This column contains the core knowledge of information theory and coding, organized by knowledge points, and can be used as a reference for teaching or learning. The markdown version has been archived to [Github repository: https://github.com/timerring/information-theory] or public account [AIShareLab] to reply to Information Theory .
Article directory
Information Theory and Coding: Definition and Classification of Channels
Channels are an essential component of any communication system. Any communication system can be regarded as composed of three parts: sending, channel and receiving. A channel usually refers to a signal channel based on a transmission medium.
When the signal is transmitted in the channel, the possible impacts mainly include channel additive noise , signal amplitude attenuation and phase distortion , nonlinearity of channel characteristics , bandwidth limitation and multipath distortion , etc.
In the actual communication system, the influence of the channel on signal distortion can be reduced by adjusting the parameters of the communication system. However, due to the physical characteristics of the transmission medium and the limitations of the electronic components used in the actual communication system, the adjustment range of the system parameters is limited. The size of the reliable information transmission rate in any communication system is limited .
Channels can be divided into: narrow channel and generalized channel
narrow channel
It only refers to the transmission medium and can be divided into two types: wired channel and wireless channel.
- Wired channels: including overhead open wires, symmetrical cables, coaxial cables and fiber optics
- Wireless channel: including ground wave propagation, short-wave ionospheric reflection, ultra-short wave or microwave radio line-of-sight transmission, satellite relay and various scattering channels, etc.
According to the changing characteristics of the transmission medium, the channel in the narrow sense can be divided into:
-
Constant parameter channel : The properties of the transmission medium are stable so that the channel characteristics are stable. For example, typically cable channels, satellite relays, etc.
-
Dependent channel : The random change of the properties of the transmission medium makes the channel characteristics also change randomly. For example, short-wave ionospheric reflection, ultra-short wave, and microwave channels.
Communication bands and common transmission media

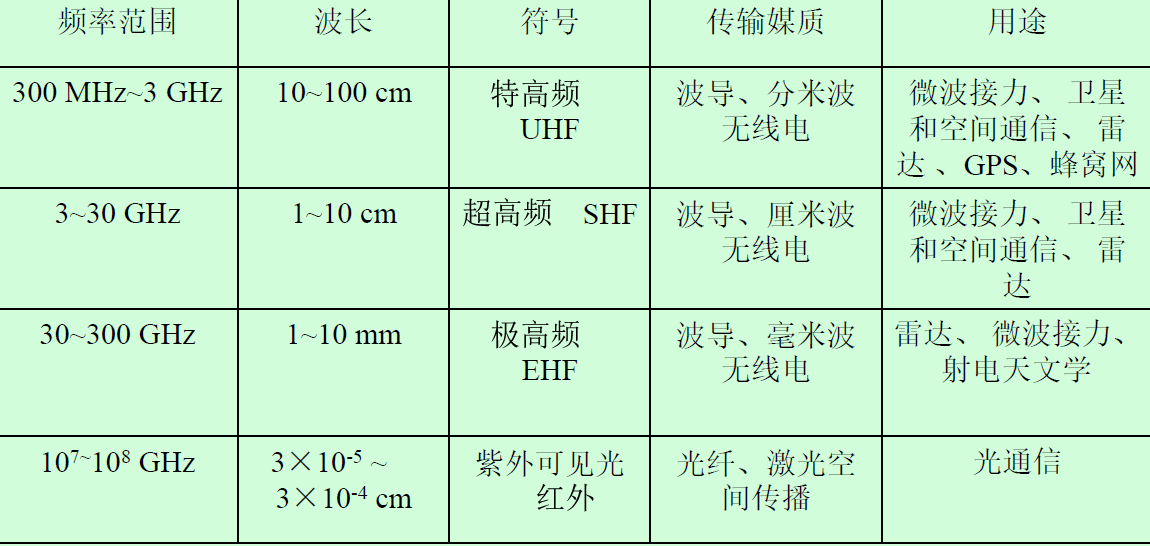
generalized channel
In addition to the transmission medium, it also includes related conversion equipment, such as sending equipment, receiving equipment, antennas, modems and so on. This extended channel is called a generalized channel.
Can be divided into: modulation channel and coding channel
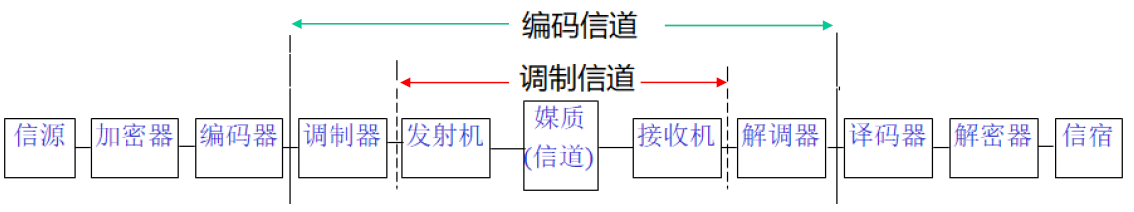
Modulation channel : defined from the perspective of researching modulation and demodulation. It ranges from the output of the modulator to the input of the demodulator .
Coding channel : defined from the perspective of studying encoding and decoding. It ranges from the output of the encoder to the input of the decoder .
Generalized channels are generally divided into: continuous channel and discrete channel
references:
- Proakis, John G., et al. Communication systems engineering. Vol. 2. New Jersey: Prentice Hall, 1994.
- Proakis, John G., et al. SOLUTIONS MANUAL Communication Systems Engineering. Vol. 2. New Jersey: Prentice Hall, 1994.
- Zhou Jiongpan. Communication Principles (3rd Edition) [M]. Beijing: Beijing University of Posts and Telecommunications Press, 2008.
- Fan Changxin, Cao Lina. Principles of Communication (7th Edition) [M]. Beijing: National Defense Industry Press, 2012.