sequence
Xiaobai can't do anything, so learn common sense
quick overview
This video is introduced from bottom to top in the order of data link layer-network layer-transport layer-application layer. Although it's only 30 minutes, it's quite complete, the density is quite high, and Xiaobai is friendly.
Computer Networks Computer Networks Crash Course Computer Science #28_哔哩哔哩_bilibili
Internet The Internet Crash Course Computer Science #29_哔哩哔哩_bilibili
The World Wide Web Crash Course Computer Science #30_哔哩哔哩_bilibili
In fact, it is still not very big, so there are some questions below
What's the difference between a hub, a switch, and a router?
What is the difference between a hub, a switch, and a router_哔哩哔哩_bilibili


 Summarize
Summarize
- The hub constructs the local area network by broadcasting
- The switch is directional forwarding to construct the LAN [according to the MAC address]
- A router is used to connect various LANs and construct several subnets into a larger thing [ip address, network number and host number]
How to understand stratification?
First of all, which layers does it have?
2.1 What are the layers of the TCP/IP network model? | Xiaolin coding (xiaolincoding.com)
Divided into 4 layers: TCP layer, IP layer, TCP layer above, IP layer below
After knowing how many layers are divided, how to understand this layering?
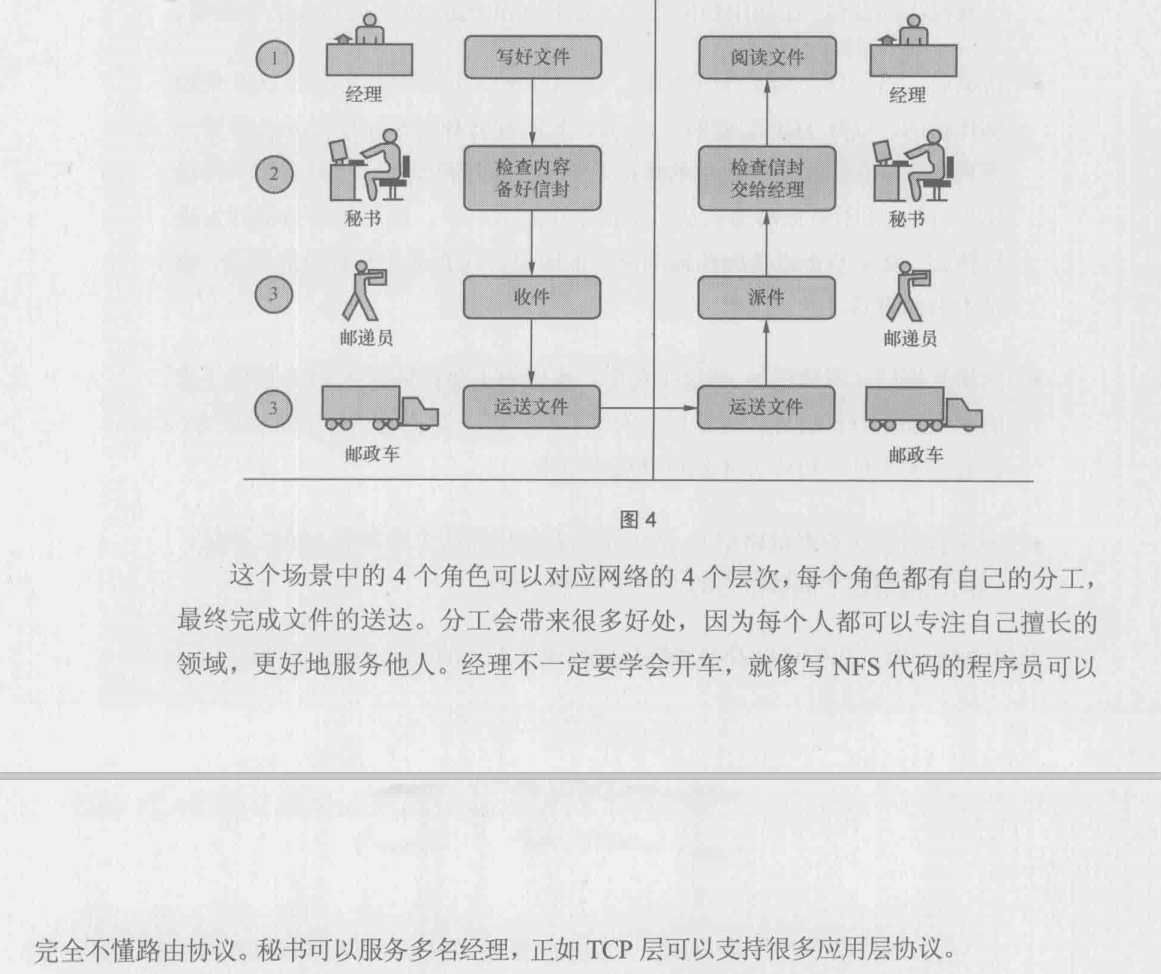
Each layer only cares about itself, regardless of others; for example, the application layer only focuses on providing application functions for users, such as HTTP, FTP, Telnet, DNS, SMTP, etc. The application layer does not need to care about how the data is transmitted, just like when we send a courier, we only need to hand over the package to the courier, and he is responsible for transporting the courier. We don't need to care about how the courier is transported.
Wireshark network analysis is so simple (Douban) (douban.com)
What is the difference between Internet and Ethernet?
page 1
What is the difference between Ethernet and the Internet? - Zhang Xiongjie's answer - Zhihu
Ethernet is a technology used to construct local area networks, in short, Ethernet is a technology, understand.
 [CSMA/CA is a narrowband interception multiple access/collision avoidance protocol, it seems to be talking about exponential backoff or something]
[CSMA/CA is a narrowband interception multiple access/collision avoidance protocol, it seems to be talking about exponential backoff or something]
page 2

