Article Directory
- OpenStack origin
- 1. Introduction to OpenStack
- 2. OpenStack node types
- 3. Common core projects of OpenStack
- to sum up
OpenStack origin
OpenStack is the OpenStack project initiated by Rackspace (a US cloud computing vendor) and the National Aeronautics and Space Administration (National Aeronautics and Space Administration, referred to as NASA) in July 2010.
The storage source code (Swift) contributed by Rackspace, and the calculation source code (Nova) contributed by NASA.
1. Introduction to OpenStack
1.1 What is OpenStack?
-
OpenStack is a cloud platform that controls computing resources, storage resources, and network resources through the data center. At the same time, it is an open source software, free software and open source projects authorized under the Apache license, supporting all types of cloud environments;
-
The goal of OpenStack is to provide cloud products that are simple to implement, scalable, and rich in feature sets. Cloud computing experts from all over the world jointly maintain the cloud project. OpenStack provides IaaS solutions through a variety of supplementary services, each of which provides a corresponding Application Programming Interface (API) to promote the integration between components;
-
OpenStack is used to provide the construction and management of public and private clouds. As an open source project, its community size covers 130 companies and 1,350 developers. These institutions and individuals all use OpenStack as the general front-end of IaaS resources;
-
OpenStack covers all aspects of networking, virtualization, operating systems, servers, and so on. Generally, the version is updated every six months or so.
1.2 OpenStack service
- OpenStack has 8 core services, the details are shown in the table below:
| service | project name | description |
|---|---|---|
| Compute (Compute Service) | Nova | Responsible for the management of the instance life cycle and the unit of computing resources. Shield the Hypervisor, support multiple virtualization technologies (Red Hat defaults to KVM), and support horizontal expansion |
| Network | Neutron | Responsible for the management of the virtual network and create the network topology for the instance. It is a tenant-oriented network management, you can define your own network, and each tenant does not affect each other |
| Identity (identity authentication service) | Keystone | Similar to LDAP service, it authenticates and authorizes users, tenants, roles, and services, and supports multiple authentication mechanisms |
| Dashboard (Control Panel Service) | Horizon | Provide a web management interface to interact with OpenStack underlying services |
| Image Service | Glance | Provide registration and management of virtual machine image templates, copy the prepared operating system as an image template, and use it directly when creating a virtual machine, and support multi-format images |
| Block Storage (block storage service) | Cinder | Responsible for providing durable block storage devices for running instances, which can be easily expanded, paid on demand, and support a variety of back-end storage |
| Object Storage | Swift | Provides cloud-based elastic storage for OpenStack and supports clusters without single point of failure |
| Telemetry (metering service) | Ceilometer | A centralized source for measurement, monitoring, and control of data resources, providing OpenStack users with a way to keep accounts |
1.3 OpenStack advantages
- OpenStack has advantages in control, compatibility, scalability, and flexibility, and it may become an industry standard in the cloud computing field.
1.控制性:
完全开源的平台,提供API接口,方便与第三方技术集成
2.兼容性:
OpenStack兼容其它公有云,方便用户进行数据迁移
3.可扩展性:
模块化设计,可以通过横向扩展,增加节点,增加资源
4.灵活性:
根据自己的需要建立相应基础设施,增加集群规模
5.行业标准:
Openstack 项目采用 Apache2 许可, 意味着第三方厂家可以重新发布源代码。
众多IT领军企业已经加入到OpenStack项目,意味着 OpenStack 在未来可能形成云计算行业标准
2. OpenStack node types
- OpenStack is composed of control nodes, computing nodes, network nodes, and storage nodes.
2.1 Control node (scheduler)
-
As the name implies, it is a node that implements data center control in OpenStack, and manages all service components of OpenStack;
no matter where all components are, they need to complete similar registration work on the control node -
Responsible for the control of the remaining points, including virtual machine creation, migration, network allocation, storage allocation, etc.
