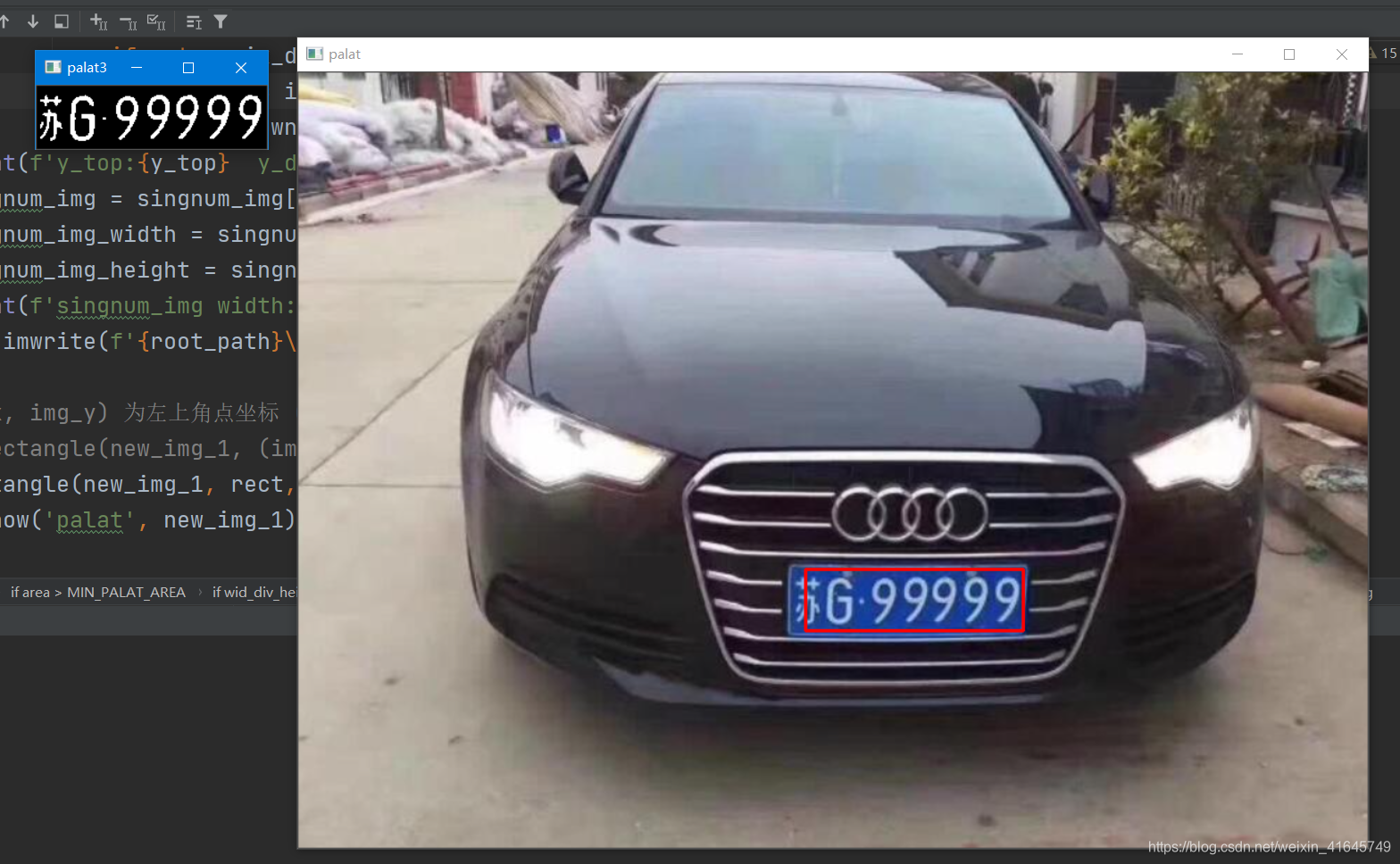
Not much to say, first look at the final result picture (if you want all the projects, I will put the github link at the end of the article):





It can be seen that the final recognized license plate number is: Su G99999.
In fact, the winter before last year, I accidentally thought about using c++ to do a small project, and then used c++ opencv to realize the extraction and segmentation of the license plate, and then found some blogs to do it myself, and then made it, but the effect was not very good, using c++ The method can only do license plate extraction and character segmentation, but the last step, the recognition of the cut out characters, read a lot of big shots, saying that CNN is the best way to do it, so the segmentation was done at that time , the last step of identification cannot be done. 

The above is the effect of running with c++ and the log of this small project at that time, only license plate extraction and segmentation.
