information system under test and the application of passwords, and
lays the foundation for writing a secret evaluation plan and carrying out on-site evaluation work.
- Input: Survey form.
Task description:
a) The evaluation party collects the materials required for evaluation, including the overall description file of the tested information system, the overall description file of the password application of the tested information system
, the network security level protection grading report, the security requirements analysis report, the overall security plan, the security Detailed design schemes,
password application schemes, user operation guides for related password products, various security rules and regulations for password applications, and related process management
records and configuration management documents, etc.
b) The evaluation party submits the survey form of the basic situation of the information system under test to the unit under test, and assists and urges the relevant personnel of the information system under test
to fill in the survey form accurately.
c) The evaluation party takes back the completed survey form, analyzes the survey results, and understands and is familiar with the actual situation of the information system under test. The content of the analysis
includes the basic information of the tested information system, industry characteristics, password management strategy, network and equipment deployment, software and hardware
importance and deployment situation, scope and boundary, business type and importance, business process, business data and important information. nature,
the network security protection level of the tested information system, user range, user type, the operating environment of the tested information system and the threats it faces,
etc.
The above information can be relied on the self-inspection results, the last network security protection level evaluation report or the credible results in the commercial encryption application security evaluation report.
d) If the survey form is filled inaccurately, incompletely or contradictory, the close review personnel should communicate
and confirm with the person who filled the form. When necessary, the evaluation party shall arrange an on-site investigation, communicate and confirm with the relevant personnel of the information system under test on site, so as to
Ensure the correctness and completeness of survey information.
——Output: Completed survey forms, various technical materials related to the information system under test.
Tools and Form Preparation
Before on-site evaluation, members of the evaluation project team should be familiar with various components related to the information system to be tested, calibrate evaluation tools, prepare
various forms, etc. The evaluation tools used in the evaluation process shall comply with the relevant management policy requirements of the national encryption management department and the requirements of relevant national standards and industry standards for encryption.
——Input: Completed survey forms, various technical materials related to the information system to be tested.
Task description:
a) Calibrate the assessment tools that will be used in this assessment process.
b) If conditions are available, it is recommended that secret evaluators simulate the information system to be tested to build an evaluation environment, conduct preliminary preparation and verification, and
provide necessary conditions for program preparation activities and on-site evaluation activities.
c) Prepare and print forms, mainly including: on-site evaluation authorization letter, risk notification letter, document handover form, meeting record form, meeting
sign-in form, etc.
——Output: List of selected evaluation tools, printed various forms, such as on-site evaluation authorization letter, risk notification letter, document handover form, meeting record form, meeting sign-in form, etc.
Output Documentation for Assessment Preparation Activities
programming activities
The goal of program preparation activities is to sort out and analyze the information related to the information system under test obtained in the assessment preparation activities, and provide the most basic documents and guidance schemes for the on-site assessment activities . Program preparation activities include five main tasks:
determination of evaluation objects, determination of evaluation indicators, determination of evaluation checkpoints, determination of evaluation content, and preparation of secret evaluation programs .
Evaluation object determination
According to the information of the tested information system that has been learned, analyze the entire tested information system and its related business application systems, as well as the
related password application, and determine the evaluation object of this evaluation.
——Input: Completed survey forms, various technical materials related to the information system to be tested.
a) Identify the basic situation of the information system under test
According to the situation of the information system under test obtained from the survey form, identify the physical environment, network topology and external
boundary connection of the information system under test, business application systems, and related important information systems. Computer hardware equipment, network security equipment, cryptographic products and cryptographic services used, etc., and identify the cryptographic applications related to the above content.
b) Describe the tested information system
Organize the identified basic situation of the tested information system and describe the tested information system. When describing the information system under test,
it is generally based on the network topology structure of the information system under test, using the total score description method, first explaining the overall structure, then describing the external boundary connection and main equipment at the boundary, and finally introducing the information system under test The composition of the network area, main business functions and related equipment nodes, and at the same time, it is necessary to describe the application of cryptography identified in these aspects.