Control node architecture:
- The control node includes the following services:
management support services, basic management services, and extended management services
2.1.1 Management support services
- Including database and message broker services
数据库作为基础/扩展服务产生的数据存放的地方
消息代理服务(也称消息中间件)为其他各种服务之间提供了统一的消息通信服务
2.1.2 Basic management services
- Includes five services: Keystone, Glance, Nova, Neutron, and Horizon
1.Keystone:认证管理服务、提供了其余所有组件的认证信息/令牌的管理、创建、修改等等、使用MySQL等数据库存储认证信息;
2.Glance:镜像管理服务,提供了对虚拟机部署的时候所能提供镜像的管理、包含镜像的导入、格式以及制作相应的模板;
3.Nova:计算管理服务,提供了对计算节点的Nova管理、使用Nova-API(入口节点)进行通信;
4.Neutron:网络管理服务、提供了对网络节点的网络拓扑管理,同时提供Neutron在Horizon的管理界面;
5.Horizon:控制台服务,提供了以Web形式对所有节点的所有服务的管理,通常把该服务成为Dashboard
2.1.3 Extended management services
- Contains five services: Cinder, Swift, Trove, Heat, and Centimeter
1.Cinder:提供管理存储节点的Cinder相关、同时提供Cinder在Horizon中的管理面板;
2.Swift:提供管理存储节点Swift相关、同时提供Swift在Horizon中的管理面板;
3.Trove:提供管理数据库节点的Trove先关、同时提供Trove在Horizon中的管理面板;
4.Heat:提供了基于模板来实现云环境中的资源的初始化,依赖关系处理,部署等基本操作;
也可以解决自动收缩、负载均衡等高级特性
5.Centimeter:提供对物理资源以及虚拟资源的监控,并记录这些书库,读数据进行分析在一定条件下出发现货供应动作。
控制节点通常来说只需要一个网络端口来用于通信和管理各个节点
2.2 Storage Node
2.2.1 Storage node type
- Nodes where storage components are installed, typically Cinder (block storage) and Swift (object storage)
1.Cinder:块存储服务,提供相应的块才能出,简单来说,就是虚拟出一块存盘,可以挂载到相应的虚拟机之上,不收
文件系统的影响,对虚拟机来说,这个操作像是加了一块硬盘,可以完成对磁盘的任何操作,包括挂载、卸载、格式化,
转换文件系统等等操作,大多应用于虚拟机空间不足的情况下的空间扩容等;
2.Swift:对象存储服务,提供相应的独享存储、简单来说,就是虚拟出一块磁盘空间,可以在这个空间当中存放文件,也
仅仅只能存放文件,不能进行格式化,转换文件系统,大多应用于云磁盘/文件。
2.2.2 Function
- Responsible for additional storage management of virtual machines, etc.;
- Storage node architecture;
- Storage nodes include Cinder, Swift and other services
2.2.3 Network port
- Storage node contains at least two network ports
端口1:与控制节点进行通信,接受控制节点任务,受控制节点统一调配;
端口2:与计算/网络节点进行通信,完成控制节点下发的各类任务。
2.3 Computing Node
2.3.1 Compute node composition
- Contains some components of Nova and some components of Neutron Nova-compute., Neutron agent
1.基础服务
Nova:提供虚拟机的创建、运行、迁移、快照等围绕虚拟机的服务、并提供API与控制节点对接、由控制节点下发任务
Neutron:提供计算节点与网络节点之间的通信
2.扩展服务
Telmeter:提供计算节点监控代理、将虚拟机的情况反馈的控制节点,是Centimeter的代理服务
2.3.2 Function
- Responsible for virtual machine operation
- Compute node architecture
- The computing node includes three services: Nova, Neutron, and Telemter
2.3.3 Network port
- The compute node contains at least two network ports
端口1:与控制节点进行通信,受控制节点统一调配
端口2:与网络节点,存储节点进行通信
2.4 Network node
- The network node only has Neutron components. Neutron on the network node installs core plugin (ML2) and service plugin (L3 service). The specific Service Plugin can be selected according to your needs.
2.4.1 Function
- Responsible for the communication between the external network and the internal network
- Network node architecture
- The network node only contains Neutron services
2.4.2 Network Port
- The network node contains three network ports
端口1:用于与控制节点进行通信
端口2:用于除了控制节点之外的计算/存储节点之间的通信
端口3:用于外部的虚拟机与相应的网络之间通信
3. Common core projects of OpenStack
- The provision of OpenStack cloud platform services mainly relies on the four core modules of Nova, Glance, Cinder, and Neutron, and the access, monitoring, permissions, and object storage functions provided by the four auxiliary modules Horizen, Ceilometer, Keystone, and Swift.
