Author: Insist--
Personal homepage: insist--personal homepage
The author will continue to update network knowledge and python basic knowledge , looking forward to your attention
foreword
This article will explain what a VPN is, its types, usage scenarios, and working principles.
Table of contents
2. Bypass geographic restrictions
1. What is a VPN?
VPN is a virtual private network , as the name suggests, it refers to the "virtual" "private network" established by our company, or the service that provides such a network.
In a VPN, dedicated routers are set up on sites that let them connect to each other, and they interconnect over public lines. At this time, on the public line, there is a special communication network that cannot read the external content of the communication. After the encryption is completed, there is no need to worry about eavesdropping on the communication content.
2. Types of VPN
1. Site-to-Site VPN
A site-to-site VPN connection is a way to connect two or more local area networks through a public network . By establishing an encrypted tunnel, data between sites can be transmitted securely, and network intercommunication between different geographical locations can be realized. It is generally used in the intranet of the same company but different locations. It can also be applied to extranets in different companies.
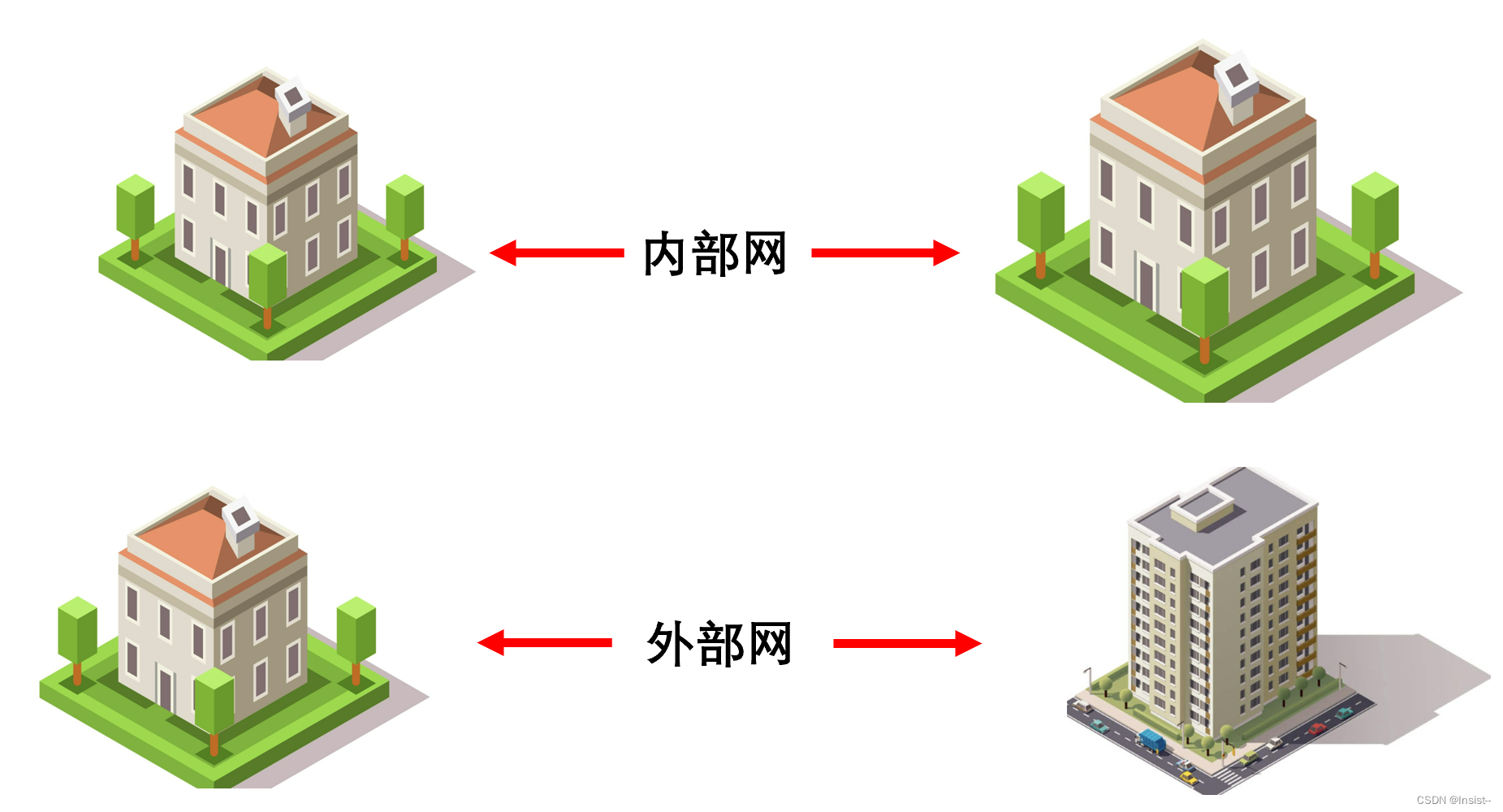
When a data packet is sent to the VPN hub, the source address of the data packet will be changed to the address of the current VPN hub, and the destination address will be changed to the address of the destination VPN hub. At this time, the data packet will be encrypted, which hides the actual original address and destination address. Let's look at another type.
