wireless communication network
The wireless communication network includes a mobile phone system for voice communication and a wireless local area network and a wireless wide area network for data transmission.
How does the bottom layer of WiFi transmit data?
1. Mobile communication
1.1 Cellular communication system
In the mid-1980s, the first generation of cellular mobile phone systems were established in Europe and Japan. A cellular network divides a geographic area into a number of cells called cells. One group of frequencies can be used in a cell to provide a group of users to communicate, and adjacent cells cannot use the same communication frequency. When the user moves to the edge of a cell, the degree of attenuation of the telephone signal reminds the adjacent base station to perform switching operations, and automatically switches to the frequency band of another cell for conversation.
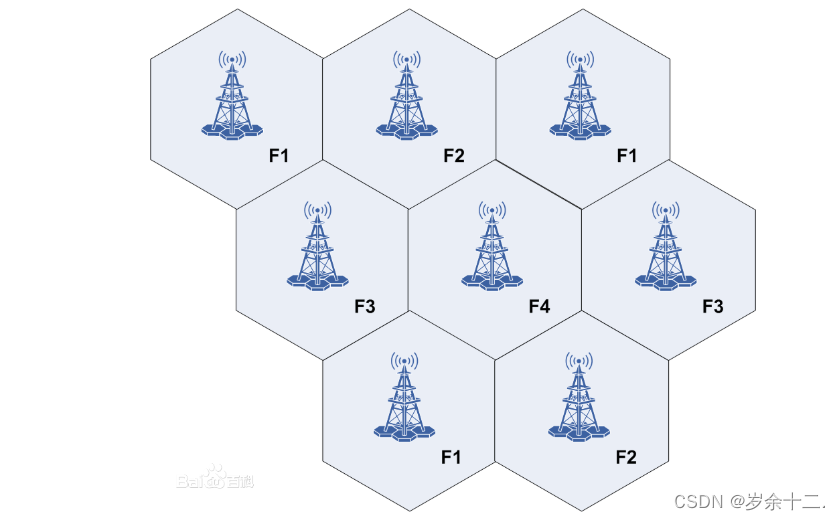
1.2 Second Generation Mobile Communication System
Global System for Mobile Communications GSM
There are 124 pairs of simplex channels, and each channel adopts time division multiplexing (TDMA) mode, which can support 8 user sessions. There is a difference of 3 time slots between the uplink and downlink specified for the same user. This is because the terminal equipment cannot send and receive at the same time, and needs to allow a certain amount of time to switch between the uplink and downlink channels.
CDMA
Code Division Multiple Access (CDMA) is a spread-spectrum multiple-access digital communication technique that uses unique code sequences to create channels. In a CDMA system, different code chip sequences are allocated to different users so that they will not interfere with each other. The chip sequence obtained by the user is composed of +1 and -1. The dot product of each sequence with itself is +1, the dot product with the complement is -1, and the dot product of a chip sequence and a different chip sequence is 0. .
In the CDMA communication system, the signals transmitted by different users are not distinguished by frequencies or time slots, but by different code chip sequences. If viewed from the frequency domain or time domain, multiple CDMA signals overlap each other. The receiver uses a correlator to select a predetermined code pattern signal among a plurality of CDMA signals.
1.3 The third generation mobile communication system
6 3G standards:
- IMT-DS: Frequency Division Duplex
- IMT-MC: frequency division duplex
- IMT-TC: proposed by China, time division duplex
- IMT-SC: is a 2.75G technology
- IMT-FT
- WiMAX, known as IMT-2000 OFDMA TDD WMAN, that is, wireless metropolitan area network technology
The third-generation digital cellular communication system provides all types of services provided by the second-generation cellular communication system, and supports mobile multimedia services.
2. Wireless LAN
2.1 Basic Concepts of WLAN
Wireless LAN technology is divided into two camps: the IEEE 802.11 standard system and the HIPERLAN standard system formulated by the European Postal and Telecommunications Commission.
IEEE 802.11 defines two wireless network topologies, one is an infrastructure network and the other is an ad hoc network.
-
In an infrastructure network, wireless terminals access backbone network devices through access points (APs). The access point is like a network bridge, which is responsible for converting between 802.11 and 802.3MAC protocols. The area covered by an access point is called a basic service area (BSA), and all terminals controlled by the access point form a basic service set (BSS). A Distributed System (DS) is formed by interconnecting multiple basic service sets. All services supported by DS are called Extended Service Set (ESS), which consists of more than two BSSs.