3.1 User authentication service keystone
- Module responsible for managing authentication, service rules and service token functions
3.1.1 Important Concepts of Keystone
- User (User) The user who
uses the service can be a person, service, or system. As long as it is an object that uses the openstack service, it can be called a user. When the user accesses OpenStack, Keystone will verify its identity - Tenant/tone (tenant/project) are mutually independent
1.租户,可以理解为一个人、项目或者组织拥有的资源的合集。在一个租户中可以拥有很多个用户,这些用户可以根据权限的
划分使用租户中的资源。
2.项目是各个服务中的一些可以访问的资源集合,用来分组或隔离资源或身份对象。不同服务中,项目所涉及的资源不同。
在Nova服务中项目可以是云主机,在 Swift和 Glance中项目可以是镜像存储,在 Neutron中项目可以是网络资源。
默认情况下,用户总是被绑定到项目中。一个项目中可以有多个用户,一个用户可以属于一个或多个项目。
- Role (role) different users, different permissions, permissions classification
1.角色,用于分配操作的权限。角色可以被指定给用户,使得该用户获得角色对应的操作权限。
安全包含两部分:Authentication(认证)和 Authorization(鉴权)
2.角色是一组用户可以访问的资源权限集合,这些资源包含虛拟机、镜像、存储资源等。
用户既可以被添加到全局的角色,也可以被添加到指定项目内的角色中。其区别是,全局的角色适用于所有项目中的资源权限
而项目内的角色只适用于某个项目内的资源权限。
- Service
1.Openstack Service,即Openstack中运行的组件服务。nova,glance都是属于一个服务,需要在keystone上进行
创建指定类型。
2.用户使用云中的资源是通过访问服务的方式实现, OpenStack中包含许多服务,如提供计算服务的Nova、提供镜像服务
的 Glance以及提供对象存储服务的 Swift。一个服务可以确认当前用户是否具有访问其资源的权限。但是当一个用户尝试
访问其项目内的 service时,该用户必须知道这个服务是否存在以及如何访问这个服务。
3.创建服务有一个服务,就创建一个endpoint,会根据服务类型去查找那个服务。Service 决定每个 Role 能做什么
事情,Service 通过各自的 policy.json 文件对 Role 进行访问控制
- Token
1.指的是一串比特值或者字符串,用来作为访问资源的令牌。Token中含有可访问资源的范围和有效时间。
2.是一串数字字符串,用于访问0 penStock服务的API以及资源。一个令牌可以在特定的时间内生效,并可以在任意时间
释放。在 keystone中主要是引入令牌机制来保护用户对资源的访问。
- Endpoint (endpoint)
an address that can access and locate an Openstack Service through the network, usually a URL
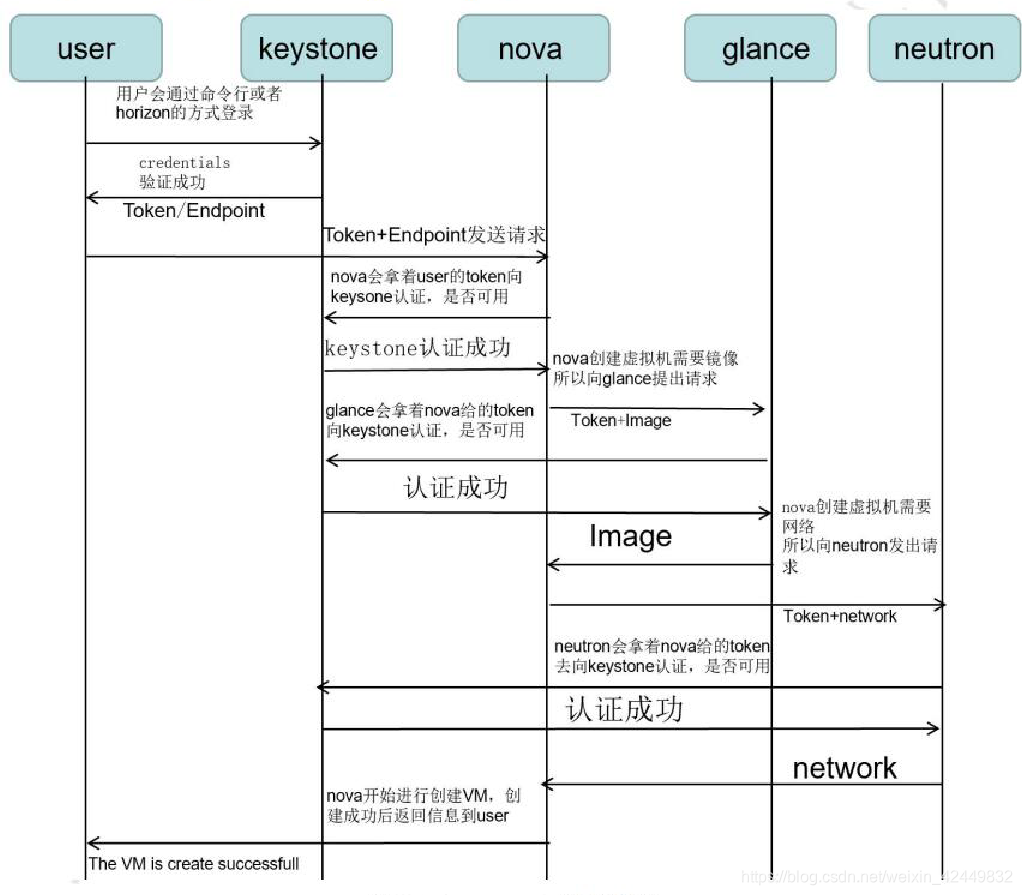
3.1.2 Keystone work flow chart
- Core: Issuance and authentication of keystone identity tokens
3.2 Console Horizon (graphical interface)
3.2.1 Overview
- Web control panel for managing and controlling OpenStack services
- Openstack is an architecture consisting of multiple node servers. These servers are virtualized to achieve the same task, integrate resources into a whole, and distribute and use externally.
