Java data structures
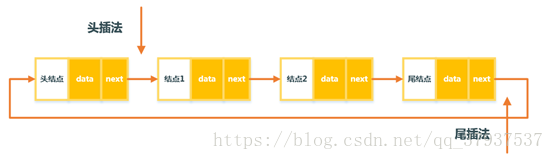
1. Circular singly linked list
For a singly linked list, the next of the tail node is empty, and the next of the tail node of the circular linked list points to the head node
1. First define the internal node class Entry, including data and next.
class Entry{
int data;
Entry next;
public Entry(){
this.data = -1;
next = null;
}
public Entry(int data){
this.data = data;
next = null;
}
}
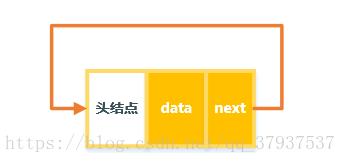
2. Initialize the linked list, create a head node, and next point to itself
public TestClink(){
head = new Entry();
this.head.next = this.head;
}
3. Header insertion method
public void headinsert(int val){
Entry tmp = new Entry(val);
tmp.next = head.next;
head.next = tmp;
}
4. Tail insertion method to insert nodes
public void tailinsert(int val){
Entry entry = new Entry(val);
Entry tmp = head;
while(tmp.next != head){
tmp = tmp.next;
}
tmp.next = entry;
entry.next = head;
}
5. Delete a node
public void delete(int val){
Entry cur;
Entry prev;
cur = head.next;
prev = head;
while(cur != head){
if(cur.data == val){
prev.next = cur.next;
cur = prev.next;
}
cur = cur. next ;
prev = prev. next ;
}
}
6. Get the length of the linked list
public int getlength(){
int len = 0;
Entry tmp = head.next;
while(tmp != head){
len++;
tmp = tmp.next;
}
return len;
}
7. Determine whether the linked list is empty, that is, determine whether the next of the head node is the head node
public boolean isEmpty(){
Entry cur = head;
if(cur.next != head){
return false;
}
return true;
}
8. Test the linked list, insert ten nodes using the tail insertion method, and obtain the length of the linked list.
public class Test17 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
TestClink tc = new TestClink();
for(int i = 0;i < 10;i++){
tc.tailinsert(i);
}
System.out.println(tc.getlength());
}
}
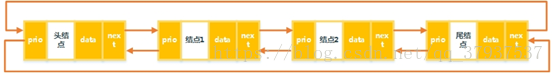
2. Doubly linked list
和单链表不同的是,每个数据结点中都有两个指针,分别指向直接后继和直接前驱。单链表只能从头结点开始访问链表中的数据元素,如果需要逆序访问单链表中的数据元素将非常低效。
1. 首先首先定义内部结点类Entry,包括数据域data,指向前一个结点的引用prio和指向下一个结点的引用next。
class Entry{
int data;
Entry next;
Entry prio;
public Entry(){
this.data = -1;
this.next = null;
this.prio = null;
}
public Entry(int val){
this.data = val;
this.next = null;
this.prio = null;
}
}
2. 初始化头结点
DoubleLink(){
head = new Entry();
}
3. 头插法插入结点
public void inserthead(int val){
Entry entry = new Entry(val);
entry.next = head.next;
entry.prio = head;
head.next = entry;
if(entry.next != null){
entry.next.prio = entry;
}
}
4. 尾插法插入结点
public void inserttail(int val){
Entry entry = new Entry(val);
Entry tmp = head;
while(tmp.next != null){
tmp = tmp.next;
}
entry.prio = tmp;
entry.next = null;
tmp.next = entry;
}
5. 删除一个结点
public void deleteEntry(int val){
Entry cur = head.next;
while(cur != null){
if(cur.data == val){
cur.prio.next = cur.next;
if(cur.next != null){
cur.next.prio = cur.prio;
}
}
cur = cur.next;
}
}
6. 测试链表,插入10个结点
public class Test18 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
DoubleLink dl = new DoubleLink();
for(int i = 0;i < 10;i++){
dl.inserttail(i);
}
}
}
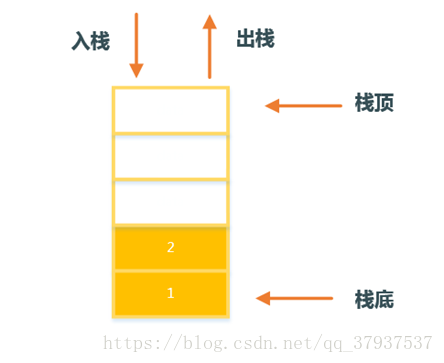
3. 顺序栈
1. 初始化栈
public Stack(){
this(10);
}
public Stack(int size){
this.elem = new int[size];
this.top = 0;
}
2. 判断栈是否满
//栈是否为满
public boolean isFull(){
if(this.top == this.elem.length){
return true;
}
return flase;
}
3. 入栈操作
//入栈
public boolean push(int val){
//判断栈满
if(isFull()){
return false;
}
this.elem[this.top++] = val;
return true;
}
4. 判断栈是否为空
//栈是否为空
public boolean isEmpty(){
return this.top == 0;
}
5. 出栈操作
//出栈
public boolean pop(){
if(isEmpty()){
return false;
}
--top;
return true;
}
6. 获取栈顶元素
//得到栈顶元素
public int gettop(){
if(isEmpty()){
return -1;
}
return this.elem[this.top-1];
}
7. 打印栈内元素
//打印栈内元素
public void show(){
for(int i = 0;i < this.top;i++){
System.out.print(this.elem[i]+" ");
}
System.out.println();
}
8. 测试栈的基本操作
public class test19 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Stack s1 = new Stack();
for(int i = 0;i < 10;i++){
s1.push(i);
}
s1.show();
s1.pop();
s1.show();
}
}