9.3 Help instructions
9.3.1 Introduction
When we are not familiar with an instruction, we can use the help instruction provided by Linux to understand how to use this instruction.
9.3.2man get help information
- Basic syntax
man[command or configuration file] (function description: get help information) - Application examples
Case: View the help information of the 1s command

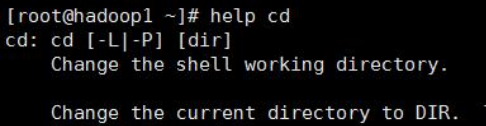
9.3.3 help command
- Basic syntax
help command (function description: get help information for shell built-in commands) - Application examples
Case: View the help information of the cd command
9.4 File Directory Class
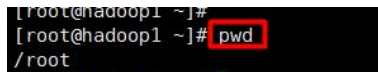
9.4.1 pwd command
- Basic syntax
pwd (function description: display the absolute path of the current working directory) - Application examples
Case: Display the absolute path of the current working directory
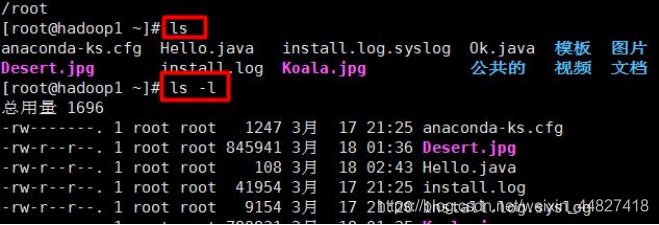
9.4.2ls instruction
- Basic syntax
ls [option][directory or file] - Common options
-a: Display all files and directories in the current directory, including hidden ones.
-l: display information in a list - Application examples
Case: View all content information of the current directory
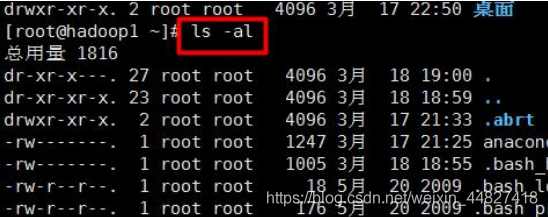
9.4.3 cd command
- Basic syntax
cd[parameter] (function description: switch to the specified directory) - Common parameter
absolute path and relative path
How to understand absolute path and relative path:
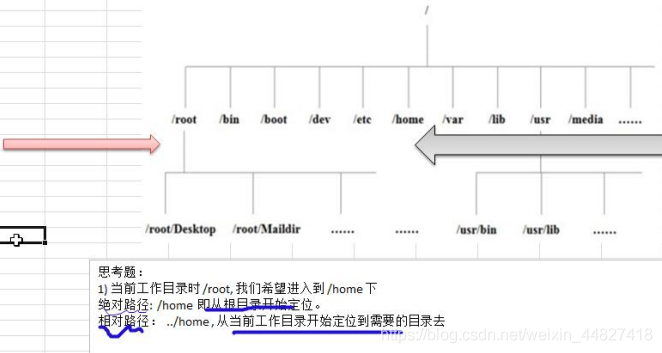
cd~ or cd: go back to your home directory
cd... go back to the upper level of the current directory - Application Examples
Case 1: Use an absolute path to switch to the root directory
cd/root
Case 2: Use a relative path to the /root directory
Here we need to know which directory the user directory is in, to write this command, suppose it is in /usr/lib
cd ././root
Case 3: Return to the upper-level directory
cd of the current directory ...
Case 4: Return to the home directory
cd
cd~
9.4.4 mkdir instruction
The mkdir command is used to create a directory (make directory)
- Basic syntax
mkdir [options] the directory to be created - Commonly used options
-p: create a multi-level directory - Application examples
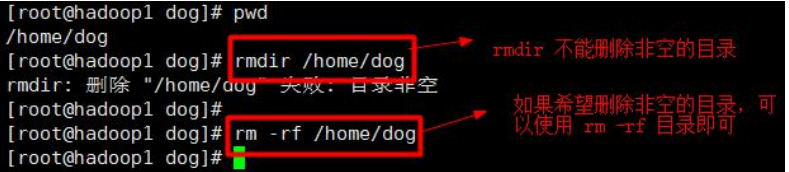
Case 1: Create a directory /home/dog
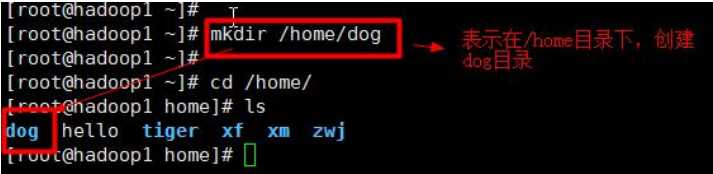
Case 2: Create a multi-level directory /home/animal/tiger
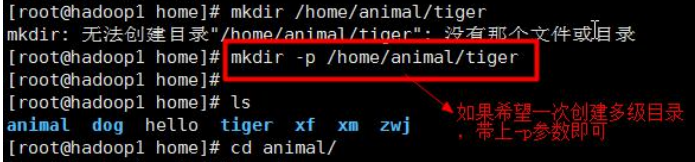
9.4.5 The rmdir command
- Introduce the
rmdir command to delete empty directories - Basic syntax
rmdir [option] empty directory to be deleted - Application examples
Case 1: Delete a directory /home/dog
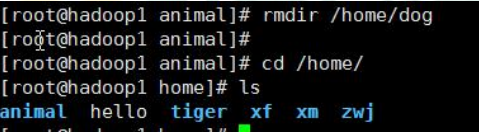
- Usage details
rmdir deletes an empty directory. If there is content in the directory, it cannot be deleted. Tip: If you need to delete a non-empty directory, you need to use rm-rf to delete the directory