![[External link picture transfer failed, the source site may have an anti-leeching mechanism, it is recommended to save the picture and upload it directly (img-TyX91bCF-1681218490726)(https://download.huawei.com/mdl/image/download?uuid=97ea89c1bb0c435198bd5be701ada45c )]](https://img-blog.csdnimg.cn/86012f7e5f6f4ab5a960086067d5f0be.png)
-
The AdHoc network is a point-to-point connection that does not require the support of wired networks and access points. Terminal devices can communicate directly through wireless network cards. This topology is suitable for rapid network deployment in mobile situations.
2.2 WLAN communication technology
Infrared communication (IR)
Infrared communication technology can be used to establish WLAN. IR communication has some important advantages over radio microwave communication. First, the infrared spectrum is infinite and therefore has the potential to provide extremely high data rates. Second, the infrared spectrum is unregulated worldwide, while some microwave spectrum requires a license. In addition, infrared rays can be reflected from the ceiling to cover the entire room, and infrared rays will not penetrate the walls, so they can work without interfering with each other. The equipment is relatively simple and cheap.
IR communication is divided into:
- Directional infrared beam: Can be used for point-to-point links, the transmission range depends on the intensity of the emission and the degree of concentration of the beam.
- Omni-directional broadcast infrared: An omni-directional broadcast network consists of a base station, typically placed on the ceiling, with transmitters on the base station that broadcast signals in all directions.
- Diffuse Infrared: All emitters are focused on a single point on the ceiling. Infrared rays hit the ceiling and are diffusely reflected back in all directions and received by all receivers in the room.
spread spectrum communication
Spread spectrum communication technology originated in military communication networks, and its main idea is to spread the signal over a wider bandwidth to reduce the chance of blocking and interference.

Spread spectrum methods are:
- Frequency Hopping Spread Spectrum (FHSS)
- Direct Sequence Spread Spectrum (DSSS)
narrowband microwave communication
Narrowband microwave refers to the use of microwave radio frequency bands for data transmission with a bandwidth just wide enough to accommodate the transmitted signal. In the past, all narrowband microwave wireless network products needed to apply for a license, but now there are narrowband microwave wireless network products in the ISM frequency band.
Radio LAN is a peer-to-peer network.
2.3 IEEE 802.11 Architecture
- data link layer:
- MAC layer:
- MAC sublayer: access control and packet disassembly
- MAC management sublayer: association management during ESS roaming, power management and registration process
- LLC layer
- MAC layer:
- physical layer
- Physical Layer Convergence Protocol (PLCP): Performs carrier sense and physical layer packet establishment
- Physical Medium Dependent Sublayer (PMD): Modulation and coding of transmitted signals
- PHY management sublayer: selection of physical channel and tuning.
①Physical layer
IEEE802.11 defines three PLCP frame formats to correspond to three different PMD sublayer communication technologies :
- Corresponds to FHSS (Frequency Hopping Spread Spectrum)
- Corresponds to DSSS (Direct Sequence Spread Spectrum)
- Corresponds to DFIR (Diffuse Infrared Reflectance)
②MAC sublayer
The function of the MAC sublayer is to provide an access control mechanism, which defines three access control mechanisms:
-
CSMA/CD agreement: Carrier Sense Multiple Access/Collision Avoidance Protocol. Collision detection is difficult in wireless networks. 802.11 defines an inter-frame interval (IFS) time, and also defines a back-off counter whose initial value is randomly set and counts down until 0.
- If a station has data to send and the channel is busy, generate a random number to set its backoff counter and keep listening
- After hearing that the channel is idle, wait for the IFS time, then start counting, and the station that counts first starts to send
- Other stations stop counting when they hear that a new station starts to send, and wait for an IFS time to continue counting after the new station completes sending, until the counting is completed and start sending.
-
Distributed Coordination Function (DCF): The medium access method used by DCF is CSMA/CA. In this way, the node to send data waits until the channel is free when it detects that the channel is being used. Once the medium is free, the node waits for a set time DIFS. If no transmission from other nodes is monitored before the end of DIFS, a random backoff time is calculated, and if the medium is still idle after the backoff time is received, data will be sent. The backoff time is random, so if there are multiple nodes waiting, they will not resend at the same time, and a node with a shorter backoff time can start sending data.
DCF includes two media access modes: basic access mode and optional RTS/CTS ((Request To Send/Clear To Send) access mode.
In the IEEE802.11 protocol, there is a parameter that can be set. This parameter is called the RTS threshold. If the size of the frame to be transmitted is higher than the RTS threshold, the RTS/CTS mechanism will be activated, that is, the RTS/CTS/DATA/ACK Transmission method; if the frame size is lower than this RTS threshold, only the DATA/ACK transmission method will be used. In the transmission mode of RTS/CTS/DATA/ACK, after other terminals discover RTS/CTS, they set a NAV signal, indicating that the channel is busy, and all terminals must not compete for the channel.

