Preface
The blogger is now participating in the Fourth Mathematical Modeling Contest in his junior year. I specialize in big data. As I may be engaged in the data analysis industry in the future, in fact, mathematical modeling and big data analysis have many similarities, and it can be said that they are almost the same. After so many competitions, individuals must fully master some of the necessary data analysis methods for modeling. Reading and researching many blogs or articles, I found that the actual application examples of the AHP method are relatively single. The vision of this blog is that I or the readers can learn the AHP method and apply it in practice through reading this blog, and be able to record your thoughts. Among. Of course, individuals who are not majors in mathematics may not have a good understanding of some professional knowledge. I hope that readers can make mistakes or opinions after reading them. The blogger will maintain the blog for a long time and update it in time. Pure sharing, I hope everyone likes it.
Tip: The following is the content of this article, the following cases are for reference
1. What is the AHP analytic hierarchy process?
AHP (Analytic Hierarchy Process) is a practical multi-plan or multi-objective decision-making method proposed by the American operations researcher Professor TL Saaty in the 1970s. It is a combination of qualitative and quantitative decision-making analysis methods. . Use the experience of the decision-maker to judge the relative importance of the standards that measure the achievability of the goals, and reasonably give the weights of each standard for each decision-making plan, and use the weights to find the advantages and disadvantages of each plan Sequence, more effectively applied to those difficult to use quantitative methods to solve the problem. , Has a very wide range of practicality.
2. Wide use of AHP
After more than 40 years of research and development, AHP has become a multi-criteria method widely used by decision makers. Its applications involve economy and planning, energy policy and resource allocation, political issues and conflicts, human resource management, forecasting, project evaluation, education development, environmental engineering, business management and production and operation decision-making, accounting, health care, military command, weapons evaluation , Law and many other fields. AHP is mainly used as an auxiliary decision-making tool. Only when it is combined with other methods can it achieve better results. From the existing research results, other methods used in combination with AHP include fuzzy set theory, fuzzy logic, digital planning, cost-benefit analysis, artificial neural network, evidence reasoning, data envelopment analysis, simulation, data mining, etc.
Three, the advantages and disadvantages of AHP
1. Advantages of Analytic Hierarchy Process
- Systemicity-treat the object as a system and make decisions according to the way of thinking of decomposition, comparison, judgment, and synthesis. Become an important tool for system analysis developed after mechanism analysis and statistical analysis;
- Practicality-The combination of qualitative and quantitative, can handle many practical problems that cannot be tackled with traditional optimization techniques, and has a wide range of applications. At the same time, this method enables decision makers and decision analysts to communicate with each other, and decision makers can even directly Apply it, which increases the effectiveness of decision-making;
- Simplicity-the calculation is simple and the results are clear. People with intermediate education can understand the basic principles of the analytic hierarchy process and master the basic steps of the method, and it is easy to be understood and mastered by decision makers. It is convenient for decision makers to directly understand and master.
(1) Establish a hierarchy of all elements (including non-quantitative and quantitative), and clearly show the relationship between each layer, each criterion and each element.
(2) The evaluation procedure is simplified, and the calculation process is simple and easy to understand.
(3) If there are omissions or deficiencies in the research data, the importance of each element can still be obtained.
2. Disadvantages of Analytic Hierarchy Process
- Old-fashioned-only one can be selected from the original plan, there is no way to come up with a better new plan;
- Rough-The process of comparison, judgment and result calculation in this method are all rough, which is not suitable for higher precision problems. ;
- Subjective-From building a hierarchical structure model to giving a paired comparison matrix, human subjective factors have a great influence on the whole process, which makes the results difficult for all decision makers to accept. Of course, adopting expert group judgment is a way to overcome this shortcoming.
(1) Pairwise comparison between elements is sometimes difficult.
(2) When there are many elements, the consistency test may not pass (so generally control the elements to 7).
(3) The analysis did not consider the relevance of the elements.
Four, application steps
When using the analytic hierarchy process to construct a system model, it can be roughly divided into the following four steps:
- Build a hierarchical model
- Construct a judgment (pair comparison) matrix
- Hierarchical order and its consistency test
- Hierarchical total ranking and its consistency check
1. Build a hierarchical model
The decision-making goals, consideration factors (decision criteria) and decision-making objects are divided into the highest level, the middle level and the lowest level according to their mutual relationship, and a hierarchical structure diagram is drawn.
- The highest level: the purpose of decision-making, the problem to be solved.
- The lowest level: alternatives when making decisions.
- Middle layer: factors to be considered and criteria for decision-making.
For the two adjacent layers, the upper layer is called the target layer, and the lower layer is called the factor layer.
For example, a unit intends to select a leader from three cadres. The selection criteria include policy level, work style, business knowledge, eloquence, writing ability, and health status. We build a hierarchical structure model as:

2. Construct a judgment (pair comparison) matrix
When determining the weight between the various factors at each level, if it is only a qualitative result, it is often not easy to be accepted by others, so someone proposed: the consistent matrix method, that is:
- Do not compare all factors together, but compare them with each other.
- At this time, a relative scale is adopted to minimize the difficulty of comparing various factors with different natures to improve accuracy.
The judgment matrix is a comparison of the relative importance of all factors at this level to a certain factor at the previous level. The element aj of the judgment matrix is given by Santy's 1-9 scale method.
Based on the example of electing leaders given above, we construct the judgment matrix as follows:

3. Hierarchical order and its consistency test
The eigenvector corresponding to the maximum eigenvalue of the judgment matrix enters max, which is normalized (to make the sum of the elements in the vector equal to 1) and then denoted as W.
The element of W is the sorting weight of the relative importance of the factors of the same level to the factors of the previous level. This process is called single-level sorting.
Whether to confirm the ordering of the level list requires a consistency test. The so-called consistency test refers to determining the allowable range of inconsistency for A.
First of all, we must first normalize the comparison matrix we constructed:
Column vector normalization: Find the sum of the squares of each component , then find its square root , and then
divide each component by the number obtained above.

![]()


(1). Calculate the consistency index

Define consistency indicators
;
, There is complete consistency;
Close to 0, with satisfactory consistency;
The larger the value, the more serious the inconsistency.
(2). In order to measure the size, the random consistency index is introduced
Find the corresponding average random consistency index RI. For n=1,...,9, Santy gives the value of RI, as shown in the following table (Table 2):
Table 2 RI value



(3). Calculate the consistency ratio CR:

Generally, when the consistency ratio is used, the degree of inconsistency of A is considered to be within the allowable range, there is a satisfactory consistency, and the consistency test is passed. The normalized eigenvector can be used as the weight vector, otherwise the comparison matrix A must be reconstructed and
adjusted.
E.g:
4. Level total ranking and its consistency check
- Calculating the relative importance of all factors at a certain level to the highest level (total goal) is called the total ranking of levels.
- This process is carried out sequentially from the highest level to the lowest level.

The order of the A-level factors
to the total target Z is
.
The factors in the B
level are sorted by the level list of the factors in the upper level A as

The consistency ratio of the total rank ordering is:, 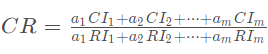 when the consistency ratio
when the consistency ratio , the total rank ordering is considered to pass the consistency test.



to sum up
There are many domain models that need to use AHP to calculate multi-factor weights, so many AHPs are used as part of the establishment of other models.
See:
https://baike.so.com/doc/5386070-5622520.html