Description
数列 f [ n ] = f [ n − 1 ] + f [ n − 2 ] , f [ 1 ] = f [ 2 ] = 1 f[n]=f[n-1]+f[n-2],f[1]=f[2]=1 f[n]=f[n−1]+f[n−2],f[1]=f[2]=1 beforennsum of n termss [n] s[n]s[n]
Input
N(1<N<231)
Output
Nth result
Sample Input
12345
Sample Output
8995
Source
elba
Problem solving ideas
Method 1: Although we have S [n] = F [n + 2] − 1 S[n]=F[n+2]-1S[n]=F[n+2]−1 , but this article does not consider this method, we want to get a more general method.
Method 2: Following the previous ideas, consider 1×3 1×31×Matrix of 3 [f [n − 2], f [n − 1], s [n − 2]] [f[n-2],f[n-1],s[n-2]]【f[n−2],f[n−1],s[n−2 ] 】 , we hope to multiply by a3 × 3 3 × 33×A matrix of 3 ,1 × 3 1 × 31×3的 矩阵 :
【f [n - 1], f [n], s [n - 1]】 = 【f [n - 1], f [n - 1] + f [n - 2], s [n - 2] + f [n - 1]】 【f [n-1], f [n], s [n-1]】 = 【f [n-1], f [n-1] + f [n -2], s [n-2] + f [n-1]】【f[n−1],f[n],s[n−1]】=【f[n−1],f[n−1]+f[n−2],s[n−2]+f[n−1 ] ]
Easy to get this3×3 3×33×The matrix of 3 is:
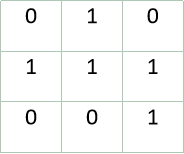
Then... It is easy to find that the matrix scale of this method is(r + 1) ∗ (r + 1) (r+1)*(r+1)(r+1)∗(r+1 ) , which is much better than the previous popular method (method one).
Code
#include<algorithm>
#include<iostream>
#include<cstdio>
#include<cmath>
#include<cstring>
const int INF=9973;
long long n;
using namespace std;
struct c{
int n,m;
int a[10][10];
}A,B,CC;
c operator *(c A,c B){
c C;
C.n=A.n,C.m=B.m;
for(int i=1;i<=C.n;i++)
for(int j=1;j<=C.m;j++)
C.a[i][j]=0;
for(int k=1;k<=A.m;k++)
{
for(int i=1;i<=C.n;i++)
for(int j=1;j<=C.m;j++)
C.a[i][j]=(C.a[i][j]+(A.a[i][k]*B.a[k][j])%INF)%INF;
}
return C;
}
void poww(long long x){
if(x==1)
{
B=A;
return;
}
poww(x>>1);
B=B*B;
if(x&1)
B=B*A;
}
int main(){
scanf("%lld",&n);
if(n==1){
printf("1");
return 0;
}
A.n=3,A.m=3;
A.a[1][1]=0,A.a[1][2]=1,A.a[1][3]=0;
A.a[2][1]=1,A.a[2][2]=1,A.a[2][3]=1;
A.a[3][1]=0,A.a[3][2]=0,A.a[3][3]=1;
poww(n-1);
CC.n=1,CC.m=3;
CC.a[1][1]=1,CC.a[1][2]=1,CC.a[1][3]=1;
CC=CC*B;
printf("%d %d\n",CC.a[1][1],CC.a[1][3]);
}