1. Black body
Any object has the property of continuously radiating, absorbing, and reflecting electromagnetic waves. The radiated electromagnetic waves have different powers at each frequency, that is, they have a certain spectral distribution. This spectral distribution is related to the characteristics of the object itself and its temperature, so it is called thermal radiation. In order to study the laws of thermal radiation that do not depend on the specific physical properties of matter, physicists have defined an ideal object—— black body (blackbody), which is used as a standard object for thermal radiation research. An ideal black body can completely absorb electromagnetic waves of any frequency and incident on its surface at any angle, and radiate the absorbed radiation energy in the form of heat energy. The spectral characteristics of its thermal radiation are only related to the temperature of the black body, and the material of the black body irrelevant.
Kirchhoff's radiation law (Kirchhoff law) points out that the ratio of the power radiated by an object in thermal equilibrium to the power absorbed by the radiation has nothing to do with the physical properties of the object itself, but only with the wavelength and temperature. According to Kirchhoff's radiation law, at a certain temperature, a black body must be the object with the largest radiation ability, which can be called a complete radiator. For example, the sun is a gas planet, and it can be considered that the electromagnetic radiation directed at the sun is difficult to be reflected back, so the sun is considered to be a black body. Theoretically, black bodies emit electromagnetic waves of all wavelengths on the spectrum.
Obviously there is no true ideal black body in nature, but many objects can be used as better approximate black bodies, as shown in the figure below.

2. Black body radiation formula
The correct black body radiation formula was derived by German physicist Planck in 1900, based on Wien displacement law and Stefan-Boltzmann law ).


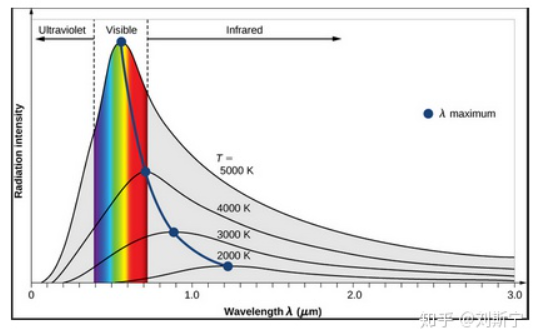
It can be seen from the figure:
- At a certain temperature, there is an extremum λm in the spectral radiance of a black body, and the position of this extremum is related to temperature, which is given by Wien's displacement law, that is, λm=b/T, b=2898(μm·K).
- When the temperature of the black body gradually increases, the extreme position of the spectral radiance of the black body moves to the short-wave (blue light) direction, and vice versa moves to the long-wave (red light) direction.
- At any wavelength, the spectral radiance of a high-temperature blackbody is absolutely greater than that of a low-temperature blackbody, regardless of whether the wavelength is at the maximum radiance of the spectrum.
If E ( λ, T ) is integrated for all wavelengths and also for each radiation direction, then the total radiation power formula of the black body can be obtained, that is, the Stepan-Boltzmann law,
E ( T )= δT^ 4 (W/m2)
Where δ =5.67×10^-8 W/m^2·K^4, which is the Stepan-Boltzmann constant.
The figure below shows the full-band radiation spectrum of the sun. It can be seen that the radiation spectrum on the surface of the sun is almost identical to the ideal black body radiation spectrum of 5500K, so the sun can be considered as an ideal black body.

3. Color temperature
Color temperature is a measure of the light color of a light source, and the unit is Kelvin. British physicist Kelvin proposed that assuming that an ideal black body can absorb all the radiation energy falling on it without loss, and at the same time release all the energy increased by absorbing radiation in the form of light, it will be due to It absorbs the level of radiant energy and presents different colors. If the color of a certain light is the same as the spectrum of light emitted by a black body at temperature T, then the color temperature of the light is defined as T.
Color temperature plays a very important role in astrophysics. Physicists have long discovered that different stars have different colors, and the color depends on the surface temperature of the star, as shown in the figure below.

Therefore, astrophysics classifies stars according to their color temperature and relative luminosity, and divides celestial bodies into main sequence stars, giant stars, supergiant stars, white dwarfs, etc. As shown below.

The figure below shows the typical color temperature and corresponding hue of several common light sources in daily life.