c) Determine the evaluation object
According to the importance of the information system under test and its related equipment and components, etc., the circulation of core assets in the information system under test is clarified
, so as to determine the evaluation object related to cryptography. The unit under test needs to determine the core assets that the information system under test needs to protect, as well as the corresponding threat model and security strategy. Core assets can be business applications, business data, or certain equipment and components of business applications. Core assets and other supporting data that need to be protected (such as audit information, configuration information, access control lists, etc.), threat models and security policies for sensitive security parameters (mainly keys) are all determined by the unit under test according to the password application scheme, network The safety level protection grading report, etc. are determined, and are checked and confirmed by the evaluation party.
d) Asset and threat assessment
Assets are valued based on their importance and criticality. Asset values are classified into high, medium and low levels. Assets with higher value
will result in higher risk when threatened. The definition of asset value can be inherited and determined by the unit under test according to the password application scheme, network security level protection grading report, etc., and it will be verified and confirmed by the evaluation party. For various assets and other sensitive information, the assessor and the unit under test need to analyze the threats they may face and the frequency of threats. The frequency of threats is divided into three levels: high, medium, and low. The higher the frequency of threats, the more likely the security of assets will be threatened. The possible threats and the frequency of threats can be inherited and determined by the unit under test according to the password application scheme, network security level protection rating report, etc., and verified and confirmed by the evaluation party.
e) Describe the evaluation objects.
The evaluation objects include computer rooms, business application software, hosts and servers, databases, network security equipment, cryptographic products, cryptographic services, and system-related personnel (including system leaders, security managers, key administrators, and cryptographic auditors). , password operator, etc.) and safety management system documents and record form documents, etc. When describing each type of evaluation object, a list is generally used. For example, when describing a hardware device, it should include the area to which the evaluation object belongs, the name of the device, its purpose, and device information.
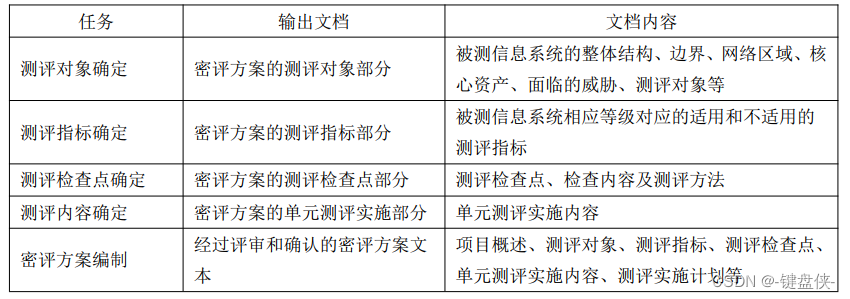
——Output: The evaluation object part of the secret evaluation plan.
Determination of evaluation indicators
According to the grading results of the tested information system, the evaluation indicators of this evaluation are determined.
- Input: completed survey form, GM/T AAAA, cryptographic application schemes that have passed the assessment, relevant industry standards or specifications.
a) Obtain the grading results of the information system under test according to the survey form of the information system under test, and select the
evaluation index corresponding to the corresponding level according to GM/T AAAA.
b) According to the industry standards or norms related to the information system under test, as well as the password application requirements of the information system under test, determine the special evaluation indicators. c) For core assets, physical environment and other data that need to be protected (such as keys, authentication data, etc.), it should be confirmed item by item
according to the security policy of the information system under test and the requirements of relevant standards .
By confirming
the cryptographic algorithms, cryptographic technologies, cryptographic products, cryptographic services, etc. involved in the core assets, physical environment, and other data that need to be protected during the entire life cycle circulation process, clarify the requirements related to
key life cycle management, and compare the requirements that have been passed The evaluated password application scheme confirms the applicability of each index item by item.
d) If there is no password application scheme, it is necessary to check and evaluate all inapplicable items one by one, and demonstrate in detail its security requirements, specific
reasons for inapplicability, and whether other alternative risk control measures that can meet security requirements have been adopted to Equivalent control is achieved
.