2. Client-to-Site VPN
Another type is a client-to-site VPN, or remote access VPN.
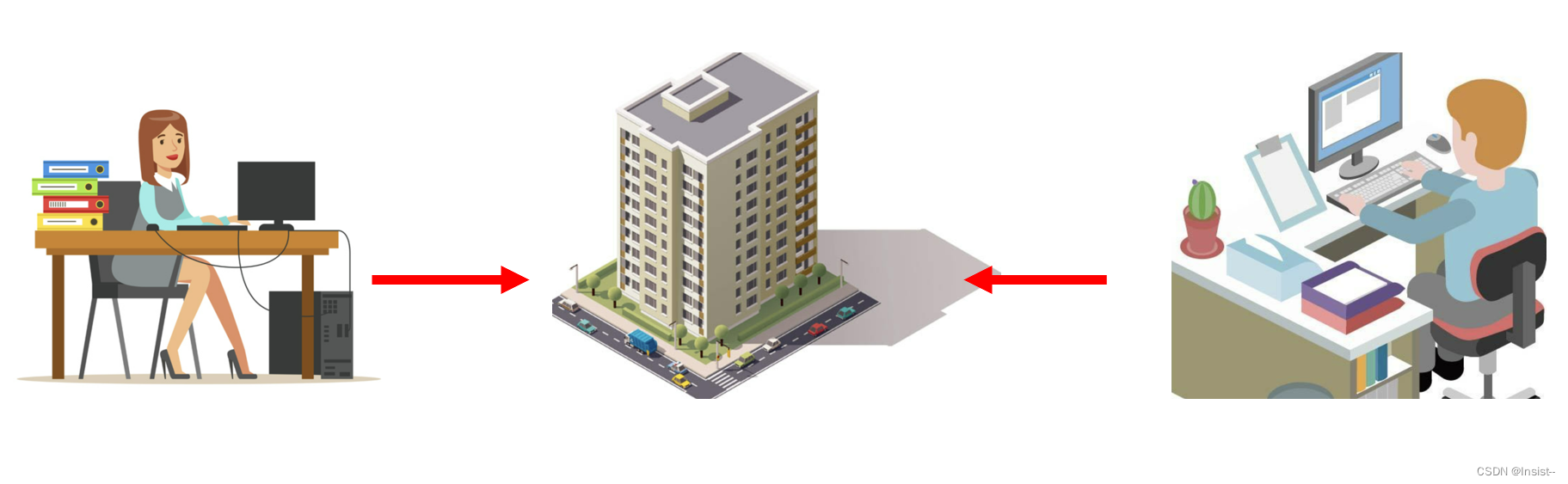
This type is more suitable for home office scenarios. The site-to-site address mentioned above is relatively fixed, but the home address of each employee is in a different location. If the employee works in another location, the IP address will change. The client-to-site VPN type can solve this problem . Compared with site-to-site VPN, it is very flexible.

This type of VPN is also available in two modes : full tunnel and half tunnel , and you can choose different modes according to different scenarios.
3. VPN Usage Scenarios
1. Public Wi-Fi network
When using a public Wi-Fi network, it is vulnerable to eavesdropping and data tampering by hackers. By connecting to a VPN, users can establish encrypted connections on public Wi-Fi networks to protect personal privacy and sensitive data.
2. Bypass geographic restrictions
Some websites and online services are restricted based on the user's geographic location. Through VPN, users can choose to connect to servers in other countries or regions, obtain access rights in the corresponding region, and bypass geographic restrictions.
3. Encrypted communication
For industries that need to protect privacy and sensitive information, such as finance and medical care, VPN can provide a secure channel for encrypted communication to prevent data leakage and illegal access.
4. Go online anonymously
Using a VPN can hide the user's real IP address and browsing history, and realize anonymous surfing. This is very important to protect personal privacy and resist online tracking.
4. Working principle of VPN
How a VPN works is useful for a deeper understanding of this functionality. The working principle behind a VPN is as follows:
When you connect to a virtual private network service (aka VPN), it authenticates the client with the VPN server .
The server will then apply an encryption protocol to all data you send and receive.
A VPN service creates an encrypted "tunnel" over the Internet . The tunnel will protect the data in transit between you and the destination.
In order to ensure the security of each data packet, the VPN packs it in an external data packet, and then encrypts it through encapsulation. The external data packet is the core element in the VPN tunnel, which will ensure the security of the data during transmission.
When the data arrives at the server, through a decryption process , the external packets are removed.