Then I learned deep learning last year. I used pytorch as a framework and trained a lot of CNN models. Then I thought about using python + opencv + pytorch to build a CNN model to solve this problem. Question, currently I use the data I collected to run this model, the accuracy rate is about 90%, and then run it with the license plate characters generated by myself, the accuracy rate is not bad. ( If you need a license plate character data set for training, you can give me a like and send me an email )
My idea is divided into three steps:
1. Extract the license plate from the picture
2. Separate the license plate characters one by
one 3. Resize the license plate into the corresponding size
4. Use CNN to train the license plate character classification model
5. Use the trained model to run the license plate characters we extracted to get the license plate number
Step 1: Cut out the license plate
This is mainly to use the expansion in opencv A series of operations of corrosion and corrosion extract the rectangle of the license plate, and then extract the license plate based on the extracted rectangle.
Step 2: Segment the extracted license plate into characters.
Here, the license plate is first binarized, and then the characters are segmented according to the projection of each pixel on the x-axis. (The effect of the method I wrote in the first and second steps is not bad, but I feel that it should be optimized again. It should be that the smaller the image noise of the extracted characters, the higher the recognition rate of CNN, so there is no need to refer to my method here. method to do it, the most important thing is... this code is so badly written, I can't bear to look back)
def readjpg():
img = cv2.imread(plate_path)
# cv2.imshow('test', img)
n = 1
img_width = img.shape[0]
img_height = img.shape[1]
img_resize_width = round(n*img_width)
img_resize_height = round(n*img_height)
print(f'width:{img_width}, height:{img_height}')
print(f'round_width:{img_resize_width}, rpund_height:{img_resize_height}')
new_img_1 = cv2.resize(img, (img_resize_height, img_resize_width))
# cv2.imshow('img2', new_img_1)
# cv2.imshow('img', img)
# 将输入的图像从一种颜色格式转化为另一种颜色格式(OpenCV中的默认颜色格式通常称为RGB,但实际上是BGR(字节是相反的)
mark = cv2.cvtColor(new_img_1, cv2.COLOR_BGR2GRAY)
# cv2.imshow('mark', mark)
# 先做高斯模糊
mark = cv2.GaussianBlur(mark, (3, 3), 3, 0)
# cv2.imshow('guss', mark)
# 边缘检测
mark = cv2.Canny(mark, 300, 200, 3)
# cv2.imshow('candy', mark)
# 腐蚀和膨胀
kernel_X = cv2.getStructuringElement(cv2.MORPH_RECT, (20, 1)) # 定义矩形卷积核
mark = cv2.dilate(mark, kernel_X, (-1, -1),iterations=2) # 膨胀操作
mark = cv2.erode(mark, kernel_X, (-1, -1), iterations=4) # 腐蚀操作
kernel_Y = cv2.getStructuringElement(cv2.MORPH_RECT, (1, 15)) # 定义矩形卷积核
mark = cv2.dilate(mark, kernel_X, (-1, -1), iterations=2) # 膨胀操作
mark = cv2.erode(mark, kernel_Y, (-1, -1), iterations=1) # 腐蚀操作
mark = cv2.dilate(mark, kernel_Y, (-1, -1), iterations=2)
mark = cv2.medianBlur(mark, 15)
mark = cv2.medianBlur(mark, 15)
# cv2.imshow('erode', mark)
conyours, h = cv2.findContours(mark, cv2.RETR_EXTERNAL, cv2.CHAIN_APPROX_SIMPLE)
# print(len(conyours))
find_palat_flag = False
for index in range(len(conyours)):
area = cv2.contourArea(conyours[index])
print(area)
if area > MIN_PALAT_AREA:
rect = cv2.boundingRect(conyours[index])
# print(rect)
print(rect[0], rect[1], rect[2], rect[3])
wid_div_height = rect[2]/rect[3]
print(f'wid_div_height:{wid_div_height}')
if wid_div_height > 3 and wid_div_height< 8:
find_palat_flag = True
print(rect)
img_x = int(rect[0])
img_y = int(rect[1])
img_width = int(rect[2])
img_height = int(rect[3])
print(f'x:{img_x}, y:{img_y}, width:{img_width}, height:{img_height}')
# imgx[110:130,50:70,2]表示一个范围:[高度起始点:高度结束点,宽度起始点:宽度结束点,哪个通道],起始点均以左上角
plate_img = new_img_1[img_y:img_y + img_height, img_x-10:img_x + img_width] # 分割出识别到的车牌的块 宽度两边加10