-
Point coordination function (PCF): PCF is an optional function implemented on top of DCF. The so-called point coordination means that the AP centrally polls all terminals to provide them with contention-free services.
③MAC management
The function of the MAC management sublayer is to realize functions such as grade process, ESS roaming, security management and power management.
- Registration process: In order to obtain the services provided by the WLAN, when the terminal enters the WLAN area, it must perform a synchronous search to locate the AP and obtain relevant information. There are two ways of synchronization: active scanning and passive scanning. After the terminal locates the AP and obtains the synchronization information, it starts the authentication process. The authentication process includes the confirmation of the identity of the workstation by the AP and the authentication of the shared key. After the authentication process is over, the association process starts. The association process includes exchanging information between the terminal and the AP, and establishing the mapping relationship between the terminal and the AP in the DS. The DS will realize the information transmission between the same BSS and different BSSs according to the mapping relationship. After the association process is completed, the workstation can obtain the services provided by the BSS.
- Mobile way: IEEE802.11 defines 3 kinds of mobile ways: no transfer mode or move within BSA, move between multiple BSSs inside an ESS, and move between ESSs. When a terminal gradually moves away from the AP, it will start the scanning function to relocate the new AP and send a connection request. The new AP will notify the DS of the request, and the DS will change the mapping relationship between the workstation and the AP.
- Security management: IEEE802.11 provides Wired Equivalent Privacy (WEP) technology, also known as wireless encryption protocol.
- Power management: allow idle stations to sleep
2.4 Mobile Ad Hoc Network
Ad Hoc network is a peer-to-peer network composed of wireless mobile nodes, without the support of network infrastructure, and can realize dynamic reconstruction according to the change of communication environment. In this network, each node is both a host and a router, and they forward packets to each other, forming a self-organizing MANET. It has a wide range of applications in war networks, sensor networks, disaster scenes, etc.
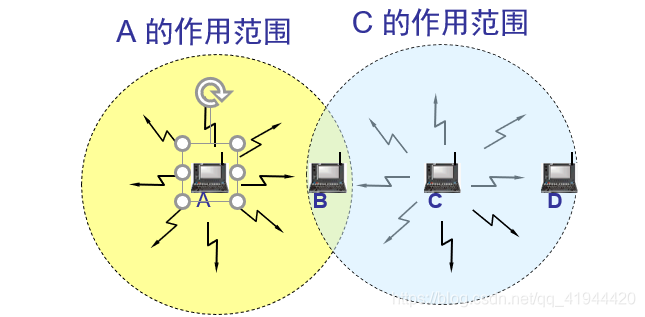
There is a special phenomenon in wireless mobile ad hoc networks, which is the problem of hidden stations and exposed stations.
C cannot detect the data sent by A to B, and the hidden station problem:
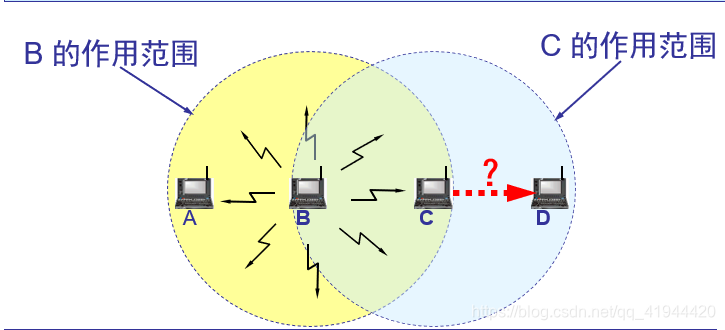
B detects the data sent by C to D, and suspends the sending process, which does not actually affect it. Exposed station issues:
Due to its particularity, the routing protocols of traditional wired networks cannot be directly applied to MANET. Specific MANET routing specifications need to be developed:
- DSDV protocol: DSDV routing protocol
- AODV protocol: Detailed explanation of AODV routing protocol
2.5 New developments in IEEE802.11
WLAN Security
- SSID access control
- Physical address filtering
- Wired Equivalent Privacy
- WPA/WPA2
WLAN transmission rate
- OFDM
- MIMO
- Smart Antenna Technology
3. Wireless Personal Network
The IEEE802.15 working group is responsible for formulating the wireless personal network (WPAN) technical specification, which is a small-scale wireless communication system with a coverage radius of about 10m.
- bluetooth technology
- ZigBee technology