——Output: The evaluation index part of the secret evaluation scheme.
Evaluation checkpoint determination
During the evaluation process, on-site inspection and confirmation of some key security points is required to prevent the
occurrence of situations where cryptographic products and cryptographic services are correctly configured but not connected to the information system under test. The compliance, correctness, and effectiveness of cryptographic algorithms, cryptographic technologies, cryptographic products, and cryptographic services can be confirmed by packet capture tests and viewing of key device configurations. These checkpoints should be determined during program development, and the feasibility and risks of the checks should be fully considered to minimize the impact on the information system under test, especially the online business system.
——Input: The detailed network structure of the information system under test, the selected cryptographic algorithm, cryptographic technology, cryptographic products, cryptographic services and other detailed information, the
cryptographic application scheme and GM/T AAAA that have passed the evaluation
a) Key equipment inspection is an important part of on-site evaluation The key equipment is generally the equipment that carries the circulation of core assets and performs key management
. Secret review personnel should list the key equipment and inspection content that need to be inspected on-site, including: whether the part involving encryption uses the encryption
algorithm, encryption technology, encryption product and encryption service approved by the national encryption management department; whether the relevant configuration is consistent with the encryption
code application requirements; whether it meets the requirements of relevant clauses in GM/T AAAA, etc.
b) When using tools for evaluation (evaluation tools include but are not limited to: protocol analysis tools, algorithm compliance detection tools,
randomness detection tools, and digital certificate format compliance detection tools, etc.), it should ensure that the information system under test In the case of normal and safe operation
, determine the test path and tool access point, and combine with the network topology diagram to describe the access point of the evaluation tool,
test purpose, test approach, test object and other related content in a graphical way. When accessing from outside the boundary of the information system under test, the test tool is
generally connected to the system boundary device (usually a switch); when accessing from different network segments inside the system, the test tool is generally connected to the
On the internal core switch that is not on the same network segment as the object under test; when accessing from the same network segment inside the system, the test tool is generally connected to the
switch on the same network segment as the object under test. When the conditions for the evaluation tool to be connected to the information system under test are not mature, the evaluation party shall
negotiate and cooperate with the unit under test to generate necessary offline data.
——Output: The evaluation checkpoint part of the secret evaluation scheme.
Evaluation content confirmed
Before the implementation of the evaluation, it is necessary to determine the specific implementation content of the on-site evaluation, that is, the content of the unit evaluation.
——Input: the completed survey form, the evaluation objects, evaluation indicators and evaluation checkpoints of the secret evaluation scheme, the password
application scheme and GM/T AAAA that passed the evaluation.
Task description:
According to the password application scheme and GM/T AAAA that have passed the evaluation, first combine the obtained evaluation indicators with the evaluation object, and then
combine the evaluation object with the specific evaluation method. The specific method is to combine the evaluation indicators at various levels with the specific evaluation objects, and explain the specific evaluation methods to form several units that can implement the evaluation. Then, combined with the selected evaluation indicators and evaluation objects, briefly explain the work content of the on-site unit evaluation implementation; when the on-site test part is involved, the corresponding test content should be compiled according to the determined evaluation checkpoints. In the close evaluation scheme, the implementation content of on-site unit evaluation is usually given in the form of a table, and the content of the table includes evaluation indicators, evaluation content description, etc.
——Output: The unit evaluation implementation part of the secret evaluation scheme.
Compilation of secret evaluation plan
The secret evaluation plan is the basis for the implementation of the evaluation work and is used to guide the on-site implementation activities of the evaluation work. The secret evaluation plan should include but not limited to the
following: project overview, evaluation objects, evaluation indicators, evaluation checkpoints, and unit evaluation implementation.
——Input: entrusted evaluation agreement, project plan, completed survey form, password application plan and GM/T
AAAA that passed the evaluation, evaluation objects, evaluation indicators, evaluation checkpoints, evaluation content, etc. in the secret evaluation plan.