# plate_img = cv2.cvtColor(plate_img, cv2.COLOR_BGR2HSV)
plate_img = cv2.cvtColor(plate_img, cv2.COLOR_BGR2GRAY) # 转化为灰度图
# plate_img = cv2.Canny(plate_img, 450, 120, 3) # 边缘检测
# 进行闭运算
# kernel = np.ones((3, 3), np.uint8)
# plate_img = cv2.morphologyEx(plate_img, cv2.MORPH_CLOSE, kernel)
# cv2.imshow('palat2', plate_img)
_, plate_img = cv2.threshold(plate_img, 140, 255, cv2.THRESH_BINARY) # 二值化
# 腐蚀和膨胀
kernel_X = cv2.getStructuringElement(cv2.MORPH_RECT, (3, 3)) # 定义矩形卷积核
plate_img = cv2.dilate(plate_img, kernel_X, (-1, -1), iterations=1) # 膨胀操作
plate_img = cv2.erode(plate_img, kernel_X, (-1, -1), iterations=1) # 腐蚀操作
cv2.imshow('palat3', plate_img) # 打印出被抠出来的车牌
cv2.imwrite('palat.jpg', plate_img)
# 分割车牌
# 竖直方向上的投影
plate_width = img_width + 10
plate_height = img_height
pix_list = []
for i in range(plate_width):
num_pix = 0
for j in range(plate_height):
if plate_img[j][i] > 0:
num_pix += 1
# print(f'plate_img[{j}][{i}]:{plate_img[j][i]}')
num_pix = num_pix - 2
if num_pix <= 0:
num_pix = 0
print(f'num_pix:{num_pix}')
pix_list.append(num_pix)
next_pix_len = 0
index_start_list = []
index_end_list = []
flag_1 = True
sum_len = 0
sum_len_list = []
print(f'pix_list_len:{len(pix_list)}')
for i in range(len(pix_list)):
if pix_list[i] > 0:
sum_len += pix_list[i]
next_pix_len += 1
if flag_1:
index_start = i
index_start_list.append(index_start)
flag_1 = False
else:
if next_pix_len >=3:
sum_len_list.append(sum_len)
# print(f'sum_len = {sum_len}')
sum_len = 0
print(f'i:{i} next_pix_len:{next_pix_len}')
flag_1 = True
index_end_list.append(next_pix_len + index_start)
next_pix_len = 0
# print(f'index_start = {index_start}')
# print(index_start_list)
print(index_end_list)
print(sum_len_list)
sum_sort = []
for index_o in range(len(sum_len_list)):
sum_sort.append(sum_len_list[index_o])
print(f'sum_sort:[{sum_sort}]')
# print(sorted(sum_len_list))
print(f'len(index_end_list) = {len(index_end_list)}')
sum_len_list_sort = sorted(sum_len_list)
print(f'sum_len_list_sort:[{sum_len_list_sort}]')
print(f'sum_sort:[{sum_sort}]')
if len(sum_len_list_sort) > 7:
for index_m in range(0, len(sum_len_list_sort) - 7):
for index_p in range(len(sum_sort)):
if sum_sort[index_p] == sum_len_list_sort[index_m]:
print(f'{sum_sort[index_p]}=={sum_len_list_sort[index_m]}')
print(f'idx = {index_p}')
# print(f'index_start_list[index_p]={index_start_list[index_p]}')
del index_start_list[index_p]
del index_end_list[index_p]
for index_i in range(len(index_end_list)):
print(f'[{index_start_list[index_i]}~{index_end_list[index_i]}]')
# cv2.imwrite(f'{index_i}.jpg', plate_img[0:plate_height, index_start_list[index_i]:index_end_list[index_i]+2])
singnum_img = plate_img[0:plate_height, index_start_list[index_i]:index_end_list[index_i]+2]
singnum_img_width = singnum_img.shape[1]
singnum_img_height = singnum_img.shape[0]
# print(f'singnum_img width:{singnum_img_width} singnum_img height:{singnum_img_height}')
y_top = 0
y_down = 0
y_pix_up_flag = True
y_pix_down_flag = True
for index_num_img_y in range(singnum_img_height):
for index_num_img_x in range(singnum_img_width):
if singnum_img[index_num_img_y][index_num_img_x] > 0:
y_pix_down_flag = False
if y_pix_up_flag:
y_top = index_num_img_y
y_pix_up_flag = False
else:
if not y_pix_down_flag:
y_down = index_num_img_y
y_pix_down_flag = True
print(f'y_top:{y_top} y_down:{y_down}')
singnum_img = singnum_img[y_top:y_down+1, 0:singnum_img_width]
singnum_img_width = singnum_img.shape[1]
singnum_img_height = singnum_img.shape[0]
print(f'singnum_img width:{singnum_img_width} singnum_img height:{singnum_img_height}')
cv2.imwrite(f'{root_path}\\single_num\\{index_i}.jpg',singnum_img)
# (img_x, img_y) 为左上角点坐标 (img_x+img_width, img_height+img_y) 为右下角点坐标,两个对角点确定一个矩形
# cv2.rectangle(new_img_1, (img_x, img_y), (img_x+img_width, img_height+img_y), (0, 0, 255), 2)
cv2.rectangle(new_img_1, rect, (0, 0, 255), 2) # 将识别到的车牌在图像中框出来
cv2.imshow('palat', new_img_1)
if not find_palat_flag:
print("Can't find palat!!!!")