3.2.2 Horizon features
- Instance management
- Access and security management
- Preferences
- Image management
- User Management
- Volume management
- Object storage processing
3.3 Mirror module Glance
- Provides mirroring services for discovery, registration and download, centralized warehouse of virtual machine mirroring
- Create a virtual machine from a virtual machine image
3.3.1 Glance main components
- glance-api
glance-api用于接收镜像API的调用,诸如镜像发现、恢复以及存储等。作为一个后台进程, glance-api对外提供
REST API接口,响应用户发起的镜像查询、获取和存储的调用
- glance- registry
glance- registry用于存储、处理和恢复镜像的元数据,元数据包括镜像的的大小和类型等属性, registry是一个内部
服务接口,不建议暴露给普通用户
- database
database用于存放镜像的元数据,可以根据需要选择数据库,如 MySQL、 SQLite等。
- storage repository for image files
一般情况下, glance并不需要存储任何镜像,而是将镜像存储在后端仓库中。 Glance支持多种 repository。
主要包括对象存储 Swift、块存储 Cinder、 VMware的ESX/ESXi或者vCenter、亚马逊的S3、HTTP可用服务器、Ceph等
3.3.2 Mirror format
- Glance supports multiple image formats, including disk format and container format
- Several commonly used image file formats are as follows
RAW VDI
QCOW2 ISO
VHD AKI,ARI,AMI
VMDK
3.4 Network module Neutron
3.4.1 Overview
- Realize the communication between instances and between instances and external networks
- Provides the abstract functions of Layer 2 Switch (internal network) and Layer 3 Router (external network). For example, the virtual machine created from the image in openstack
3.4.2 Realization of functions
Router:为用户提供路由,NAT等服务
Network:对应于一个真实物理网络中的二层局域网(VLAN)
Subnet:指定一段IPV4或IPV6地址并描述其相关的配置信息
3.5 Calculation module Nova
3.5.1 Overview of Nova
-
Nova is a module responsible for providing computing resources and a core module in OpenStack. Its main function is to be responsible for the lifecycle management of virtual machine instances, network management, storage volume management, user management, and other related cloud platform management functions.
-
OpenStack uses computing services to host and manage cloud computing systems. OpenStack computing service is the main component of the infrastructure service (IaaS) system, and the module is mainly implemented by Python.