Task description:
a) According to the entrusted evaluation agreement and the completed survey form, extract the source of the project, the overall information construction of the tested unit, and the
connection between the tested information system and other systems.
b) Combined with the actual situation of the tested information system, according to the evaluated cryptographic application scheme and GM/T AAAA, clarify the standards and specifications related to
cryptographic algorithms, cryptographic technologies, cryptographic products, and cryptographic services that the evaluation activities should be based on and referenced. c) Estimate the workload of on-site evaluation based on the entrusted evaluation agreement and the information system under test. Specifically, it can be estimated
based on the number of nodes for configuration inspection , access points for tool testing, and test content. d) According to the division of labor among the members of the evaluation project team, prepare work arrangements. e) Based on the past experience in evaluation and the scale of the information system to be tested, prepare a specific evaluation implementation plan, including the division of labor and time arrangement of on-site staff . When making time arrangement, try to avoid the business peak period of the information system under test, so as to avoid affecting the normal operation of the information system under test. At the same time, in the evaluation plan, the personnel, materials, places and other guarantee requirements required for the specific evaluation work should be put forward together to ensure the smooth development of the on-site evaluation work. f) Summarize the above content and the content obtained from other tasks in the program preparation activities to form a secret evaluation program.
g) After the secret evaluation plan is approved by the evaluation party's internal review, it shall be submitted to the unit under test for signature confirmation.
——Output: The text of the closed evaluation plan that has been reviewed and confirmed.
Output documentation from programming activities
On-site evaluation activities
The goal of the on-site evaluation activities is to communicate and coordinate with the units under test, implement the on-site evaluation work according to the secret evaluation plan, and obtain
sufficient evidence and materials required for analysis and report preparation activities. On-site assessment activities include three main tasks: on-site assessment preparation, on-site assessment and result recording, result confirmation and data return.
On-site assessment preparation
This task starts the on-site evaluation work to ensure that the evaluation party can implement the evaluation smoothly.
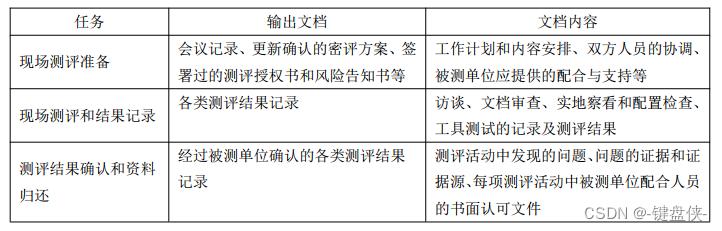
——Input: On-site evaluation authorization letter, reviewed and confirmed secret evaluation plan, risk notification letter, etc.
Task description:
a) Hold the first meeting of the evaluation site, the evaluation party introduces the evaluation work, further clarifies the content of the evaluation plan and program, and explains the
specific implementation work content, evaluation schedule, and possible safety risks in the evaluation process, etc. .
b) The evaluation party and the measured unit confirm the various resources required for on-site evaluation, including the cooperating personnel of the tested unit and the evaluation conditions that need to be provided
, and confirm that the tested information system has backed up the system and related data.
c) The unit under test signs the authorization letter for on-site evaluation and the risk notification letter.
d) According to the communication results of the meeting, the close evaluators will make necessary updates to the evaluation result recording form and evaluation procedures.
——Output: meeting minutes, updated and confirmed secret evaluation plan, signed evaluation authorization letter and risk notification letter, etc.
On-site assessment and documentation of results
This task is mainly based on the secret evaluation plan and the results of on-site evaluation preparations. The evaluation party arranges secret evaluation personnel to complete the evaluation work on site.
——Input: updated and confirmed secret evaluation plan, evaluation result record form, and various technical materials related to the information system to be tested.