cv2.waitKey(0)
return 0
This interface encapsulates the first step of license plate extraction and the second step of license plate segmentation, and the writing is relatively poor...
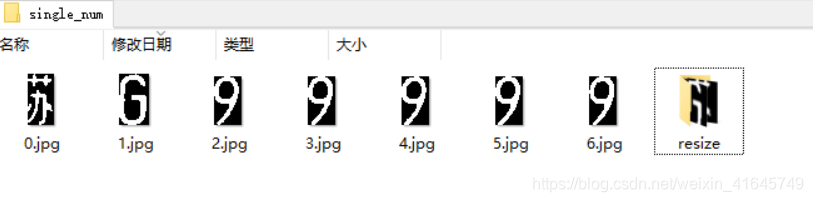
Step 3: Resize the license plate to the corresponding size.
The main purpose here is to put the pictures into the trained model and run them in a unified size. Specifically, fill the pictures with a size of width = 4:5 and then resize them into 32x40, which can ensure that the extracted image will not be stretched and deformed when resized.
def resize_image(image, height = IMAGE_HEIGHT, width = IMAGE_WIDTH):
top, botton, left, right = 0, 0, 0, 0
h, w, c = image.shape
loggest_edge = max(h, w)
# 计算短边需要多少增加多少宽度使之长宽相等
if h < loggest_edge:
dh = loggest_edge - h
top = dh // 2
botton = dh - top
elif w < loggest_edge:
dw = IMG_WIDTH - w
left = dw // 2
right = dw - left
else:
pass
BLACK = [0, 0, 0]
# 将图像转换为一个正方形的image,两边或者上下缺少的的用黑色矩形填充
constant = cv2.copyMakeBorder(image, top, botton, left, right, cv2.BORDER_CONSTANT, value=BLACK)
return cv2.resize(constant, (height, width))
def readpath(path_name):
for dir_item in os.listdir(path_name):
full_path = os.path.abspath(os.path.join(path_name, dir_item)) # 组合照片和路径的名字
if os.path.isdir(full_path): # 如果是文件夹,递归调用
readpath(full_path)
else:
if dir_item.endswith('.jpg'):
image = cv2.imread(full_path)
image = resize_image(image, IMAGE_WIDTH, IMAGE_HEIGHT)
images.append(image)
# print('full_path:', full_path)
# print('dir_item:', dir_item)
labels.append(dir_item)
return images, labels
def load_dataset(path_name):
images, labels = readpath(path_name)
resizedata_path = RESIZE_IMG_PATH
# resizedata_path = 'D:\\DeapLearn Project\\Face_Recognition\\moreface\\7219face\\test\\resizeface\\'
for i in range(len(images)):
if not os.path.exists(resizedata_path):
os.mkdir(resizedata_path)
img_name = '%s//%s' % (resizedata_path, labels[i])
cv2.imwrite(img_name, images[i])

Step 4: Use CNN to train the license plate character classification model.
I found a data set of license plate characters. There are a total of 0-9 numbers and AZ, except for the 24 uppercase English letters of 'I' and ''O', there are 6 The abbreviation of a province: 

There are several binarized character pictures in each classified folder, and then the model is trained based on this data set.