4. Light source and color temperature
According to the provisions of ISO3664:2000, the D50 light source with a color temperature of 5000K is a standard light source for observing colors, and the light source is slightly warmer. From the blackbody radiation spectrum in the figure below, we can see that the intensity of red light in the spectrum at 5000K is slightly greater than that of blue light, which is the main reason for the warmer side of D50.
Other commonly used light sources and color temperatures are,
- D65 light source is an artificial light source with a color temperature of 6500K and a slightly cooler tone. It has been gradually replaced by D50 light source in Europe and is still widely used in China.
- The D75 light source is a cool-toned light source with a color temperature of 7500K, simulating the average sunlight in the north.
- CWF light source is a cool white light source with a color temperature of 4200K. It is the standard light source in American stores. The full English name is Cool White Fluorescent
- TL84 light source is a white light source with a color temperature of 4000K, which is the standard light source for stores in Europe, Japan and China
- TL83 light source is a warm white light source with a color temperature of 3000K, the standard warm white light source (WarmWhite) used in European shops
- The U30 light source is a warm light source with a color temperature of 3000K. It is a warm white light source (WarmWhite) used in American stores. It is a white flag lamp.
- The U35 light source is a warm light source with a color temperature of 3500K, and the American retailer Target specifies the color matching lamp tube
- A light source is a warm light source with a color temperature of 2856K, American-style kitchen window spotlight white flag lamp
- F light source is a warm light source with a color temperature of 2700K, used in homes and hotels
- The Horizon light source is a warm light source with a color temperature of 2300K, simulating sunlight at sunrise and sunset
The figure below shows the visible light radiation spectrum of several common light sources such as sunlight, incandescent lamps, fluorescent lamps, halogen lamps, cool white LED lamps, and fluorescent bulbs. It can be seen that among all common light sources, only the sun has the most abundant spectral lines, and the power distribution in the visible light band is also the flattest. Therefore, daylight is the best light source for observing colors, and its color rendering index is defined as 1 .
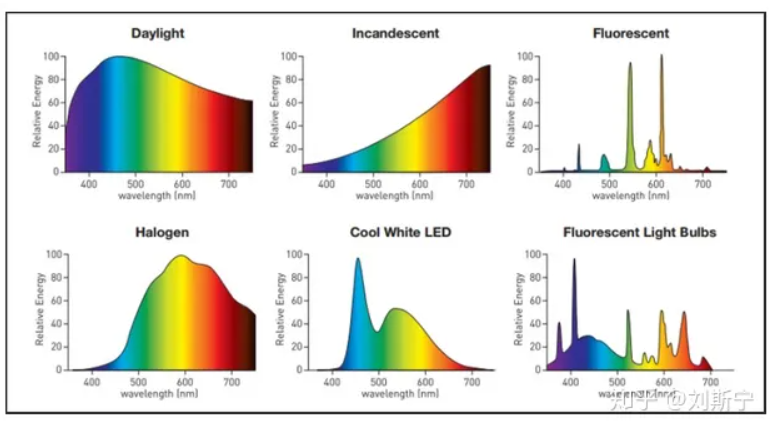
It is worth noting that the cool white LED light source has a radiation peak at blue light that is significantly higher than other spectral lines, which is the reason for the cooler tone of the light source.
5. White light and white
White light is defined as colorless light that contains all wavelengths in the visible light spectrum with equal radiant intensity, as shown in the figure below.

An object appears white to the human eye when its surface emits or reflects white light . An object appears black to the human eye when its surface does not emit or reflect any light .
The logarithmic relationship between white and black is divided into several levels, called " gray level". Generally the range is from 0 to 255 with 0 for black and 255 for white, or from 0 to 4095 with 0 for black and 4095 for white. Black and white pictures are also called grayscale images, which are widely used in the fields of medicine and image recognition.
The International Association of Illumination once stipulated that the standard white light used for observing colors is a D65 light source with a color temperature of 6500K, and the spectrum is close to daylight. Recent regulations have revised the color temperature standard to 5000K, but the earlier standard of 6500K is still widely adopted in regions such as China.
6. Application of color temperature
Studies have found that different color temperatures can cause different emotional responses. Generally, the color temperature of light sources can be divided into three categories, namely
- Warm color light, the color temperature is below 3300K, which is close to the color of incandescent light. There are more red light components in the spectrum, giving people a warm, healthy and comfortable feeling. It is suitable for families, hotels, supermarket food areas and other occasions.
- Warm white light, the color temperature is between 3300~5300K, the light is soft, giving people a comfortable, pleasant and peaceful feeling. It is suitable for the most common places such as shops, hospitals and offices.
- Cool white light, color temperature above 5300K, spectrum close to daylight, giving people a bright and sober feeling, making people concentrate, suitable for offices, conference rooms, libraries, factory workshops and other occasions that require high concentration.
The figure below is a comparison of the effects of light sources with different color temperatures when they are applied to indoor lighting.