Task description: a) The evaluation party arranges the secret evaluation personnel to conduct interviews with personnel (individuals/groups) related to the information system under test, document review, on-site inspection, and conduct configuration checks and tool tests at the evaluation checkpoints
at the agreed evaluation time
Etc., to evaluate
whether the information system under test meets the requirements of the corresponding level.
b) For cryptographic products that have obtained the corresponding certificates, they will not be repeatedly tested during the evaluation, but will mainly be checked for compliance and
configuration. If there is any doubt about the conformity, you can contact the cryptographic product approval department or the corresponding testing and certification agency for verification .
c) When conducting configuration checks, first confirm that the actual deployment of the encryption products is consistent with the claimed situation according to the commercial encryption product certification certificate (copy), security policy document or
user check the configuration. correctness, and record
relevant evidence. If there are unclear problems, the unit under test can notify the encryption product manufacturer to provide evidence on site (such as encryption
product inspection documents, etc.).
d) When conducting tool testing, it is necessary to select testing tools according to the actual situation of the information system under test. If the configuration inspection cannot provide strong evidence, the
relevant data of the information system under test should be captured and analyzed through tool testing.
Several approaches to data collection and analysis are listed below :
- It is necessary to focus on collecting the data communicated between the information system under test and the outside world, as well as the data transmitted and stored inside the information system under test,
analyze whether the cryptographic algorithm, cryptographic protocol, and key data structure (such as digital certificate format) used are in compliance, and check the transmitted
password , user privacy data and other important data are protected (such as randomness detection of ciphertext, check
whether key fields appear in plaintext), verify whether the hash value and signature value are correct; if conditions permit, the
collection can be replayed The key data (such as identity authentication data) to verify whether the information system under test has the ability to prevent replay attacks, or
modify the transmitted data to verify whether the information system under test protects the integrity of the transmitted data. - In order to verify whether the cryptographic product is used correctly and effectively, the communication data between the cryptographic product and its caller can be collected, and through the
collected cryptographic product invocation instructions and response messages, it is possible to analyze whether the invocation of the cryptographic product meets expectations (such as cryptographic
calculation Whether the request is initiated in real time, whether the data content and length are logical); if
the test tool cannot be connected between
the cryptographic product and the caller (for example, the cryptographic product is a software cryptographic module), and the information system under test cannot provide source code and other relevant evidence Under the circumstances, the application program of the information system under test can be reversely analyzed by reverse analysis and other methods to explore the internal
structure and working principle of the application program, and check the rationality of the application program calling the password function. - Without affecting the normal operation of the information system under test, detect
whether the specific port services corresponding to IPSec VPN and SSL VPN and other cryptographic protocols are enabled, use tools such as vulnerability scanning and penetration testing to analyze the information system under test, and
view the Whether there are password-related security vulnerabilities in the information system.
e) The secret evaluators fill in the evaluation result record form according to the on-site evaluation results.
——Output: Records of various evaluation results.
Result Confirmation and Data Return
- Inputs: Records of evaluation results, records of electronic outputs after tool testing is completed.
Task description:
a) After the on-site evaluation is completed, the close evaluators should first summarize the evaluation records of the on-site evaluation, and
conduct supplementary evaluation on the missing and further verification content.
b) Hold the on-site end meeting of the evaluation, and the evaluation party and the unit under test shall communicate and confirm on-site the records of various evaluation results obtained during the evaluation process
.
c) The assessor returns all the documents borrowed during the assessment process, restores the assessment site environment to the pre-assessment state, and
confirms with the signature of the document provider of the unit under test.
——Output: Records of various evaluation results confirmed by the unit under test.
Output documentation for on-site assessment activities
Analysis and Reporting
After the on-site evaluation work is completed, the evaluation party shall conduct a summary analysis of the evaluation results (or evaluation evidence) obtained from the on-site evaluation, form an
evaluation conclusion, and prepare a secret evaluation report.
After the close evaluation personnel initially determine the evaluation results of each evaluation object involved in each evaluation unit, they need to conduct unit evaluation, overall evaluation,
quantitative evaluation and risk analysis. After the overall evaluation, the evaluation results of some evaluation objects may change, and the evaluation results need to be further revised, followed by quantitative evaluation and risk analysis, and finally form an evaluation conclusion. The analysis and report preparation activities include six main tasks: unit evaluation, overall evaluation, quantitative evaluation, risk analysis, formation of evaluation conclusions and preparation of secret evaluation report.
unit evaluation
This task is mainly to objectively and accurately analyze the evaluation evidence for each evaluation object in each evaluation index, and
carry out evaluation implementation and result judgment for each evaluation object. Summarize the evaluation implementation results of all evaluation objects involved in each evaluation unit, obtain
the judgment results of each evaluation unit, and list them one by one in the form of a table.