# 数据集类
class MyDataSet(Dataset):
def __init__(self, data_path:str, transform=None): # 传入训练样本路径
super(MyDataSet, self).__init__()
self.data_path = data_path
if transform is None:
self.transform = transforms.Compose(
[
transforms.Resize(size=(32, 40)), # 原本就是 32x40 不需要修改尺寸
transforms.ToTensor(),
transforms.Normalize((0.5, 0.5, 0.5), (0.5, 0.5, 0.5)),
# transforms.Normalize((0.485, 0.456, 0.406), (0.229, 0.224, 0.225)),
]
)
else:
self.transform = transform
self.path_list = os.listdir(data_path)
def __getitem__(self, idx:int):
img_path = self.path_list[idx]
label = int(img_path.split('.')[1])
label = torch.as_tensor(label, dtype=torch.int64)
img_path = os.path.join(self.data_path, img_path)
img = Image.open(img_path)
img = self.transform(img)
return img, label
def __len__(self)->int:
return len(self.path_list)
train_ds = MyDataSet(train_path)
test_data = MyDataSet(test_path)
# for i, item in enumerate(tqdm(train_ds)):
# print(item)
# break
# 数据加载
new_train_loader = DataLoader(train_ds, batch_size=32, shuffle=True, pin_memory=True, num_workers=0)
new_test_loader = DataLoader(test_data, batch_size=32, shuffle=False, pin_memory=True, num_workers=0)
# for i, item in enumerate(new_train_loader):
# print(item[0].shape)
# break
#
# img_PIL_Tensor = train_ds[1][0]
# new_img_PIL = transforms.ToPILImage()(img_PIL_Tensor).convert('RGB')
# plt.imshow(new_img_PIL)
# plt.show()
# 设置训练类
class Net(torch.nn.Module):
def __init__(self):
super(Net, self).__init__()
self.conv1 = torch.nn.Conv2d(3, 64, kernel_size=3, padding=1)
self.conv2 = torch.nn.Conv2d(64, 64, kernel_size=3, padding=1)
self.conv3 = torch.nn.Conv2d(64, 128, kernel_size=3, padding=1)
self.conv4 = torch.nn.Conv2d(128, 128, kernel_size=3, padding=1)
self.conv5 = torch.nn.Conv2d(128, 256, kernel_size=3, padding=1)
self.conv6 = torch.nn.Conv2d(256, 256, kernel_size=3, padding=1)
self.maxpooling = torch.nn.MaxPool2d(2)
self.avgpool = torch.nn.AvgPool2d(2)
self.globalavgpool = torch.nn.AvgPool2d((8, 10))
self.bn1 = torch.nn.BatchNorm2d(64)
self.bn2 = torch.nn.BatchNorm2d(128)
self.bn3 = torch.nn.BatchNorm2d(256)
self.dropout50 = torch.nn.Dropout(0.5)
self.dropout10 = torch.nn.Dropout(0.1)
self.fc1 = torch.nn.Linear(256, 40)
def forward(self, x):
batch_size = x.size(0)
x = self.bn1(F.relu(self.conv1(x)))
x = self.bn1(F.relu(self.conv2(x)))
x = self.maxpooling(x)
x = self.dropout10(x)
x = self.bn2(F.relu(self.conv3(x)))
x = self.bn2(F.relu(self.conv4(x)))
x = self.maxpooling(x)
x = self.dropout10(x)
x = self.bn3(F.relu(self.conv5(x)))
x = self.bn3(F.relu(self.conv6(x)))
x = self.globalavgpool(x)
x = self.dropout50(x)
x = x.view(batch_size, -1)
x = self.fc1(x)
return x

Step 5: Use the trained model to run the license plate characters we extracted to get the license plate number
Here directly load the model trained in the previous step, and then import our resized license plate character picture into the model to get the predicted license plate number.
def test():
correct = 0
total = 0
with torch.no_grad():
for _, data in enumerate(new_test_loader, 0):
inputs, _ = data[0], data[1]
inputs = inputs.to(device)
outputs = model(inputs)
# print(outputs.shape)
_, prediction = torch.max(outputs.data, dim=1)
print('-'*40)
# print(target)
# print(prediction)
print(f'Predicted license plate number:'
f'{SINGLE_CHAR_LIST[prediction[0]]}'
f'{SINGLE_CHAR_LIST[prediction[1]]}'
f'{SINGLE_CHAR_LIST[prediction[2]]}'
f'{SINGLE_CHAR_LIST[prediction[3]]}'
f'{SINGLE_CHAR_LIST[prediction[4]]}'
f'{SINGLE_CHAR_LIST[prediction[5]]}'
f'{SINGLE_CHAR_LIST[prediction[6]]}')

It can be seen that the predicted license plate number is: Su G99999
is consistent with the license plate number on the picture we input.
The above is the entire process of license plate recognition. Here I only posted the code of some key steps. If you need the whole project, you can go to GitHub to get it.
Reference article:
Xinggeer Daxie's c++ realizes license plate recognition
"PyTorch Deep Learning Practice" course by Mr. Liu at Station B
Project GitHub: Github link (please give me a star, thank you)
send me an email if you want the data set [email protected]