The figure below is a comparison of the effects of light sources with different color temperatures when they are applied to portrait lighting.

7. Typical application scenarios
Factory workshop: 4500-5000K for special and meticulous work, 5000-5500K for other general work

Hospital: 4000-4500K for general wards, 5000-5500K for consulting rooms, so that patients can be quiet, trust doctors, and cooperate with doctors' examination and treatment.

School: classroom, library, science laboratory 4500-5000K
Art classroom, liberal arts activity room 3000-4500K

The main lighting of the shopping mall: 3500-4500K, the color temperature is natural and lively. It can arouse people's desire to buy, and the reflection of color on the product can give people a feeling of reassurance and comfort.

Shopping mall food area: 3000-3500K, can stimulate appetite.

8. Color constancy
Perceptual constancy is an important feature of human perception of objective things. When objective conditions change within a certain range, our perceptual image maintains its stability to a considerable extent, that is, perceptual constancy. For example, if an adult moves from near to far, although the image on our retina shrinks accordingly, it will not perceive him as a child.
Perceptual constancy can be divided into size constancy, shape constancy, color constancy, distance constancy, speed constancy, etc.
Color constancy is a kind of perceptual constancy. When the color of the object changes due to changes in lighting conditions, the individual's color perception of familiar objects still tends to the same perceptual property.
For a specific object, due to changes in the environment (especially the lighting environment), the reflectance spectrum of the surface of the object will be different. The human visual recognition system can recognize this change and can judge that the change is caused by a change in the lighting environment. When the lighting change changes within a certain range, the human recognition mechanism will consider the change within this range The surface color of an object is constant.
From an evolutionary point of view, this is because most objects in the natural world do not change color, but the light source usually changes. Therefore, the brain has evolved color constancy to adjust the final color of the object according to the light source and the information of various objects around it. One view is that the visual system is trying to eliminate the influence of light sources on color perception all the time, so when the color of an object is uncertain, it will find a way to "discard" the light source.
The image below is a photo of a dress that research has shown appears to some people as platinum and gold, while to others it appears blue and black. This experiment shows that different people interpret the same color stimulus differently.

We can use PS software to simulate the color correction process in the brain: when using PS to remove the blue, you can see platinum (left in the picture below); and remove the platinum with PS, you can see Blue and black clothes (below right).

9. Color temperature and white balance
In the field of cameras, the CMOS/CCD sensor device used for photosensitive imaging is essentially a linear element used in photonic technology. It will try to faithfully record the number of photons incident on the pixel unit, but it is impossible to have the automatic function like the human eye. Suppress the light source components to realize the color constant function, so the parameters of the sensor must be adjusted in real time through the camera control software to achieve a similar color constant effect. This process is white balance. The obtained object image is equivalent to the effect effect under standard sunlight.
For more information on this topic, please refer to the similar articles of Zhiyou. Color temperature, white balance and color constancy-Knowledge
10. National lighting standard data
The National Standard of the People's Republic of China "Architectural Lighting Design Standards" GB 50034-2013 specifies the general illuminance standard values for new, rebuilt and expanded residential, public and industrial buildings.

When one or more of the following conditions are met, the illuminance of the working surface or the reference plane can be graded and increased by one level according to the standard value of the illuminance.
- For fine work places with high visual requirements, when the distance from the eyes to the recognition object is greater than 5 ( X ) nun;
- When continuous long-term intense visual work has adverse effects on visual organs;
- When identifying moving objects, the identification time is short and identification is difficult;
- When visual operations have a significant impact on operational safety;
- When the brightness contrast of the identified object is less than 0.3;
- When the operation accuracy is required to be high, and errors will cause great losses;
- When visual ability is below normal ability;
- When the building grade and function requirements are high.
When one or more of the following conditions is met, the illuminance of the working surface or the reference plane can be graded and reduced by one level according to the standard value of the intensity.
- When working for a short period of time;
- When precision or speed of work is not critical;
- When the building grade and functional requirements are low.
In general, the design illuminance value may have a deviation of -10%-+10% compared with the illuminance standard value.