——Input: Records of various evaluation results confirmed by the unit under test, GM/T AAAA.
Task description: a) According to GM/T AAAA, for each evaluation object involved in each evaluation unit, compare the
multiple evaluation results actually obtained with the expected evaluation results, and judge the conformity between each evaluation result and the expected results respectively
comprehensively judge the evaluation results of the evaluation object , so as to obtain the evaluation results corresponding to each evaluation object, including four situations:
conformity, non-compliance, partial conformity and inapplicability . b) In accordance with GM/T AAAA, summarize the results of the implementation of the evaluation of all evaluation objects involved in each evaluation unit, and judge the results of each evaluation unit. The judgment principles are as follows:
- If the evaluation results of all the evaluation objects included in the evaluation unit are consistent, then the results of the corresponding evaluation unit are judged to be consistent.
- If the evaluation results of all the evaluation objects contained in the evaluation unit are non-conforming, the corresponding evaluation unit results are judged as non-conforming.
- If the evaluation results of all the evaluation objects contained in the evaluation unit are not applicable, then the corresponding evaluation unit results are judged as not applicable.
- If the evaluation results of all the evaluation objects included in the evaluation unit are not all satisfied or not satisfied, the corresponding evaluation unit results are judged to be partially satisfied.
- Output: The unit assessment section of the secret assessment report.
Overall evaluation
This task adopts the method of judging items one by one for the evaluation objects whose evaluation results are partially satisfied or not, and gives the specific
results of the overall evaluation.
- Input: Unit assessment part of the secret assessment report.
Task description:
a) For a single evaluation item that "partially meets" and "does not meet" requirements of the evaluation object, analyze whether the evaluation objects of other units related to the evaluation item can be associated with it, and what kind of association relationship
occurs, these Whether the effect of the association relationship can "make up
" the deficiency of the assessment item, and whether the deficiency of the assessment item will affect the assessment results of other assessment items related to it.
b) For a single evaluation item that "partially meets" and "does not meet" the requirements of the evaluation object, analyze whether other levels of evaluation objects related to the evaluation item can be
associated with it, what kind of association occurs, and these associations generate Whether the role of the
evaluation item can "make up" for the deficiency of the assessment item, and whether the deficiency of the assessment item will affect the assessment results of other assessment items related to it.
c) Combining the results of the unit evaluation and the overall evaluation results, the physical and environmental security, network and communication security, equipment and computing security, application and data security, management
system, personnel management, construction operation, emergency response, etc. The evaluation results of the objects
are summarized and analyzed again, and the statistics are matched.
——Output: The unit evaluation result correction part of the secret evaluation report
Quantitative evaluation
This task integrates the unit evaluation results and the overall evaluation results, calculates the evaluation result
scores , and applies passwords to the information system under test. An overall assessment of the safety of the situation.
——Input: The summary of unit evaluation results and the overall evaluation part of the secret evaluation report.
Task description:
a) According to the overall evaluation results, calculate the conformity score of the evaluation results of each evaluation object for each evaluation index after correction.
b) Calculate the score of each evaluation unit according to the conformity score of each evaluation object.
c) Calculate the scores of each safety level according to the scores of each evaluation unit.
d) Calculate the overall score based on the scores of each security level.
e) According to each evaluation unit, each level and the overall score, make an overall evaluation of the effective protection measures taken by the tested information system and the existing
password application security problems.
——Output: The overall evaluation results and quantitative evaluation part of the secret evaluation report, as well as the overall evaluation part.
Risk Analysis
This task is based on relevant norms and standards, using the method of risk analysis to analyze the security problems in the evaluation results and the possible
impact on the security of the tested information system.