Ethernet seems to include the kind of wired?
What is ether, ether, ethereum - Zhihu (zhihu.com)
 WLAN:Wireless Local Area Network
WLAN:Wireless Local Area Network
Probably this kind of wireless
Why do we need an ip address when we have a mac address?
To answer this question, a series of preparations are required:
What is a mac address?
A unique binary string, and a hub switch they are a set.
What is an ip address?
ipv4, 32 bits, these 32 bits are divided into two sections, network number + host number, and the network number can be obtained by performing & operation with the subnet mask. From this network number + host number, combined with the fact that the router is used to connect to the subnet, you can probably have some vague feelings-it feels like this thing is a logical address? It is used to identify which host in which subnet it is
What is the use of ip address?
The ip address seems to be a pair with the routing.
What is the use? What would happen without it? With it or without it, the usefulness is highlighted after such a comparison
No routing: fixed line, not very flexible

With Routing: Flexible, Fault Tolerant

How does routing jump according to ip?
Quoted from: 5.1 IP Basics Family Bucket | Xiaolin coding (xiaolincoding.com)
The network address part of the IP address is used for routing control.
The routing control table records the network address and the address that should be sent to the router next. Both hosts and routers have their own router control tables.
When sending an IP packet, first determine the destination address in the IP packet header, and then find the record with the same network address as the address from the routing control table, and forward the IP packet to the corresponding next router according to the record. If there are multiple records with the same network address in the routing control table, the network address with the most identical digits is selected, that is, the longest match.
The network link in the following figure is used as an example to illustrate
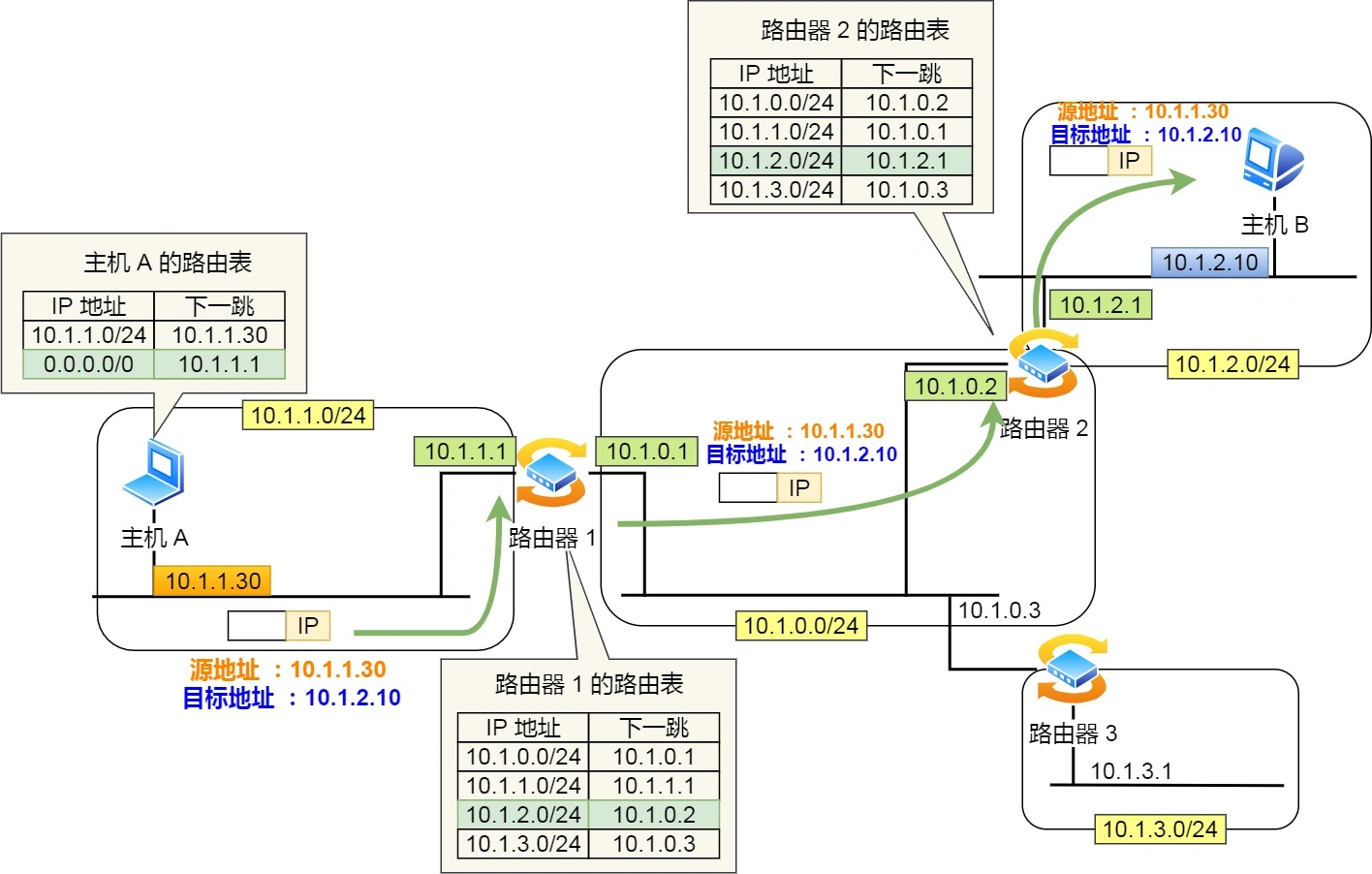
- Host A wants to send an IP packet, whose source address is
10.1.1.30and destination address is10.1.2.10, because the10.1.2.10same network address as the destination address is not found in the routing table of host A, the packet is forwarded to the default route (router1) 1After the router receives the IP packet, it also1matches the network address record with the same destination address in the routing table of the router, and finds that the match is found, so it forwards the IP data packet to10.1.0.2this router2- After the router
