1. The label in the parser rule
1.1 Introduction
- Antrl4 grammar file
Calculator.g4, the two parser rules of stat and expr contain multiple rule elements, and each rule element of our two parse rules has added Alternative labels (label for short)

- According to the grammar rules of Antlr4:
- The label is generally located at the end of each rule element,
#beginning with . - At the same time, either add a label to each rule element of the parser rule, or add none
// 定义stat,不添加label stat: expr | ID '=' expr ; // 定义expre,每个rule element都添加label expr: expr op=(MUL|DIV) expr | expr op=(ADD|SUB) expr | INT | ID | '(' expr ')' ;
- The label is generally located at the end of each rule element,
1.2 The influence of label on parse tree
- Use IDEA's Antlr4 plugin to test the grammar rules prog
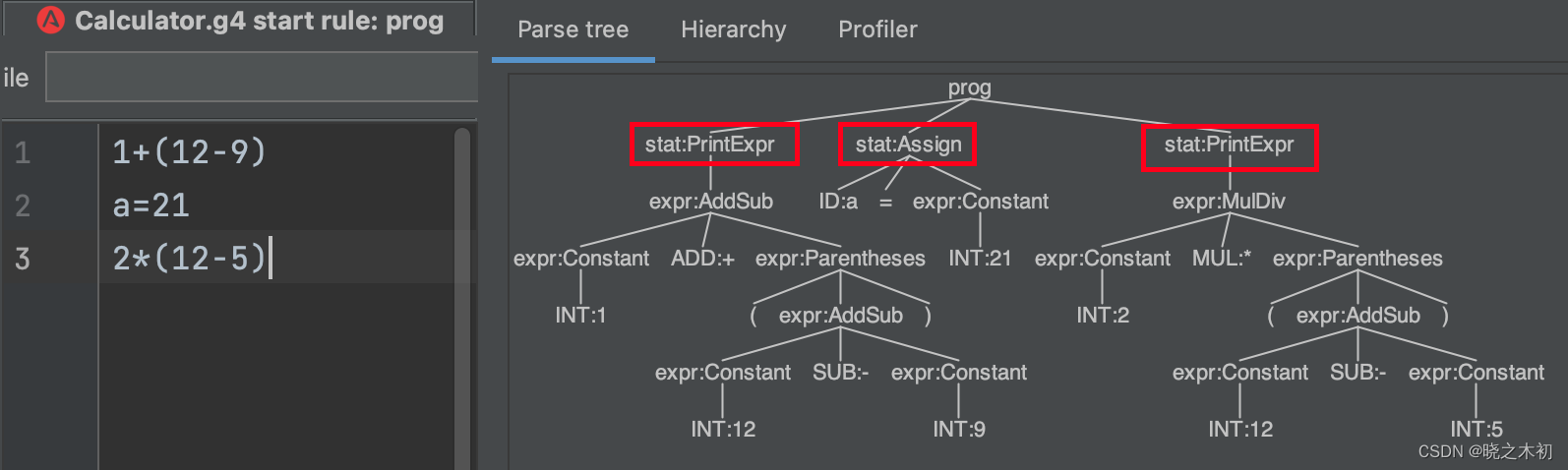
- After adding a label to the rule element of the stat, the parsed stat will be identified by the label
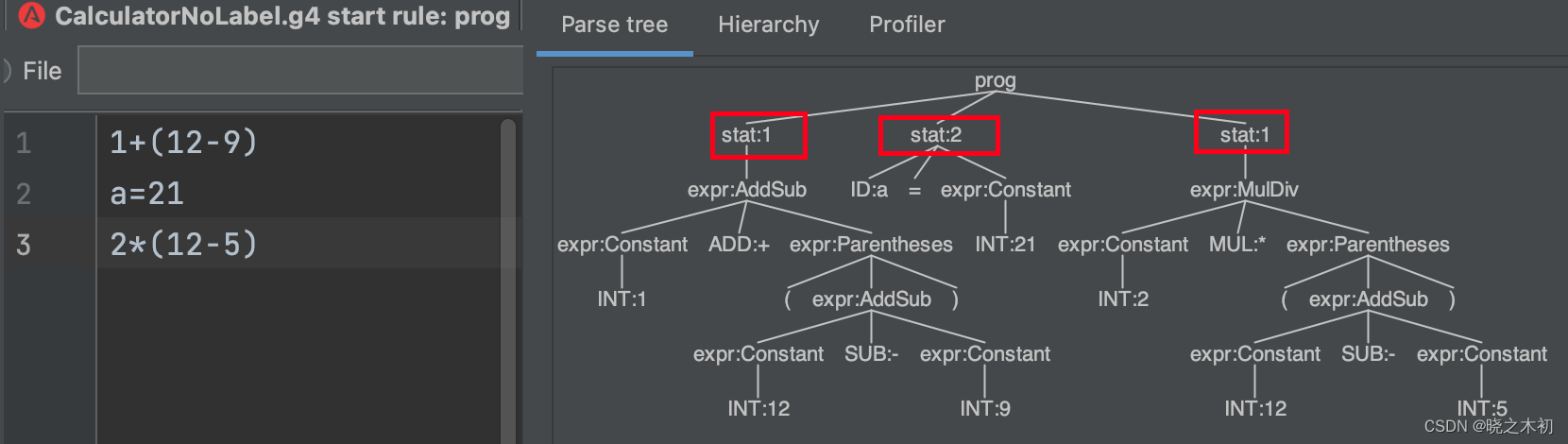
- After removing the label of the rule element, only the serial number can be used for identification
- After adding a label to the rule element of the stat, the parsed stat will be identified by the label
- It can be said that using label to identify rule element can bring unexpected convenience to grammar analysis
1.3 The role of labels
- The Antlr4 official website introduces the label like this:
- Labeling Rule Alternatives for Precise Event Methods, we can get more precise parse-tree listener events by labeling the outermost alternatives of a rule using the # operator.