——Input: The completed survey form, the overall evaluation results and the quantitative evaluation part of the closed evaluation report, and the relevant risk evaluation standards.
Task description:
a) According to the type of threat and the frequency of threat occurrence, judge the possibility of security problems caused by some conforming items or non-conforming items in the summary of evaluation results being
exploited by threats. The value range of the possibility is high, medium and low.
b) According to the value of the assets, judge the degree of impact on the business information security of the tested information system after the security problems caused by some conforming items or non-conforming items in the summary of the evaluation results are threatened
and exploited for high, medium and low. c) Based on the analysis results of the first two steps, the evaluation party assigns a value to the cryptographic application security risk faced by the information
system under test based on its own experience and the requirements of relevant standards such as GM/T BBBB. The range of risk values is high, medium and low
.
d) Evaluate the risk analysis results in combination with the network security protection level of the tested information system, that is, the
risks to national security, social order, public interests, and legitimate rights and interests of citizens, legal persons, and other organizations. If there are high-risk items, it is considered that
the information system under test faces high risks; at the same time, it is also necessary to consider the high-risk problems that may be caused by the superposition of multiple medium and low risks.
- Output: The risk analysis part of the secret evaluation report.
Formation of assessment conclusions
This task forms an evaluation conclusion based on the summary of evaluation results, quantitative evaluation and risk analysis.
——Input: the comprehensive score and overall evaluation part of the tested information system in the secret evaluation report, and the risk analysis part.
Task description:
draw an evaluation conclusion based on the comprehensive score and risk analysis results of the information system under test. The evaluation conclusions are divided into the following three situations: a) Conformity: No security problems are found in the information system under test, and the statistical results of
some compliance and non-conformity items in the evaluation results of all units in the evaluation results are all 0, and the comprehensive score is 100 points. b) Basically conform: There are security problems in the tested information system, and the statistical results of some conforming and non-conforming items are not all 0, but the existing security problems will not cause the tested information system to face high-level security risks, and the comprehensive score is not low at the threshold. c) Nonconformity: There are security problems in the tested information system, and the statistical results of some conforming and nonconforming items are not all 0, and the existing security problems will cause the tested information system to face high-level security risks, or the comprehensive score is lower than the threshold . - Output: The assessment conclusion part of the secret assessment report.
Compilation of Secret Evaluation Report
This task forms a secret evaluation report based on the output of various tasks in the analysis and report preparation activities. The secret evaluation report shall comply with
the requirements of the information system password application security evaluation report template, including but not limited to the following contents: Overview of evaluation items, situation of the system under test, evaluation scope and methods, unit evaluation, overall evaluation, quantitative evaluation, risk analysis, evaluation Conclusions, overall evaluation, safety issues and suggestions for improvement, etc. Among them, the overview part describes the overall situation of the tested information system, the purpose and basis of the test and so on.
——Input: completed survey form, secret evaluation plan, summary of unit evaluation results, overall evaluation, overall evaluation, risk analysis, evaluation conclusion, etc.
Task description:
a) Secret review personnel sort out the output of each task and prepare the corresponding part of the secret review report.
A secret evaluation report shall be formed separately for each rated information system under test .
b) Aiming at the security problems existing in the tested information system, put forward corresponding improvement suggestions, and prepare the security document and improvement suggestion part of the secret evaluation report.
c) Provide the list of on-site evaluation documents and evaluation records in the form of a list, as well as the judgment of the evaluation results of each evaluation item, and prepare the result
records of the unit evaluation of the secret evaluation report, the overall evaluation results, risk analysis and evaluation conclusions.
d) After the secret evaluation report is compiled, the evaluation party shall
conduct an internal review of the secret evaluation report according to the entrusted evaluation agreement, relevant documents submitted by the tested unit, original records of evaluation and other auxiliary information.
e) After the secret evaluation report passes the internal review, it will be signed by the authorized signatory and submitted to the unit under test.
——Output: Reviewed and confirmed secret review report
Output documentation from analysis and reporting activities