2receives it, it also compares its own routing table and finds that it matches, so it sends the IP packet out from this interface2of the router10.1.2.1, and finally forwards the IP packet to the target host through the switch
Among them, the source IP address and destination IP address will not change during the transmission process (premise: no NAT network is used), only the source MAC address and destination MAC address have been changing - from this sentence, there may be some ambiguity feeling.
Summarize
The bedding is over, it's time to summarize
page 1
5.1 Basic knowledge of IP family bucket | Xiaolin coding (xiaolincoding.com)
This is what the site says roughly:
Suppose I want to go from here to here, starting point, destination; analogy source ip, destination ip.


It seems like this analogy:
| Navigation software is equivalent to a router. In this specific case, it plans the entire route into 16 stations based on the entire subway network, combined with the destination and departure point. | 15 segments, that is equivalent to 15 next hops of the router? |
| In these 15 sections, the general starting point of Forest Park and the general end point of South Railway Station have remained unchanged; it will not be said that as I walked, my final destination changed from South Railway Station to Shenzhen. | Among them, the source IP address and destination IP address will not change during the transmission process (premise: no NAT network is used) |
| But in these 15 paragraphs, the stations at the two ends of each paragraph will change | Among them, only the source MAC address and destination MAC are constantly changing |
How do you go? Navigation software can't take you to move instantly, it can only tell you where to go at each fork. Transmission...it doesn't care]
You can't rely on the navigation software, but on the specific means of transportation:

The APP of navigation software is equivalent to the pile of ip, routing, and next hop, and the transportation tool of the subway is equivalent to the pile of mac address, exponential backoff, Ethernet, switch, and hub.
page 2
2.1 What are the layers of the TCP/IP network model? | Xiaolin coding (xiaolincoding.com)
page 3
5.1 Basic knowledge of IP family bucket | Xiaolin coding (xiaolincoding.com)
It seems that ip is used to indicate the direction: for example, you can check the routing table through the unchanged destination ip address. It is currently on router 1, and the next hop is going to router 2 instead of router 3. Specifically how to go from Router 1 to Router 2? Rely on the MAC address. [MAC address, CSMA/CD, exponential backoff, Ethernet, switch, hub, LAN data transmission, are they a set]