- All alternatives within a rule must be labeled, or none of them. Here are two rules with labeled alternatives.
- Alternative labels do not have to be at the end of the line and there does not have to be a space after the # symbol. ANTLR generates a rule context class definition for each label.
It can be summed up as follows:
-
Adding a label can generate a corresponding rule element for each rule element
ParserRuleContext, so as to quickly access each rule element- Since no label is added to the rule element of stat,
CalculatorParser.StatContextthe rule element can only be obtained through the getter methodpublic static class StatContext extends ParserRuleContext { // getter方法 public ExprContext expr() { return getRuleContext(ExprContext.class,0); } public TerminalNode ID() { return getToken(CalculatorNoLabelParser.ID, 0); } ... // 其他代码省略 } - With the addition of label, a more specific Context will be created based on StatContext, which is conducive to accessing each node in the parse tree
public static class StatContext extends ParserRuleContext { public StatContext(ParserRuleContext parent, int invokingState) { super(parent, invokingState); } @Override public int getRuleIndex() { return RULE_stat; } public StatContext() { } public void copyFrom(StatContext ctx) { super.copyFrom(ctx); } } public static class AssignContext extends StatContext { public TerminalNode ID() { return getToken(CalculatorParser.ID, 0); } public ExprContext expr() { return getRuleContext(ExprContext.class,0); } ... // 其他代码省略 } public static class PrintExprContext extends StatContext { public ExprContext expr() { return getRuleContext(ExprContext.class,0); ... // 其他代码省略 }
- Since no label is added to the rule element of stat,
-
At the same time,
CalculatorListenerthe listener methods in the interface are also richer, so as to more accurately monitor the node access events in the parse tree// 未添加label,只能监听stat节点。具体是赋值节点还是打印节点,需要在代码中区分 void enterStat(CalculatorNoLabelParser.StatContext ctx); void exitStat(CalculatorNoLabelParser.StatContext ctx); // 添加label后的监听器方法更加有针对性 void enterPrintExpr(CalculatorParser.PrintExprContext ctx); void exitPrintExpr(CalculatorParser.PrintExprContext ctx); void enterAssign(CalculatorParser.AssignContext ctx); void exitAssign(CalculatorParser.AssignContext ctx); -
My own supplement:
CalculatorVisitorthe visitXxx() method in the interface will also become richer, so as to access the rule element more precisely, and thus access each node in the parse tree// 未给添加label,只能访问stat节点。具体是赋值节点还是打印节点,需要在代码中区分 T visitStat(CalculatorNoLabelParser.StatContext ctx); // 添加label后,visitStat()方法被以下有针对性的方法替代 T visitPrintExpr(CalculatorParser.PrintExprContext ctx); T visitAssign(CalculatorParser.AssignContext ctx);
2. Tips
-
Suggestion: add labels to rule elements, so that it will be more convenient to obtain specific nodes
-
Take the implementation of calculator in visitor mode as an example. If you do not add a label to the rule element of stat, you need to judge the type of node independently when
CalculatorVisitorImplrewriting the method inCalculatorVisitor.visitStat()@Override public Integer visitStat(CalculatorNoLabelParser.StatContext ctx) { if (ctx.ID() != null) { // 存在ID说明是赋值语句 String variable = ctx.ID().getText(); Integer value = visit(ctx.expr()); variables.put(variable, value); } else { // 否则是打印语句 if (ctx.expr() instanceof CalculatorNoLabelParser.ConstantContext) { System.out.printf("%d\n", visit(ctx.expr())); } else { System.out.printf("%s = %d\n", ctx.expr().getText(), visit(ctx.expr())); } } return 0; // 打印语句统一返回0 } -
If the label is defined, there is no need to independently judge the type of the node, and you can directly access the specific node
@Override public Integer visitPrintExpr(CalculatorParser.PrintExprContext ctx) { Integer result = visit(ctx.expr()); if (ctx.expr() instanceof CalculatorParser.ConstantContext) { System.out.println("打印常量的值: " +result); } else { System.out.printf("打印计算结果: %s = %d\n", ctx.expr().getText(), result); } return result; } @Override public Integer visitAssign(CalculatorParser.AssignContext ctx) { String variable = ctx.ID().getText(); Integer value = visit(ctx.expr()); variables.put(variable, value); return value; }