-
The OpenStack computing component requests the OpenStack Identity service for authentication, requests the OpenStack Image service to provide disk mirroring, and provides user and administrator interfaces for the OpenStack Dashboard. Disk mirroring access is restricted to projects and users, and quotas are set for each project
3.5.2 The main components of computing services
- Nova-api service
receives and responds to computing API requests from end users, provides an external interface to interact with cloud infrastructure, and is also the only external component that can be used to manage infrastructure - Nova-api-metadata service
receives metadata requests sent from virtual machines. Nova-api-metadata service is generally used in multi-host mode with Nova-Network service installed - Nova-Compute service
A continuously working daemon process that creates and destroys virtual machine instances through Hypervisor's API - Nova- placement-api service
Nova- placement-api is used to track and record resource provider directories and resource usage. These resources include computing, storage, and IP address pools, etc. - Nova-Conductor module The
Nova-Conductor module acts between the Nova-Compute service and the database, avoiding direct access to the cloud database by the Nova-Compute service. It can be scaled horizontally. However, do not deploy it on the host node running the Nova-Compute service. - Nova- Scheduler service
1.接收到一个来自队列的运行虚拟机实例请求,然后决定在哪台计算服务器主机来运行该虚拟机。通过恰当的调度算法从可
用资源池获得一个计算服务。Nova- Scheduler服务将根据负载、内存、可用域的物理距离、CPU构架等信息,并运行调度
算法,最终做出调度决策。
2.最终OpenStack计算模块Nova中的各个组件是以数据库和队列为中心进行通信的
3.6 Virtual Network
3.6.1 Overview
- Abstraction and management of the Layer 2 physical network (communication between LANs and VMs)
- The Layer 2 physical network includes:
虚拟交换机/网桥
虚拟路由器
Namespace
DHCP
浮动IP地址
3.6.2 Networking model
- VXLAN of Local, Flat, VLAN, Overlay (the internal layer is two physics, and data information is transmitted through the tunnel)
3.7 Block Storage Cinder
- Provides classification of the entire life cycle of Volume from creation to deletion
3.7.1 Cinder function
- Provide REST API
- Schedule Volume creation requests to reasonably optimize the allocation of storage resources
- Support multiple back-end (back-end) storage methods
3.7.2 Cinder main service components
-
Cinder-api
Cinder-api is used to accept API requests and route them to Cinder-Volume for execution. -
Cinder-Volume
Cinder-Volume is used to directly interact with the block storage service and the Cinder-Scheduler process.
It can also interact with these processes through a message queue. -
Cinder-Scheduler The
Cinder-Scheduler daemon selects the optimal storage node to create the volume, and its working mechanism is similar to that of Nova-Scheduler. -
Cinder-Backup daemon The
Cinder-Backup service provides any kind of backup volume to a backup storage provider. Just like the Cinder-Volume service, it interacts with a variety of storage providers under the drive architecture. -
message queue
消息队列作用是在块存储的进程之间路由信息。 Cinder各个子服务通过消息队列实现进程间通信和相互协作。
以创建卷为例, Cinder的工作流程如下:
1.用户向 Cinder-API发送创建卷请求:“帮我创建一个卷“
2.Cinder-API对请求做一些必要处理后,向消息队列发送一条消息:“让Cinder- Scheduler创建一个卷”;
3.Cinder- Scheduler从消息队列获取到消息,然后执行调度算法,从若干存储节点中选出节点A
4.Cinder- Scheduler向消息队列发送一条消息:“让存储节点A创建这个卷”;
5.存储节点A的 Cinder- Volume从消息队列中获取到消息,然后通过卷提供者的驱动创建卷。
3.8 Object storage swift
3.8.1 Overview of swift
- Use ordinary hardware to build a redundant, scalable distributed object storage cluster. Storage capacity can reach PB level
- Swift belongs to object storage, used for long-term storage of permanent static data (such as virtual machine mirroring, image storage, email storage and archive backup)
3.8.2 Features of Swift
- Very high data durability (single point of failure)
- Fully symmetrical system architecture (simple, dependable)
- Unlimited scalability
3.8.3 Swift components
代理服务(ProxyServer)
认证服务(AuthenticationServer)
缓存服务(CacheServer)
账户服务(AccountServer)
复制服务(Replicator)
更新服务(Updater)
容器服务(ContainerServer)
对象服务(ObjectServer)
审计服务(Auditor)
账户清理服务(AccountReaper)
3.8.4 Swift storage structure
- Objects
- Accounts
- Containers
- Tmp
- async_pending
- quarantined
3.9 Extension
- OpenStack-ironic bare metal
In short, OpenStack Ironic is a project for bare metal deployment and installation.
The so-called bare metal refers to a computer without an operating system. From bare metal to application, the following operations are also required:
(1)硬盘RAID、分区和格式化;
(2)安装操作系统、驱动程序;
(3)安装应用程序。
ronic实现的功能,就是可以很方便的对指定的一台或多台裸机,执行以上一系列的操作。
例如部署大数据群集需要同时部署多台物理机,就可以使用Ironic来实现。Ironic可以实现硬件基础设施资源的快速交付。
to sum up
1.OpenStack 是一系列开源工具(或开源项目)的组合,主要使用池化虚拟资源来构建和管理私有云及公共云。
2.其中的六个项目主要负责处理核心云计算服务,包括计算、网络、存储、身份和镜像服务。
3.还有另外十多个可选项目,用户可把它们捆绑打包,用来创建独特、可部署的云架构。